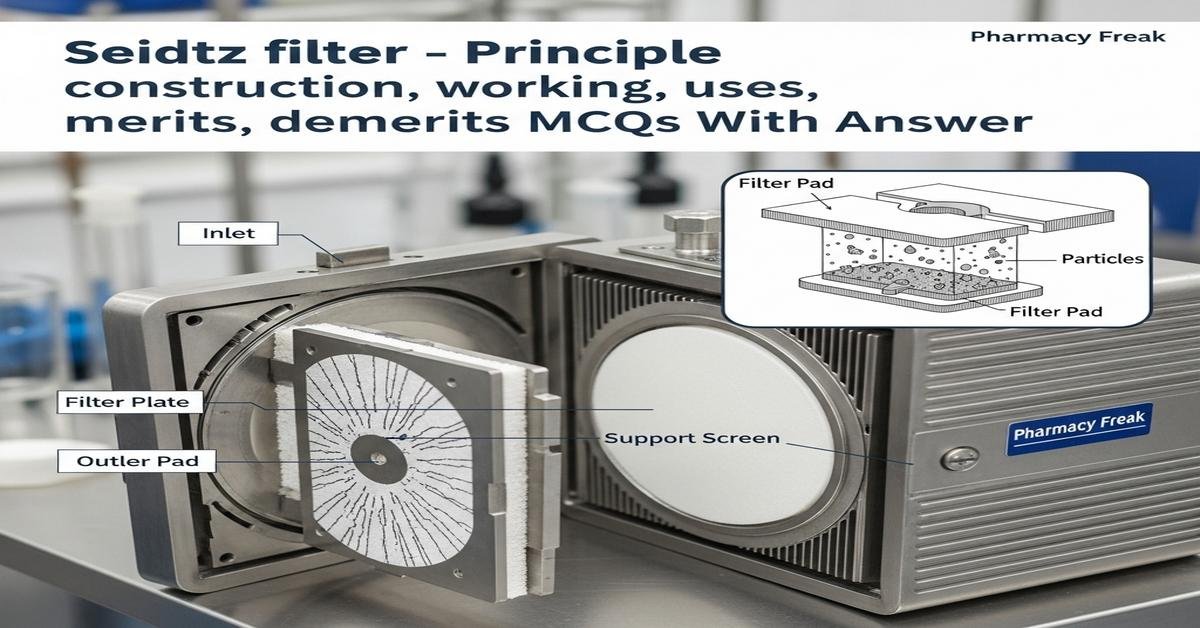
Seidtz filter is an important depth/membrane filtration device widely studied in pharmaceutics for sterilizing and clarifying heat-sensitive liquids. This introduction explains the Seidtz filter principle, construction, working mechanism, practical uses, merits and demerits, and typical operating parameters relevant to B. Pharm students. You will learn about pore structure, flow dynamics, filter aids, pressure and vacuum operation, cleaning and sterilization protocols, and common pharmaceutical applications such as sterile filtration of injectables, vaccines, and biological media. Understanding these concepts helps optimize filtration efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance. The content is Student-friendly, keyword-rich and tailored for exam preparation and practical lab work. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the principal mechanism by which a Seidtz filter retains particles?
- Adsorption onto activated carbon
- Size exclusion and depth filtration through a porous medium
- Centrifugal separation by rotation
- Magnetic attraction of impurities
Correct Answer: Size exclusion and depth filtration through a porous medium
Q2. Which component is essential in the construction of a typical Seidtz filter?
- A porous filter element or cartridge
- An ultrasonic transducer
- A heating mantle
- A cyclone separator
Correct Answer: A porous filter element or cartridge
Q3. Seidtz filters are most suitable for which type of pharmaceutical liquids?
- High-viscosity molten polymers
- Heat-sensitive sterile liquid formulations
- Bulk powdered solids
- Gaseous mixtures
Correct Answer: Heat-sensitive sterile liquid formulations
Q4. Which operating mode is commonly used with Seidtz filters?
- Vacuum or pressure-driven filtration
- Purely gravitational settling without pressure
- Electrostatic precipitation
- Membrane distillation
Correct Answer: Vacuum or pressure-driven filtration
Q5. A key advantage of Seidtz filters in pharmaceutical processing is:
- Ability to autoclave large solid particles without disintegration
- Efficient removal of microorganisms while preserving active ingredients
- Complete removal of dissolved salts
- Generating sterile powders directly
Correct Answer: Efficient removal of microorganisms while preserving active ingredients
Q6. Which property of the filter medium primarily determines the retention of bacteria?
- Pore size distribution
- Color of the filter material
- Electrical conductivity
- Magnetic susceptibility
Correct Answer: Pore size distribution
Q7. In validation of a Seidtz filter, which integrity test is commonly applied?
- pH titration test
- Bubble point or pressure-hold test
- UV absorbance at 600 nm
- Thermogravimetric analysis
Correct Answer: Bubble point or pressure-hold test
Q8. Typical pore size for sterilizing-grade Seidtz filter media is around:
- 10–20 micrometers
- 0.22–0.45 micrometers
- 100–200 micrometers
- 1–5 millimeters
Correct Answer: 0.22–0.45 micrometers
Q9. Filter aids used with Seidtz filters (e.g., diatomaceous earth) primarily function to:
- Act as antimicrobial agents
- Create a porous precoat or body to improve flow and clarify
- Change product color
- Reduce pH of the liquid
Correct Answer: Create a porous precoat or body to improve flow and clarify
Q10. One common demerit of Seidtz filtration is:
- Inability to remove particulate matter
- Potential adsorption or loss of product to filter medium
- Complete thermal sterilization is required afterward
- It always increases product viscosity
Correct Answer: Potential adsorption or loss of product to filter medium
Q11. During filtration, the phenomenon of ‘cake formation’ refers to:
- Deposition of retained solids on the filter surface forming a cake layer
- Crystallization of dissolved salts into cubes
- Formation of bubbles inside the filter pores
- Melting of filter material
Correct Answer: Deposition of retained solids on the filter surface forming a cake layer
Q12. How can the flow rate through a Seidtz filter be increased without changing pore size?
- Decrease applied pressure
- Use a precoat or thinner feed and increase pressure
- Increase viscosity of the feed liquid
- Block some pores intentionally
Correct Answer: Use a precoat or thinner feed and increase pressure
Q13. For sterile filtration of injectable solutions, the Seidtz filter should be made from materials that are:
- Inert, non-shedding and compatible with the formulation
- Highly soluble in the product
- Strongly acidic
- Magnetic
Correct Answer: Inert, non-shedding and compatible with the formulation
Q14. Which parameter is most important to monitor during a filtration run to detect clogging?
- Color of feed
- Transmembrane pressure or differential pressure across the filter
- Ambient room noise
- Humidity of laboratory air
Correct Answer: Transmembrane pressure or differential pressure across the filter
Q15. Compared to membrane cartridge filters, Seidtz depth filters typically offer:
- Higher adsorption capacity for suspended solids and longer service life for turbid feeds
- Absolute sterilizing retention for gases
- Lower hold-up volumes only for gaseous systems
- Complete removal of dissolved organics
Correct Answer: Higher adsorption capacity for suspended solids and longer service life for turbid feeds
Q16. A precoat in Seidtz filtration refers to:
- A protective disposable outer casing
- A layer of filter aid deposited on the filter support before filtration
- A heating cycle to sterilize the housing
- An electrical coating to increase conductivity
Correct Answer: A layer of filter aid deposited on the filter support before filtration
Q17. Which cleaning method is generally used for reusable Seidtz filter housings?
- Alkaline or acidic cleaning followed by thorough rinsing and sterilization
- Ignition at 800 °C to burn residues
- Soaking in concentrated HCl for weeks
- Dry brushing only without rinsing
Correct Answer: Alkaline or acidic cleaning followed by thorough rinsing and sterilization
Q18. The Darcy’s law relates filtration flow to which factors?
- Viscosity, pressure drop, filter thickness and permeability
- Color intensity and taste of filtrate
- Magnetic field strength
- Humidity and ambient light
Correct Answer: Viscosity, pressure drop, filter thickness and permeability
Q19. Which of the following is a common maintenance task for a Seidtz filter?
- Replacing or regenerating filter cartridges or precoat material
- Polishing the product to a shine
- Adding preservatives to the filter medium
- Changing product formulation daily
Correct Answer: Replacing or regenerating filter cartridges or precoat material
Q20. What is a likely consequence of using an overly fine pore size for a Seidtz filter?
- Increased flow rate with no change in pressure
- Excessive pressure build-up and rapid clogging
- Complete dissolution of the filter
- No retention of microbes
Correct Answer: Excessive pressure build-up and rapid clogging
Q21. Which analytical method can be used to verify sterile filtration performance?
- Microbial challenge test with a defined organism
- Measuring refractive index only
- Flame photometry of the housing
- pH paper of the filter medium
Correct Answer: Microbial challenge test with a defined organism
Q22. In pharmaceutical filtration, ‘hold-up volume’ refers to:
- Volume of product retained in the filter and piping after flow stops
- Total batch size
- Amount of time filtration is paused
- Volume of solvent used for cleaning
Correct Answer: Volume of product retained in the filter and piping after flow stops
Q23. What is the primary reason to perform a pre-filtration step before Seidtz sterile filtration?
- To concentrate the product by evaporation
- To remove coarse particulates and reduce burden on sterilizing filter
- To sterilize the air in the room
- To chemically modify the API
Correct Answer: To remove coarse particulates and reduce burden on sterilizing filter
Q24. Which of the following best describes a depth filter used in Seidtz systems?
- A thin membrane with uniform pores only at the surface
- A thick porous matrix that traps particles throughout its depth
- A rotating screen with large openings
- A filter that works only by surface adsorption
Correct Answer: A thick porous matrix that traps particles throughout its depth
Q25. Which operating precaution is important when filtering sterile protein solutions through Seidtz filters?
- Use of harsh organic solvents to increase flow
- Control of shear and adsorption to minimize protein loss or denaturation
- Heating the protein to 121 °C during filtration
- Adding metal shavings to the feed
Correct Answer: Control of shear and adsorption to minimize protein loss or denaturation
Q26. Which parameter is used to express filter capacity for particulate removal?
- Microbial colony count of air
- Dust holding capacity or total solids retained per unit area
- Electrical resistance
- Optical rotation
Correct Answer: Dust holding capacity or total solids retained per unit area
Q27. What is a typical corrective action when differential pressure across the Seidtz filter increases sharply?
- Continue operation indefinitely
- Stop flow, replace or regenerate filter medium and inspect feed for solids
- Add sugar to the feed to reduce pressure
- Increase ambient room temperature
Correct Answer: Stop flow, replace or regenerate filter medium and inspect feed for solids
Q28. Which regulatory concern is relevant when using Seidtz filters for injectable products?
- Demonstration of consistent sterile retention and validated cleaning to prevent contamination
- Use of colorful filter housings for branding
- Ensuring filter changes every hour regardless of use
- Eliminating all records to save space
Correct Answer: Demonstration of consistent sterile retention and validated cleaning to prevent contamination
Q29. Which material is commonly used as a filter aid or precoat in Seidtz filtration?
- Diatomaceous earth (celite)
- Polyethylene glycol 4000 as a solvent
- Liquid nitrogen
- Metal filings
Correct Answer: Diatomaceous earth (celite)
Q30. How does temperature generally affect filtration viscosity and flow in Seidtz systems?
- Higher temperature usually decreases viscosity and increases flow
- Temperature has no effect on viscosity
- Higher temperature always clogs the filter immediately
- Lower temperature reduces flow by dissolving the medium
Correct Answer: Higher temperature usually decreases viscosity and increases flow
Q31. In the context of Seidtz filters, ‘sterile filtration’ implies removal of:
- Dissolved ions only
- Viable microorganisms to meet sterility assurance levels
- All molecules below 100 Da
- Only visible particulates larger than 1 mm
Correct Answer: Viable microorganisms to meet sterility assurance levels
Q32. What is the typical response if a Seidtz filter fails an integrity (bubble point) test after sterilization?
- The filter is declared fit for use without replacement
- The filter must be discarded or revalidated before use
- Proceed with filtration but reduce flow
- Invert the filter to fix the bubble point
Correct Answer: The filter must be discarded or revalidated before use
Q33. Which advantage does pre-coating the Seidtz filter provide?
- Reduces initial turbidity and protects the fine filter medium from rapid clogging
- Increases ionic content of filtrate
- Guarantees chemical sterilization
- Makes the filter hydrophobic only
Correct Answer: Reduces initial turbidity and protects the fine filter medium from rapid clogging
Q34. Which test can detect sub-visible particles in filtrate after Seidtz filtration?
- Light obscuration particle count method
- Visual observation only
- pH measurement
- X-ray crystallography
Correct Answer: Light obscuration particle count method
Q35. Which phenomenon can cause late breakthrough of microbes in filtration?
- Improper wetting of filter medium leading to channeling
- Adding extra solvent to improve flow
- Overcooling the feed below 0 °C
- Using oversized housings
Correct Answer: Improper wetting of filter medium leading to channeling
Q36. When selecting a Seidtz filter for an acidic formulation, you should:
- Choose filter materials and gaskets compatible with the acid to avoid degradation
- Always use steel wool as gasket
- Ignore chemical compatibility if pore size is correct
- Use rubber gaskets without checking
Correct Answer: Choose filter materials and gaskets compatible with the acid to avoid degradation
Q37. Which maintenance action helps prolong filter life in heavy particulate feeds?
- Installing a coarse pre-filter or clarifier upstream
- Running the filter dry between batches
- Removing filter aids from the feed
- Increasing feed concentration of solids
Correct Answer: Installing a coarse pre-filter or clarifier upstream
Q38. In calculating flux (J) during filtration, which units are typically used?
- mL per minute per square centimeter or L/m2·hr
- Kilograms per mole
- Degrees Celsius
- Lumens
Correct Answer: mL per minute per square centimeter or L/m2·hr
Q39. Which is a merit of using Seidtz filters for biotechnology products?
- Low shear and gentle processing suitable for labile biomolecules
- Total chemical modification of proteins
- Guaranteed removal of endotoxins without additional steps
- Instant evaporation of solvents
Correct Answer: Low shear and gentle processing suitable for labile biomolecules
Q40. A common reason for discoloration of filtrate after Seidtz filtration is:
- Leaching or adsorption of product components onto filter aid or medium
- Presence of bubbles only
- Ambient light levels
- Magnetic interference
Correct Answer: Leaching or adsorption of product components onto filter aid or medium
Q41. Which step is critical prior to starting sterile filtration with a Seidtz filter cartridge?
- Performing a leak and integrity check and proper wetting of the filter
- Filling the lab coat pockets with solvents
- Measuring the room temperature only
- Adding preservatives to the product always
Correct Answer: Performing a leak and integrity check and proper wetting of the filter
Q42. The term ‘absolute rating’ of a filter refers to:
- The nominal thickness of the housing
- The pore size at which the filter retains ≥99.9% of particles of that size
- The electrical charge rating of the filter
- The cost of the filter per run
Correct Answer: The pore size at which the filter retains ≥99.9% of particles of that size
Q43. To minimize product adsorption on Seidtz filters, one may:
- Optimize flow conditions, pre-wet the filter and select low-binding materials
- Increase contact time to hours
- Add metal ions to bind product
- Run filtration at extremely low pH regardless of product stability
Correct Answer: Optimize flow conditions, pre-wet the filter and select low-binding materials
Q44. Which of the following is a demerit when Seidtz filters are used without proper pre-treatment of feed?
- Rapid fouling and reduced throughput
- Complete chemical sterilization of feed
- Instant color correction of the product
- Automatic pH adjustment
Correct Answer: Rapid fouling and reduced throughput
Q45. Which operational control prevents accidental introduction of air during Seidtz filtration?
- Ensuring proper priming and venting procedures
- Always running the system empty
- Using open trays instead of closed housings
- Pouring product from great height
Correct Answer: Ensuring proper priming and venting procedures
Q46. When scaling up Seidtz filtration from lab to production, a key consideration is:
- Maintaining similar linear velocities, residence times and filter area to feed ratios
- Using identical small lab housings only
- Doubling product concentration arbitrarily
- Changing product formulation completely
Correct Answer: Maintaining similar linear velocities, residence times and filter area to feed ratios
Q47. Which waste handling consideration applies to filter aids used in Seidtz filtration?
- Proper disposal per local regulations and avoiding release of hazardous particulates
- Dumping into sinks without concern
- Burning on open lab benches
- Using as fertilizer without testing
Correct Answer: Proper disposal per local regulations and avoiding release of hazardous particulates
Q48. Which change indicates the end of effective life for a disposable Seidtz filter during a run?
- Sharp rise in differential pressure and decline in permeate flow
- Increase in ambient lighting
- Completion of one hour of operation irrespective of performance
- Change in operator
Correct Answer: Sharp rise in differential pressure and decline in permeate flow
Q49. In a multiple-stage filtration process using Seidtz filters, the downstream (final) stage is typically designed for:
- Sterile retention and fine clarification
- Coarse sludge removal only
- Heating the product to dryness
- Introducing particulates intentionally
Correct Answer: Sterile retention and fine clarification
Q50. Which documentation is essential for regulatory compliance when using Seidtz filters in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
- Filter validation reports, integrity test records, cleaning and maintenance logs
- Only marketing brochures
- Personal notes kept off-site without dates
- Hand-drawn sketches without specifications
Correct Answer: Filter validation reports, integrity test records, cleaning and maintenance logs

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com