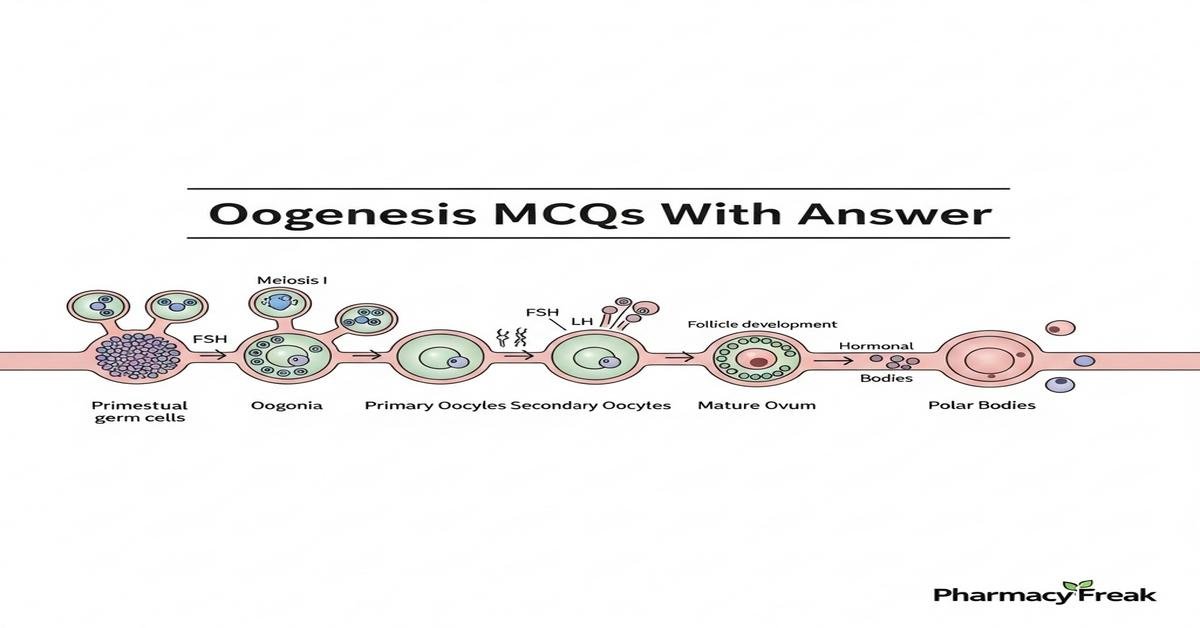
Oogenesis MCQs With Answer provides B. Pharm students a focused, exam-ready review of female gametogenesis, folliculogenesis and oocyte maturation. This concise introduction covers key concepts—meiotic arrest, hormonal regulation by FSH/LH, roles of granulosa cells, cortical granules, zona pellucida proteins, and molecular regulators like MPF, cAMP, GDF9/BMP15—presented in clear, high-yield MCQs. Ideal for pharmacology, reproductive biology and clinical pharmacy revisions, these questions emphasize mechanisms, clinical correlations (IVF, aneuploidy, ovarian reserve) and drug influences on oocyte quality. Each MCQ includes the correct answer to reinforce learning and retention. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which stage of meiosis are primary oocytes arrested in until puberty?
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase I
- Prophase I
- Telophase II
Correct Answer: Prophase I
Q2. Oogonia proliferate by mitosis predominantly during which period?
- Postnatal childhood
- Puberty
- Fetal development
- Menopause
Correct Answer: Fetal development
Q3. Which hormone surge triggers ovulation and resumption of meiosis in the dominant follicle?
- Progesterone surge
- FSH surge
- LH surge
- Estrogen surge only
Correct Answer: LH surge
Q4. After fertilization, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis II and produces which structure?
- Two daughter oocytes
- First polar body
- Second polar body
- Primordial follicle
Correct Answer: Second polar body
Q5. Which structure surrounds the oocyte and mediates sperm binding in mammals?
- Cumulus oophorus
- Zona pellucida
- Corona radiata
- Granulosa membrane
Correct Answer: Zona pellucida
Q6. Which proteins compose the mammalian zona pellucida critical for sperm recognition?
- ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3
- GDF9 and BMP15
- Connexin 43 and Connexin 37
- MPF and cyclin B
Correct Answer: ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3
Q7. Cytoplasmic maturation of the oocyte refers to development of which features?
- Chromosome segregation only
- Organelle redistribution, mRNA stores and cortical granules
- Only zona pellucida synthesis
- Only polar body extrusion
Correct Answer: Organelle redistribution, mRNA stores and cortical granules
Q8. Which molecular complex is essential to trigger entry into M phase during oocyte maturation?
- AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
- Maturation promoting factor (MPF)
- Proteasome complex
- mTORC1
Correct Answer: Maturation promoting factor (MPF)
Q9. High intra-oocyte cAMP levels maintain meiotic arrest by activating which kinase pathway?
- PKA (protein kinase A)
- PKC (protein kinase C)
- MAPK pathway
- PI3K/Akt pathway
Correct Answer: PKA (protein kinase A)
Q10. Granulosa cell–oocyte communication via gap junctions depends mainly on which protein type?
- Integrins
- Connexins
- Cadherins
- Matrix metalloproteinases
Correct Answer: Connexins
Q11. Which growth factors secreted by oocytes regulate surrounding granulosa cells and follicle development?
- Inhibin A and Inhibin B
- GDF9 and BMP15
- VEGF and FGF
- Insulin and IGF-1
Correct Answer: GDF9 and BMP15
Q12. The ovarian reserve is commonly assessed clinically by measuring which parameter?
- Serum progesterone on day 21
- Antral follicle count and AMH levels
- Estradiol at baseline only
Correct Answer: Antral follicle count and AMH levels
Q13. Which statement best describes atresia in ovarian follicles?
- Programmed follicle degeneration by apoptosis
- Ovulation of an immature oocyte
- Conversion of follicle to corpus luteum
- Rapid maturation without hormonal input
Correct Answer: Programmed follicle degeneration by apoptosis
Q14. Primary oocytes are diploid; how many chromatids are present per chromosome during prophase I arrest?
- One chromatid per chromosome
- Two chromatids per chromosome
- Three chromatids per chromosome
- Four chromatids per chromosome
Correct Answer: Two chromatids per chromosome
Q15. Maternal age increases risk of aneuploidy primarily because of defects in which process?
- Sperm chromatin condensation
- Oocyte meiotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation
- Cumulus expansion
- Zona pellucida synthesis
Correct Answer: Oocyte meiotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation
Q16. The first polar body is expelled after which meiotic division?
- Meiosis II
- Meiosis I
- Mitosis of oogonia
- Fertilization
Correct Answer: Meiosis I
Q17. Which hormone produced by granulosa cells is increased by FSH stimulation during follicular phase?
- Testosterone
- Estrogen (estradiol)
- Progesterone
- Inhibin B only
Correct Answer: Estrogen (estradiol)
Q18. Cumulus expansion is important for ovulation and is driven by which matrix component?
- Hyaluronic acid
- Collagen type I
- Elastin
- Keratan sulfate
Correct Answer: Hyaluronic acid
Q19. Which event in the oocyte is directly caused by sperm entry and leads to block to polyspermy?
- Increased cAMP synthesis
- Cortical granule exocytosis and zona hardening
- Immediate second polar body extrusion
- Granulosa cell apoptosis
Correct Answer: Cortical granule exocytosis and zona hardening
Q20. Which cellular organelle is maternally inherited and critical for early embryonic energy supply?
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Centrosomes
- Lysosomes
Correct Answer: Mitochondria
Q21. In IVF, immature oocytes can be matured in vitro; what is a key indicator of nuclear maturation?
- Presence of cortical granules
- Extrusion of the first polar body
- Accumulation of mitochondria
- Thickening of zona pellucida
Correct Answer: Extrusion of the first polar body
Q22. Which enzyme activity in the zona pellucida is crucial for sperm penetration during fertilization?
- Hyaluronidase from sperm
- DNA polymerase activity
- Proteasome activity
- ATP synthase activity
Correct Answer: Hyaluronidase from sperm
Q23. Oocyte quality declines with age; which mitochondrial change is most implicated?
- Increased mitochondrial DNA mutations and decreased function
- Overproliferation of mitochondria
- Complete loss of mitochondria
- Replacement by paternal mitochondria
Correct Answer: Increased mitochondrial DNA mutations and decreased function
Q24. Which kinase cascade is activated downstream of LH to promote resumption of meiosis in the oocyte?
- cGMP-dependent kinase only
- MAPK pathway and reduction of cGMP in granulosa cells
- JAK-STAT exclusively
- Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Correct Answer: MAPK pathway and reduction of cGMP in granulosa cells
Q25. Which statement about primordial follicles is correct?
- They contain a secondary oocyte arrested in metaphase II
- They are formed at puberty
- They consist of an oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flattened granulosa cells
- They secrete large amounts of estrogen
Correct Answer: They consist of an oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flattened granulosa cells
Q26. The zona pellucida thickens and acquires sperm-binding capacity during which process?
- Folliculogenesis and oocyte maturation
- Corpus luteum formation
- Atresia
- Menopause
Correct Answer: Folliculogenesis and oocyte maturation
Q27. Which of the following best describes the role of inhibin B in follicular phase?
- Stimulates LH release
- Inhibits FSH secretion from pituitary
- Directly causes ovulation
- Promotes luteal regression
Correct Answer: Inhibits FSH secretion from pituitary
Q28. Which marker is produced by granulosa cells and used clinically to estimate ovarian reserve?
- Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Progesterone
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Correct Answer: Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
Q29. What is the typical fate of most primordial follicles throughout life?
- They all mature and ovulate
- They remain quiescent forever
- They undergo atresia
- They transform into corpus luteum
Correct Answer: They undergo atresia
Q30. Which drug class is commonly used to induce multiple follicle development for assisted reproduction?
- Beta-blockers
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Gonadotropins (FSH preparations)
- Thyroid hormones
Correct Answer: Gonadotropins (FSH preparations)
Q31. Meiotic spindle stability in the oocyte is especially sensitive to disruption by which of the following?
- Temperature changes and cytoskeletal toxins
- Excessive glucose only
- High oxygen tension only
- Low extracellular potassium
Correct Answer: Temperature changes and cytoskeletal toxins
Q32. Which condition involves premature depletion of ovarian follicles and early loss of fertility?
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI)
- Endometriosis
- Hyperprolactinemia
Correct Answer: Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI)
Q33. Which process in the oocyte requires localized maternal mRNA and protein stores for early embryo development?
- Zygotic genome activation immediately post-fertilization
- Preimplantation embryonic divisions before zygotic transcription
- Late fetal organogenesis
- Formation of corpus luteum
Correct Answer: Preimplantation embryonic divisions before zygotic transcription
Q34. The maternal-effect genes important in oogenesis and early development include which examples?
- GDF9, BMP15 and MOS
- FSH and LH
- Estrogen receptor only
- Inhibin and activin
Correct Answer: GDF9, BMP15 and MOS
Q35. Which change in granulosa cells is a hallmark of luteinization after ovulation?
- Decreased progesterone production
- Increased steroidogenic capacity producing progesterone
- Reversion to primordial state
- Complete apoptosis without steroid production
Correct Answer: Increased steroidogenic capacity producing progesterone
Q36. Which measurement best reflects the number of remaining recruitable follicles in a reproductive-age woman?
- Serum estradiol alone
- Antral follicle count by ultrasound
Correct Answer: Antral follicle count by ultrasound
Q37. Which cellular event typically precedes cortical granule exocytosis at fertilization?
- Calcium oscillations within the oocyte
- Immediate DNA replication
- Mitochondrial DNA degradation
- Zona pellucida thinning
Correct Answer: Calcium oscillations within the oocyte
Q38. Which of the following best explains why only one follicle usually becomes dominant each cycle?
- Random selection independent of hormones
- Dominant follicle acquires greater FSH sensitivity and suppresses others via estrogen and inhibin
- Corpus luteum formation selects it post-ovulation
- LH inhibition of all other follicles
Correct Answer: Dominant follicle acquires greater FSH sensitivity and suppresses others via estrogen and inhibin
Q39. Oocyte vitrification (cryopreservation) success depends most on which factor?
- Number of prior pregnancies
- Age and oocyte quality at time of freezing
- Duration of infertility only
- Type of anesthesia used during retrieval
Correct Answer: Age and oocyte quality at time of freezing
Q40. Which ion change in the oocyte cytoplasm is the immediate trigger for cortical granule release?
- Decrease in intracellular potassium
- Increase in intracellular calcium
- Increase in intracellular chloride
- Decrease in intracellular sodium
Correct Answer: Increase in intracellular calcium
Q41. Which statement about secondary oocytes is true?
- They are diploid and arrested in prophase I
- They have completed meiosis II prior to ovulation
- They are haploid and arrested in metaphase II until fertilization
- They are created only after fertilization
Correct Answer: They are haploid and arrested in metaphase II until fertilization
Q42. Which protein complex degrades cyclin B to allow exit from M phase when appropriate?
- Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C)
- mTORC2
- Protease inhibitor complex
- DNA helicase complex
Correct Answer: Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C)
Q43. Which factor secreted by the oocyte promotes granulosa cell proliferation and differentiation?
- BMP15
- Testosterone
- Prolactin
- Thyroxine
Correct Answer: BMP15
Q44. Which clinical test is most useful to predict response to controlled ovarian stimulation in ART?
- Serum LH on day 14
- Basal FSH and AMH levels
- Serum progesterone in luteal phase
- Urinary estrogen metabolites
Correct Answer: Basal FSH and AMH levels
Q45. During follicular growth, the antrum forms within which follicle stage?
- Primordial follicle
- Primary follicle
- Secondary (antral) follicle
- Corpus luteum
Correct Answer: Secondary (antral) follicle
Q46. Which drug used in IVF cycles mimics LH surge to induce final oocyte maturation?
- Recombinant FSH
- hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
- Aromatase inhibitor
- GnRH antagonist only
Correct Answer: hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
Q47. Which cellular structure organizes the meiotic spindle in mammalian oocytes despite lacking centrosomes?
- Centrioles inherited from sperm
- Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs)
- Golgi-derived microfilaments
- Nuclear envelope fragments only
Correct Answer: Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs)
Q48. Which extracellular signal from theca interna cells supports androgen production used for estrogen synthesis in granulosa cells?
- FSH acting on theca cells
- LH stimulating theca interna to produce androgens
- Prolactin directly converting androgens to estrogens
- AMH producing androgens
Correct Answer: LH stimulating theca interna to produce androgens
Q49. Which component of the oocyte cytoplasm is essential for early cleavage and is donated maternally?
- Paternal ribosomes
- Maternal mRNAs and proteins
- Lipids only
- Extracellular matrix proteins
Correct Answer: Maternal mRNAs and proteins
Q50. Which preventative measure can preserve ovarian reserve in patients undergoing gonadotoxic chemotherapy?
- High-dose estrogen therapy during treatment
- Ovarian tissue cryopreservation or oocyte cryopreservation before therapy
- Delay in chemotherapy without preservation
- Post-treatment hormone replacement only
Correct Answer: Ovarian tissue cryopreservation or oocyte cryopreservation before therapy

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com