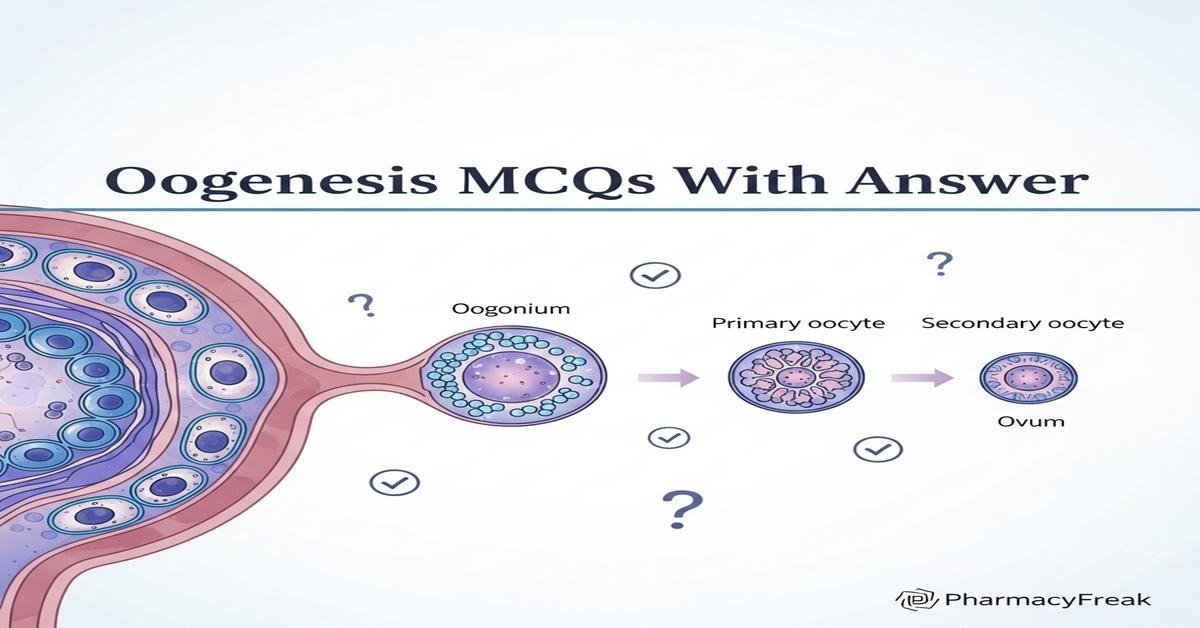
Oogenesis MCQs With Answer provide B. Pharm students a focused, exam-oriented way to master female gametogenesis, ovarian follicle dynamics, meiotic divisions, and hormonal regulation. This concise question set covers primordial to Graafian follicle changes, meiotic arrest and resumption, cytoplasmic maturation, polar bodies, aneuploidy risk, and clinical concepts like in vitro maturation and ovulation induction. Carefully designed Oogenesis MCQs help reinforce key terms—oogenesis, meiosis I and II, folliculogenesis, granulosa and theca cell functions, zona pellucida, AMH, FSH, LH—and improve retention for pharmacology, reproductive physiology, and clinical pharmacy topics. Ideal for revision before exams and interviews. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the first permanent female germ cell formed during fetal ovary development?
- Primary oocyte
- Secondary oocyte
- Oogonium
- Ovum
Correct Answer: Oogonium
Q2. At which stage of meiosis are human primary oocytes arrested until puberty?
- Metaphase II
- Dictyate stage of prophase I
- Telophase I
- Anaphase II
Correct Answer: Dictyate stage of prophase I
Q3. Completion of meiosis I in the oocyte typically occurs at which time?
- Immediately after fertilization
- During fetal development
- Just before or during ovulation
- At menopause
Correct Answer: Just before or during ovulation
Q4. Which structure is formed from the oocyte and surrounding granulosa cells before ovulation?
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus luteum
- Graafian (mature) follicle
- Primordial follicle
Correct Answer: Graafian (mature) follicle
Q5. Which hormone surge triggers ovulation and resumption of meiosis in the oocyte?
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Progesterone
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Prolactin
Correct Answer: Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Q6. Which cells primarily produce estrogen in antral follicles?
- Oocyte
- Theca interna cells and granulosa cells via aromatase
- Corpus luteum only
- Stromal fibroblasts
Correct Answer: Theca interna cells and granulosa cells via aromatase
Q7. Which glycoprotein layer surrounds the oocyte and mediates sperm binding?
- Cortical granules
- Zona pellucida
- Corona radiata
- Basal lamina
Correct Answer: Zona pellucida
Q8. What is the primary function of cortical granules in the oocyte?
- Initiate meiosis
- Prevent polyspermy by modifying the zona pellucida after fertilization
- Produce estrogen
- Provide ATP to sperm
Correct Answer: Prevent polyspermy by modifying the zona pellucida after fertilization
Q9. Which of the following best describes the fate of most ovarian follicles during a woman’s life?
- They all mature into ovulated oocytes
- They remain primordial indefinitely
- They undergo atresia and degenerate
- They transform into corpus luteum directly
Correct Answer: They undergo atresia and degenerate
Q10. Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is secreted by which follicular cells and indicates what?
- Theca cells; luteal activity
- Antral and preantral granulosa cells; ovarian reserve and follicle pool size
- Corpus luteum; progesterone levels
- Oocyte; meiotic competence
Correct Answer: Antral and preantral granulosa cells; ovarian reserve and follicle pool size
Q11. The first polar body formation is a result of which meiotic event?
- Completion of meiosis II
- Completion of meiosis I
- Initiation of meiosis during fetal life
- Fertilization
Correct Answer: Completion of meiosis I
Q12. Which meiotic division is completed only after sperm penetration in human oocytes?
- Meiosis I
- Premeiotic DNA replication
- Meiosis II
- Interphase
Correct Answer: Meiosis II
Q13. During folliculogenesis, theca interna cells primarily provide:
- FSH receptors and estrogen production
- Androgen precursors for estrogen synthesis under LH stimulation
- Zona pellucida synthesis
- Oocyte mitochondrial replication
Correct Answer: Androgen precursors for estrogen synthesis under LH stimulation
Q14. Which protein family forms the structural components of the human zona pellucida?
- Cytokines
- ZP glycoproteins (e.g., ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, ZP4)
- Keratins
- Collagens
Correct Answer: ZP glycoproteins (e.g., ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, ZP4)
Q15. Mitochondrial DNA in the embryo is primarily inherited from:
- The father via sperm mitochondria
- Both parents equally
- The oocyte (maternal inheritance)
- The granulosa cells
Correct Answer: The oocyte (maternal inheritance)
Q16. Which process during prophase I increases genetic diversity in oocytes?
- DNA methylation
- Crossing over (homologous recombination)
- Spindle assembly checkpoint
- Apoptosis of follicles
Correct Answer: Crossing over (homologous recombination)
Q17. Advanced maternal age increases the risk of which oocyte-related chromosomal error?
- Chromosomal translocation repair
- Aneuploidy due to nondisjunction
- Mitochondrial duplication errors
- Increased zona pellucida thickness only
Correct Answer: Aneuploidy due to nondisjunction
Q18. In vitro maturation (IVM) of oocytes refers to:
- Maturing oocytes in the ovarian follicle only
- Maturing immature oocytes in culture to metaphase II for assisted reproduction
- Cryopreserving mature oocytes instantly
- Inducing atresia of follicles
Correct Answer: Maturing immature oocytes in culture to metaphase II for assisted reproduction
Q19. Which drug is commonly used to induce ovulation by antagonizing estrogen receptors centrally?
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Clomiphene citrate
- Progesterone only
- Metformin
Correct Answer: Clomiphene citrate
Q20. The term “follicular atresia” best describes:
- Ovulation of multiple follicles
- Apoptotic degeneration of follicles not selected for ovulation
- Conversion of follicle to corpus luteum
- Oocyte fertilization
Correct Answer: Apoptotic degeneration of follicles not selected for ovulation
Q21. Which factor secreted by granulosa cells inhibits recruitment of primordial follicles?
- FSH
- AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone)
- LH
- hCG
Correct Answer: AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone)
Q22. The cumulus oophorus refers to:
- The layer of theca externa cells
- The oocyte plus its immediately surrounding granulosa cell matrix released at ovulation
- The corpus luteum structure
- The basal lamina around the follicle
Correct Answer: The oocyte plus its immediately surrounding granulosa cell matrix released at ovulation
Q23. Which event marks meiotic spindle formation for chromosome segregation in the oocyte?
- Cortical granule release
- Germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD)
- Zygote cleavage
- Zona pellucida hardening
Correct Answer: Germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD)
Q24. Which cell type expresses receptors for FSH and is essential for estrogen synthesis?
- Theca interna cells exclusively
- Granulosa cells
- Stromal cells only
- Oocyte membrane only
Correct Answer: Granulosa cells
Q25. Which anatomical structure remains after luteolysis if pregnancy does not occur?
- Corpus luteum of pregnancy
- Corpus albicans
- Graafian follicle
- Primordial follicle
Correct Answer: Corpus albicans
Q26. Which assessment is commonly used clinically to estimate ovarian reserve relevant to oogenesis?
- Serum progesterone on day 14
- Basal serum FSH only
- Serum AMH level and antral follicle count
- Serum prolactin level
Correct Answer: Serum AMH level and antral follicle count
Q27. The zona pellucida induces the acrosome reaction in sperm primarily via which glycoprotein ligand?
- ZP1
- ZP2
- ZP3
- ZP4
Correct Answer: ZP3
Q28. Which of the following best describes oocyte cytoplasmic maturation?
- Only chromosomal segregation without cytoplasmic changes
- Accumulation of RNAs, proteins, mitochondria, and cortical granules required for early embryogenesis
- Loss of mitochondria to adjacent granulosa cells
- Complete breakdown of ER and Golgi apparatus
Correct Answer: Accumulation of RNAs, proteins, mitochondria, and cortical granules required for early embryogenesis
Q29. Polar bodies usually contain:
- Most of the cytoplasm and organelles
- Little cytoplasm and a haploid set of chromosomes
- Diploid chromosome sets
- Extra mitochondria to support embryo
Correct Answer: Little cytoplasm and a haploid set of chromosomes
Q30. Which laboratory technique removes an oocyte from the ovary for assisted reproduction?
- Hysteroscopy
- Transvaginal ultrasound-guided oocyte retrieval
- Laparoscopic oophorectomy in all cases
- Endometrial biopsy
Correct Answer: Transvaginal ultrasound-guided oocyte retrieval
Q31. Which cell–cell communication structure connects granulosa cells and the oocyte?
- Tight junctions only
- Gap junctions allowing transfer of small molecules
- Desmosomes for strength only
- No direct connections exist
Correct Answer: Gap junctions allowing transfer of small molecules
Q32. Which event in oogenesis is directly responsible for reducing chromosome number from diploid to haploid?
- Mitochondrial segregation
- Meiotic divisions (meiosis I and II)
- Follicular atresia
- Zona pellucida formation
Correct Answer: Meiotic divisions (meiosis I and II)
Q33. Which substance released by the dominant follicle contributes to suppression of other follicles?
- Testosterone only
- Inhibin and estradiol
- Cortisol
- hCG from corpus luteum
Correct Answer: Inhibin and estradiol
Q34. A primary oocyte arrested in prophase I contains which nuclear structure visible microscopically?
- Germinal vesicle
- Prometaphase plate
- Synaptonemal complex only after ovulation
- Polar body II
Correct Answer: Germinal vesicle
Q35. Which of the following contraceptive mechanisms directly prevents ovulation and thus oogenesis progression?
- Barrier methods like condoms
- Combined oral contraceptives suppressing LH/FSH via negative feedback
- Spermicides affecting sperm motility only
- Intrauterine devices that allow ovulation
Correct Answer: Combined oral contraceptives suppressing LH/FSH via negative feedback
Q36. Which genetic test can be performed on polar bodies to assess maternal chromosomal status?
- Y-chromosome microarray only
- Polar body biopsy for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
- Sperm DNA fragmentation assay
- Endometrial receptivity array
Correct Answer: Polar body biopsy for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
Q37. Which factor is most critical for synchronizing nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation during oocyte development?
- Exclusive LH signaling without FSH
- Coordinated endocrine (FSH/LH) and paracrine signaling from granulosa and theca cells
- Only mitochondrial biogenesis independent of hormones
- Mechanical stretching of the follicle
Correct Answer: Coordinated endocrine (FSH/LH) and paracrine signaling from granulosa and theca cells
Q38. Which pathological process in the ovary directly reduces the pool of available oocytes prematurely?
- Polycystic ovary syndrome increasing ovulation
- Premature ovarian insufficiency leading to early follicle depletion
- Prolonged antral follicle growth
- Excessive luteinization only
Correct Answer: Premature ovarian insufficiency leading to early follicle depletion
Q39. Which of the following is NOT a feature of a competent oocyte for fertilization?
- Proper chromosomal alignment on meiotic spindle
- Adequate cytoplasmic stores and mitochondria
- Destroyed zona pellucida
- Intact cortical granules prior to fertilization
Correct Answer: Destroyed zona pellucida
Q40. Which enzyme activity in granulosa cells is essential for converting androgens to estrogens?
- 5-alpha reductase
- Aromatase (CYP19A1)
- Monoamine oxidase
- DNA polymerase
Correct Answer: Aromatase (CYP19A1)
Q41. During assisted reproduction, hCG is often used to:
- Stimulate follicular atresia
- Mimic LH surge to trigger final oocyte maturation and ovulation
- Suppress estrogen production permanently
- Induce AMH secretion
Correct Answer: Mimic LH surge to trigger final oocyte maturation and ovulation
Q42. Which molecular event at fertilization prevents additional sperms from fusing with the oocyte?
- Formation of multiple pronuclei
- Cortical reaction modifying the zona pellucida leading to zona hardening
- Increase in follicular atresia
- Oocyte returns to prophase I
Correct Answer: Cortical reaction modifying the zona pellucida leading to zona hardening
Q43. The majority of oocyte growth and accumulation of cytoplasmic components occurs during which follicular stage?
- Primordial follicle stage
- Preantral and early antral follicle stages
- Post-ovulatory corpus luteum stage
- After implantation
Correct Answer: Preantral and early antral follicle stages
Q44. Which laboratory marker typically rises immediately after ovulation and indicates luteal function?
- Serum LH surge persists after ovulation
- Serum progesterone levels increase during the luteal phase
- AMH increases dramatically
- FSH remains elevated only
Correct Answer: Serum progesterone levels increase during the luteal phase
Q45. Which cellular organelle distribution is particularly important in oocyte quality and early embryo development?
- Lysosomes only
- Mitochondria distribution and functionality
- Peroxisomes only
- Ribosomes absent in oocytes
Correct Answer: Mitochondria distribution and functionality
Q46. Which statement about primordial follicles is correct?
- They contain a secondary oocyte surrounded by multiple layers of granulosa cells
- They are the resting pool with primary oocyte arrested in prophase I and a single layer of squamous granulosa cells
- They are always destined to ovulate
- They secrete high levels of estrogen
Correct Answer: They are the resting pool with primary oocyte arrested in prophase I and a single layer of squamous granulosa cells
Q47. Which change occurs in the dominant follicle that allows it to outgrow others?
- Loss of FSH receptors on granulosa cells
- Increased aromatase activity and responsiveness to FSH
- Decreased blood supply only
- Immediate luteinization before ovulation
Correct Answer: Increased aromatase activity and responsiveness to FSH
Q48. Which pharmacological agent is used as a GnRH agonist trigger alternative to hCG to reduce ovarian hyperstimulation risk?
- Clomiphene citrate
- GnRH agonist trigger (e.g., leuprolide) to induce endogenous LH surge
- Metformin only
- Progesterone-only pill
Correct Answer: GnRH agonist trigger (e.g., leuprolide) to induce endogenous LH surge
Q49. Which of the following best explains why older oocytes have higher rates of chromosomal abnormalities?
- Improved spindle checkpoint with age
- Degradation of cohesion proteins and weakened centromeric cohesion over time leading to nondisjunction
- Increased AMH protecting chromosomes
- Higher mitochondrial numbers correct chromosome segregation
Correct Answer: Degradation of cohesion proteins and weakened centromeric cohesion over time leading to nondisjunction
Q50. Which clinical technique aims to preserve female fertility by storing oocytes prior to chemotherapy?
- Ovarian transposition only
- Oocyte cryopreservation (egg freezing)
- Endometrial scraping
- Vasectomy of partner
Correct Answer: Oocyte cryopreservation (egg freezing)

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com