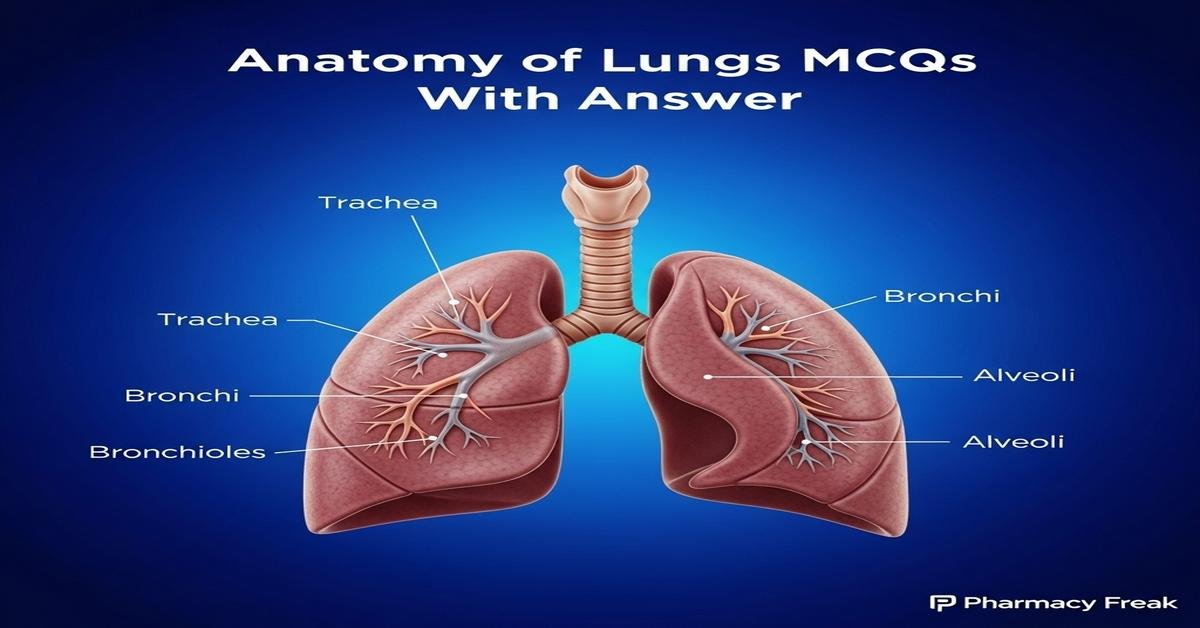
Mastering the Anatomy of Lungs MCQs With Answer is essential for B. Pharm students preparing for pharmacology, physiology and clinical exams. This focused guide covers lung structure — including trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleura and pulmonary vasculature — and highlights functional aspects like gas exchange, ventilation and defense mechanisms. Clear, exam-oriented explanations and targeted keywords help improve recall and search visibility. Practicing MCQs strengthens understanding of respiratory pharmacotherapy, drug delivery and pathophysiology relevant to pharmacy practice. Use these practice questions to solidify concepts and identify weak areas before practicals and assessments. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which structure marks the beginning of the lower respiratory tract?
- Nasal cavity
- Pharynx
- Trachea
- Alveoli
Correct Answer: Trachea
Q2. The carina is located at the bifurcation of which airway?
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Primary bronchi
- Secondary bronchi
Correct Answer: Trachea
Q3. Which bronchus is more vertical and wider, making it more likely for aspirated objects to enter?
- Left primary bronchus
- Right primary bronchus
- Left secondary bronchus
- Right tertiary bronchus
Correct Answer: Right primary bronchus
Q4. Which cells in the alveoli secrete surfactant?
- Type I pneumocytes
- Type II pneumocytes
- Alveolar macrophages
- Club (Clara) cells
Correct Answer: Type II pneumocytes
Q5. The primary function of Type I pneumocytes is:
- Surfactant production
- Gas exchange
- Phagocytosis of bacteria
- Mucus secretion
Correct Answer: Gas exchange
Q6. The conducting zone of the respiratory system ends at which structure?
- Terminal bronchioles
- Respiratory bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
- Alveolar sacs
Correct Answer: Terminal bronchioles
Q7. Which pleural space lies between the visceral and parietal pleura?
- Pericardial cavity
- Pleural cavity
- Mediastinum
- Peritoneal cavity
Correct Answer: Pleural cavity
Q8. The bronchopulmonary segment is supplied by which artery?
- Pulmonary artery
- Bronchial artery
- Coronary artery
- Intercostal artery
Correct Answer: Bronchial artery
Q9. Which structure provides the major lymphatic drainage for the lungs?
- Axillary nodes
- Hilar (bronchopulmonary) nodes
- Inguinal nodes
- Mesenteric nodes
Correct Answer: Hilar (bronchopulmonary) nodes
Q10. The epithelium lining the trachea is best described as:
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
- Transitional epithelium
Correct Answer: Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Q11. Which structure reduces friction between the lung and chest wall during respiration?
- Surfactant
- Pleural fluid
- Pericardial fluid
- Alveolar macrophages
Correct Answer: Pleural fluid
Q12. The right lung has how many lobes?
- Two
- Three
- Four
- One
Correct Answer: Three
Q13. Which nerve provides motor innervation to the diaphragm?
- Vagus nerve (CN X)
- Phrenic nerve
- Intercostal nerves
- Accessory nerve (CN XI)
Correct Answer: Phrenic nerve
Q14. The primary site for gas exchange in the lung is:
- Trachea
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- Bronchi
Correct Answer: Alveoli
Q15. Pulmonary arteries carry which type of blood?
- Oxygenated blood from heart to lungs
- Deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
- Oxygenated blood to systemic circulation
- Deoxygenated blood to the liver
Correct Answer: Deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
Q16. The respiratory membrane is composed of all EXCEPT:
- Alveolar epithelium
- Capillary endothelium
- Fused basal laminae
- Hyaline cartilage
Correct Answer: Hyaline cartilage
Q17. Which cells are primary phagocytes in the alveoli?
- Type I pneumocytes
- Alveolar macrophages
- Type II pneumocytes
- Endothelial cells
Correct Answer: Alveolar macrophages
Q18. Bronchopulmonary segments are surgically important because they are:
- Indivisible functional units with overlapping blood supply
- Separable with their own bronchus and artery
- Only found in the left lung
- Not supplied by bronchi
Correct Answer: Separable with their own bronchus and artery
Q19. The obtuse and cardiac notches are features of which lung?
- Right lung only
- Left lung only
- Both lungs
- Neither lung
Correct Answer: Left lung only
Q20. The fissure separating upper and middle lobes of the right lung is the:
- Oblique fissure
- Horizontal fissure
- Interlobar fissure
- Cardiac fissure
Correct Answer: Horizontal fissure
Q21. Which cell type detoxifies inhaled substances and contributes to bronchiolar regeneration?
- Type I pneumocyte
- Club (Clara) cell
- Goblet cell
- Alveolar macrophage
Correct Answer: Club (Clara) cell
Q22. The area where pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and bronchi enter the lung is called the:
- Hilum
- Apex
- Base
- Cardiac notch
Correct Answer: Hilum
Q23. Which structure prevents collapse of the upper airway during inspiration?
- Alveolar surfactant
- Hyaline cartilage rings in trachea
- Type II pneumocytes
- Pleural cavity
Correct Answer: Hyaline cartilage rings in trachea
Q24. The costodiaphragmatic recess is clinically important because:
- It is the site for cardiac auscultation
- It is the lowest part of pleural cavity where fluid accumulates
- It contains the bronchopulmonary segments
- It connects to the peritoneal cavity
Correct Answer: It is the lowest part of pleural cavity where fluid accumulates
Q25. Ventilation-perfusion mismatch commonly affects which process?
- Neuromuscular transmission
- Gas exchange efficiency
- Gastric absorption
- Bone remodeling
Correct Answer: Gas exchange efficiency
Q26. The bronchial arteries primarily arise from which vessel?
- Pulmonary trunk
- Aorta
- Superior vena cava
- Inferior vena cava
Correct Answer: Aorta
Q27. Which structure forms the majority of the respiratory zone surface area?
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- Trachea
Correct Answer: Alveoli
Q28. The epithelia transition from pseudostratified to simple cuboidal occurs at:
- Terminal bronchioles
- Trachea
- Alveolar ducts
- Primary bronchi
Correct Answer: Terminal bronchioles
Q29. Pulmonary surfactant mainly reduces:
- Surface tension in alveoli
- Vascular resistance
- Bronchial smooth muscle tone
- Lymph formation
Correct Answer: Surface tension in alveoli
Q30. The mediastinal surface of the lung contains the:
- Costal grooves
- Hilum
- Diaphragmatic dome
- Anterior median fissure
Correct Answer: Hilum
Q31. Which embryologic origin gives rise to the respiratory epithelium?
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Neural crest
Correct Answer: Endoderm
Q32. The apex of the lung projects into which area?
- Above the clavicle into the root of the neck
- Into the abdominal cavity
- Into the pericardial sac
- Below the 12th rib
Correct Answer: Above the clavicle into the root of the neck
Q33. Which of the following decreases alveolar surface tension?
- Surfactant deficiency
- Increased alveolar radius
- Type II pneumocyte secretion
- Fibrosis of alveolar walls
Correct Answer: Type II pneumocyte secretion
Q34. The visceral pleura is supplied by which of the following nerves for sensory innervation?
- Phrenic nerve
- Somatic intercostal nerves
- Autonomic (visceral) nerves; mainly vagus and sympathetic fibers
- Accessory nerve
Correct Answer: Autonomic (visceral) nerves; mainly vagus and sympathetic fibers
Q35. The primary determinant of airway resistance in the bronchial tree is the:
- Length of the trachea
- Radius of the bronchioles
- Number of alveoli
- Thickness of the pleura
Correct Answer: Radius of the bronchioles
Q36. The term “respiratory bronchiole” indicates a structure that:
- Only conducts air
- Has both conducting and gas-exchanging functions
- Is lined with stratified squamous epithelium
- Is the main site of mucus production
Correct Answer: Has both conducting and gas-exchanging functions
Q37. Pulmonary veins carry blood to which chamber of the heart?
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
Correct Answer: Left atrium
Q38. Which structure is not part of the respiratory zone?
- Alveolar ducts
- Respiratory bronchioles
- Terminal bronchioles
- Alveolar sacs
Correct Answer: Terminal bronchioles
Q39. The pleura that directly covers the lung surface is the:
- Parietal pleura
- Visceral pleura
- Fibrous pleura
- Mucous pleura
Correct Answer: Visceral pleura
Q40. The major component of bronchial cartilage in main bronchi is:
- Elastic cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Epiglottic cartilage
Correct Answer: Hyaline cartilage
Q41. Which structure helps propel mucus and trapped particles out of the airways?
- Ciliary action of respiratory epithelium
- Surfactant secretion
- Alveolar macrophages
- Bronchial smooth muscle contraction
Correct Answer: Ciliary action of respiratory epithelium
Q42. In emphysema, which anatomical change primarily impairs gas exchange?
- Thickened pleura
- Destruction of alveolar walls and loss of surface area
- Increased bronchial cartilage
- Hyperplasia of Type II pneumocytes
Correct Answer: Destruction of alveolar walls and loss of surface area
Q43. The pleural reflection where the diaphragmatic pleura meets the costal pleura is called the:
- Costomediastinal recess
- Costodiaphragmatic recess
- Interpleural fold
- Hilum
Correct Answer: Costodiaphragmatic recess
Q44. The term “respiratory membrane thickness” influences which parameter most directly?
- Heart rate
- Diffusion rate of gases
- Bronchial tone
- Blood glucose
Correct Answer: Diffusion rate of gases
Q45. Which pulmonary cells are the main source of lung surfactant proteins?
- Type I pneumocytes
- Type II pneumocytes
- Club cells
- Endothelial cells
Correct Answer: Type II pneumocytes
Q46. The region of the pleura sensitive to pain and temperature is the:
- Visceral pleura
- Parietal pleura
- Alveolar pleura
- Pulmonary pleura
Correct Answer: Parietal pleura
Q47. Which factor favors deposition of inhaled particles deep into the lungs for drug delivery?
- Large particle size (>10 µm)
- Small particle size (1–5 µm)
- High humidity only
- Low inspiratory flow rate only
Correct Answer: Small particle size (1–5 µm)
Q48. A pulmonary embolus most directly affects which of the following?
- Airway smooth muscle tone
- Pulmonary blood flow and ventilation-perfusion matching
- Bronchial mucus secretion
- Surfactant production
Correct Answer: Pulmonary blood flow and ventilation-perfusion matching
Q49. Which structure forms the supportive framework of bronchi and prevents collapse?
- Smooth muscle only
- Cartilaginous plates or rings
- Elastin fibers only
- Type II pneumocytes
Correct Answer: Cartilaginous plates or rings
Q50. The dominant muscle of inspiration that increases thoracic volume is the:
- External oblique
- Internal intercostals
- Diaphragm
- Transversus thoracis
Correct Answer: Diaphragm

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com