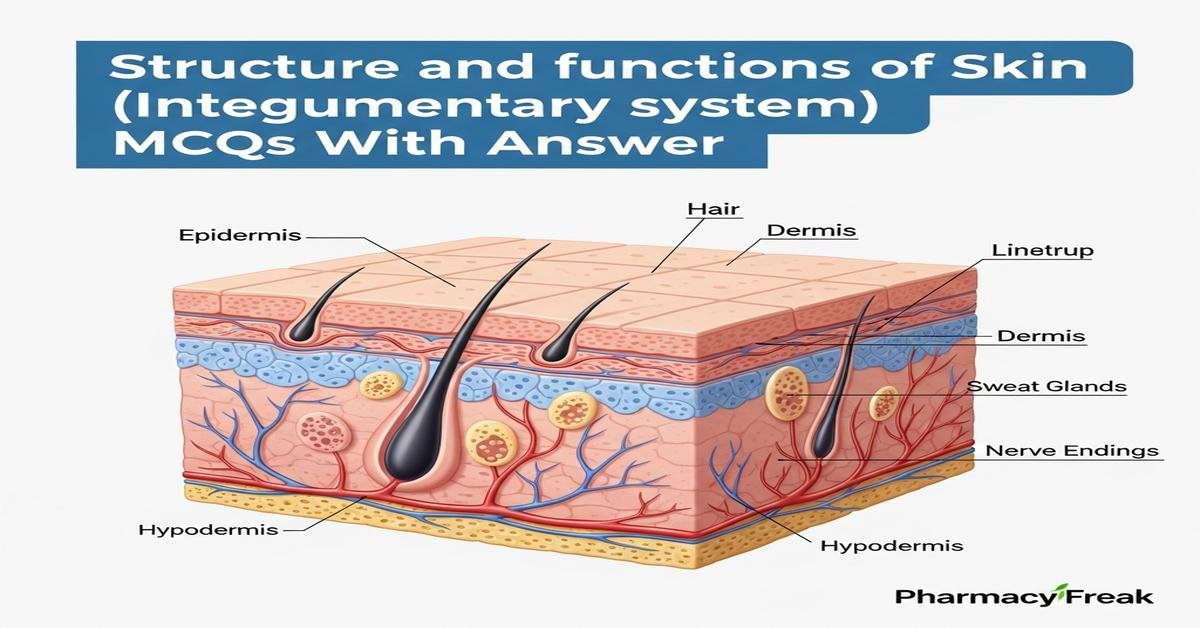
Understanding the structure and functions of skin is essential for B. Pharm students learning the integumentary system. This concise guide covers epidermis, dermis and hypodermis architecture, keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans and Merkel cells, and extracellular matrix components such as collagen and elastin. It explains appendages—hair follicles, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands—and physiological roles like barrier function, thermoregulation, sensation, immunity, wound healing, and fluid balance. Pharmacologically relevant topics include transdermal drug delivery, percutaneous absorption, skin pH, and factors affecting bioavailability and topical therapy. Core keywords reinforce concepts for exams and clinical practice. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which layer of the epidermis contains actively dividing keratinocytes?
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum basale
- Stratum lucidum
Correct Answer: Stratum basale
Q2. Which cell type in the epidermis is primarily responsible for melanin production?
- Langerhans cell
- Keratinocyte
- Melanocyte
- Merkel cell
Correct Answer: Melanocyte
Q3. Langerhans cells in the skin function mainly as:
- Pigment producers
- Antigen-presenting immune cells
- Touch receptors
- Sweat-secreting cells
Correct Answer: Antigen-presenting immune cells
Q4. Which dermal component provides tensile strength and is most abundant in the dermis?
- Elastin
- Keratin
- Collagen
- Hyaluronan
Correct Answer: Collagen
Q5. The primary function of the stratum corneum is:
- Melanin synthesis
- Barrier to water loss and microbes
- Sensory transduction
- Temperature regulation
Correct Answer: Barrier to water loss and microbes
Q6. Which structure is responsible for oily secretions that lubricate hair and skin?
- Sweat gland
- Sebaceous gland
- Apocrine gland
- Meibomian gland
Correct Answer: Sebaceous gland
Q7. Transdermal drug delivery primarily targets which skin layer for systemic absorption?
- Stratum corneum
- Viable epidermis and dermis
- Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
- Nail plate
Correct Answer: Viable epidermis and dermis
Q8. Which factor increases percutaneous absorption of a topical drug?
- Increased molecular weight
- Hydrophilic vehicle only
- Occlusion over the application site
- Intact thick stratum corneum
Correct Answer: Occlusion over the application site
Q9. Merkel cells are primarily associated with which function?
- Thermoregulation
- Light touch sensation
- Immune defense
- Melanin transfer
Correct Answer: Light touch sensation
Q10. Which junctional structure provides strong cell–cell adhesion between keratinocytes?
- Tight junctions (zonula occludens)
- Gap junctions
- Desmosomes
- Hemi-desmosomes
Correct Answer: Desmosomes
Q11. Which layer lies immediately below the dermis and is rich in adipose tissue?
- Stratum basale
- Hypodermis (subcutis)
- Stratum spinosum
- Papillary dermis
Correct Answer: Hypodermis (subcutis)
Q12. Filaggrin deficiency is associated with which skin condition commonly relevant to pharmacists?
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
- Vitiligo
- Impetigo
Correct Answer: Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Q13. A major role of eccrine sweat glands is:
- Scent production
- Thermoregulatory evaporative cooling
- Sebum secretion
- Keratinization
Correct Answer: Thermoregulatory evaporative cooling
Q14. Percutaneous absorption is lowest for drugs that are:
- Highly lipophilic with low molecular weight
- Highly hydrophilic and large molecular size
- Applied with penetration enhancers
- Formulated in lipid-rich vehicles
Correct Answer: Highly hydrophilic and large molecular size
Q15. Which pigment-producing pathway determines skin phototype and UV protection?
- Carotenoid synthesis
- Melanin synthesis via tyrosinase
- Hemoglobin oxidation
- Lipid peroxidation
Correct Answer: Melanin synthesis via tyrosinase
Q16. Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) increases when:
- Skin barrier is intact
- Stratum corneum lipids are disrupted
- Occlusive emollients are applied
- Hydration is optimal
Correct Answer: Stratum corneum lipids are disrupted
Q17. Which phase of wound healing involves collagen deposition by fibroblasts?
- Hemostasis
- Inflammatory phase
- Proliferative phase
- Remodeling (maturation) phase
Correct Answer: Proliferative phase
Q18. Which skin appendage is NOT involved in thermoregulation?
- Eccrine sweat gland
- Arrector pili muscle attached to hair follicle
- Sebaceous gland
- Blood vessels in dermis
Correct Answer: Sebaceous gland
Q19. The basement membrane zone between epidermis and dermis contains which specialized structure for attachment?
- Gap junctions
- Hemidesmosomes
- Desmosomes
- Focal adhesions only in dermis
Correct Answer: Hemidesmosomes
Q20. Which enzyme is rate-limiting in melanin synthesis and a target for depigmenting agents?
- Collagenase
- Tyrosinase
- Elastase
- Keratinase
Correct Answer: Tyrosinase
Q21. In topical corticosteroid therapy, potency and systemic absorption depend on all EXCEPT:
- Vehicle formulation
- Area and integrity of the skin
- Duration of application
- Patient’s hair color
Correct Answer: Patient’s hair color
Q22. Which structure in the dermis contains sensory receptors for pressure and vibration?
- Meissner corpuscles
- Pacinian (lamellar) corpuscles
- Free nerve endings
- Merkel discs
Correct Answer: Pacinian (lamellar) corpuscles
Q23. Acid mantle of the skin refers to:
- Alkaline surface pH that prevents microbes
- Acidic surface pH that supports barrier and antimicrobial defense
- Layer of sebum only
- Subcutaneous fat layer acidity
Correct Answer: Acidic surface pH that supports barrier and antimicrobial defense
Q24. Which skin protein is the main structural component of the stratum corneum providing water resistance?
- Keratin
- Elastin
- Collagen type I
- Actin
Correct Answer: Keratin
Q25. Topical antibiotics for superficial skin infections are chosen to target common pathogens such as:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa exclusively
- Fungal dermatophytes primarily
Correct Answer: Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci
Q26. Which molecule in the dermal extracellular matrix retains water and supports hydration?
- Keratin
- Hyaluronic acid
- Melanin
- Lactic acid
Correct Answer: Hyaluronic acid
Q27. Nails are modifications of which epidermal structure?
- Stratum corneum and nail matrix (keratinized cells)
- Dermal papillae only
- Apocrine glands
- Subcutaneous fat
Correct Answer: Stratum corneum and nail matrix (keratinized cells)
Q28. Which condition is characterized by hyperproliferation and abnormal keratinization of the epidermis?
- Psoriasis
- Acne vulgaris
- Urticaria
- Tinea corporis
Correct Answer: Psoriasis
Q29. For intradermal or subcutaneous injections, pharmacists must consider that the hypodermis primarily affects:
- Drug taste
- Absorption rate and depot formation
- Hepatic first-pass metabolism
- Pulmonary distribution
Correct Answer: Absorption rate and depot formation
Q30. Which statement best describes the skin’s immunological role?
- Skin has no immune cells and only mechanical defense
- Skin houses innate and adaptive immune cells that detect and respond to pathogens
- Immune responses occur only in the bloodstream, not skin
- Keratinocytes cannot produce cytokines
Correct Answer: Skin houses innate and adaptive immune cells that detect and respond to pathogens

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com