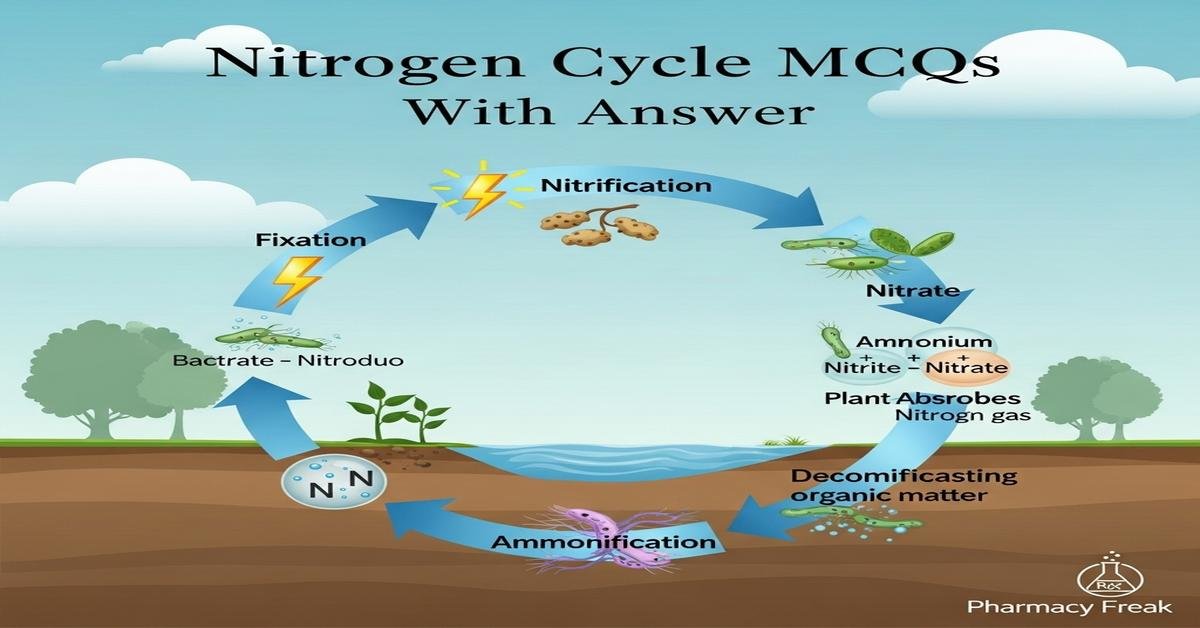
Understanding the nitrogen cycle is essential for B. Pharm students, especially when studying drug biosynthesis, microbial metabolism, and environmental pharmacology. This concise guide on Nitrogen cycle MCQs With Answer covers core processes—nitrogen fixation, ammonification, nitrification, denitrification, assimilation—and key players like Rhizobium, Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, and denitrifiers. Learn about enzymes (nitrogenase, nitrate reductase), chemical forms (NH3, NH4+, NO2−, NO3−), industrial fixation, and clinical/environmental impacts such as nitrate toxicity and eutrophication. These focused questions deepen mechanistic understanding and link biochemical pathways to pharmaceutical and environmental applications. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which enzyme complex is primarily responsible for converting atmospheric N2 to ammonia in biological nitrogen fixation?
- Nitrate reductase
- Nitrogenase complex
- Ammonia monooxygenase
- Nitrite oxidoreductase
Correct Answer: Nitrogenase complex
Q2. Which group of organisms includes common free-living nitrogen fixers used in soil fertilization?
- Rhizobium species
- Azotobacter species
- Nitrobacter species
- Pseudomonas species
Correct Answer: Azotobacter species
Q3. What is the primary product of ammonification (organic nitrogen mineralization)?
- Nitrate (NO3−)
- Nitrite (NO2−)
- Ammonium (NH4+)
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
Correct Answer: Ammonium (NH4+)
Q4. Which bacteria are chiefly responsible for oxidizing ammonia to nitrite during nitrification?
- Nitrobacter species
- Nitrosomonas species
- Rhizobium species
- Azotobacter species
Correct Answer: Nitrosomonas species
Q5. Which process converts nitrate back to molecular nitrogen under anaerobic conditions?
- Nitrification
- Ammonification
- Denitrification
- Assimilation
Correct Answer: Denitrification
Q6. Which enzyme catalyzes the first step of assimilatory nitrate reduction in plants and microbes?
- Nitrogenase
- Nitrate reductase
- Nitrite oxidoreductase
- Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase
Correct Answer: Nitrate reductase
Q7. Which industrial process produces ammonia on a large scale, impacting the global nitrogen cycle?
- Haber-Bosch process
- Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
- Burgess process
- Solvay process
Correct Answer: Haber-Bosch process
Q8. Leghemoglobin in legume root nodules primarily functions to:
- Transport nitrate into nodules
- Provide oxygen to nitrogenase
- Bind oxygen to protect nitrogenase from inactivation
- Reduce N2 to NH3
Correct Answer: Bind oxygen to protect nitrogenase from inactivation
Q9. Which form of nitrogen is most mobile in soil and prone to leaching into groundwater?
- Ammonium (NH4+)
- Organic nitrogen
- Nitrate (NO3−)
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
Correct Answer: Nitrate (NO3−)
Q10. Which compound accumulation in drinking water is associated with infant methemoglobinemia?
- Ammonium
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen gas
- Organic nitrogen
Correct Answer: Nitrate
Q11. Anammox bacteria perform which reaction relevant to wastewater nitrogen removal?
- Oxidation of nitrite to nitrate
- Reduction of nitrate to nitrite
- Anaerobic oxidation of ammonium with nitrite to produce N2
- Ammonia fixation from N2
Correct Answer: Anaerobic oxidation of ammonium with nitrite to produce N2
Q12. Which gas produced by incomplete denitrification is a potent greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance?
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Nitric oxide (NO)
- Methane (CH4)
Correct Answer: Nitrous oxide (N2O)
Q13. Which functional group in soil strongly adsorbs ammonium ions, reducing leaching?
- Negative charged clay surfaces and organic matter (cation exchange sites)
- Silica gel pores
- Neutral organic molecules
- Free oxygen molecules
Correct Answer: Negative charged clay surfaces and organic matter (cation exchange sites)
Q14. Which microbial enzyme initiates nitrification by oxidizing ammonia?
- Ammonia monooxygenase (AMO)
- Nitrate reductase
- Nitrite reductase
- Nitrogenase
Correct Answer: Ammonia monooxygenase (AMO)
Q15. Biological nitrogen fixation is energetically expensive because it requires:
- High concentrations of oxygen
- ATP and reducing power
- Direct sunlight
- High nitrate levels
Correct Answer: ATP and reducing power
Q16. Which plant-associated bacteria form symbiotic nodules on legume roots for N2 fixation?
- Pseudomonas
- Rhizobium
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
Correct Answer: Rhizobium
Q17. In the nitrogen cycle, “assimilation” refers to the incorporation of inorganic nitrogen into:
- Atmospheric gases
- Microbial and plant organic molecules like amino acids
- Mineral salts
- Sulfate pools
Correct Answer: Microbial and plant organic molecules like amino acids
Q18. Which factor typically inhibits nitrifying bacteria and slows nitrification?
- Neutral pH
- High oxygen levels
- Low soil pH (acidic conditions)
- Warm temperature
Correct Answer: Low soil pH (acidic conditions)
Q19. Which isotope is commonly used to trace nitrogen pathways in ecological and fermentation studies?
- Carbon-14 (14C)
- Nitrogen-15 (15N)
- Oxygen-18 (18O)
- Hydrogen-2 (2H)
Correct Answer: Nitrogen-15 (15N)
Q20. Which of the following is NOT a direct step in the classical nitrogen cycle?
- Ammonification
- Photosynthesis
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
Correct Answer: Photosynthesis
Q21. Which genus includes bacteria known for reducing nitrate to nitrogen gas under anaerobic conditions?
- Paracoccus
- Azotobacter
- Nitrobacter
- Rhizopus
Correct Answer: Paracoccus
Q22. In wastewater treatment, which combination is often used to remove nitrogen efficiently?
- Only aerobic nitrification
- Only anoxic denitrification
- Sequential nitrification followed by denitrification (nitrification-denitrification)
- Direct ammonification to nitrogen gas
Correct Answer: Sequential nitrification followed by denitrification (nitrification-denitrification)
Q23. Which intermediate compound is formed during ammonia oxidation before nitrite production?
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen gas
- Hydroxylamine (NH2OH)
- Urea
Correct Answer: Hydroxylamine (NH2OH)
Q24. Which statement best describes “biological nitrogen fixation” relevance to pharmaceuticals?
- It produces nitrate used in drug formulations
- It supplies bioavailable nitrogen for microbial production of antibiotics and amino-acid-derived drugs
- It removes nitrogen from cultures used in fermentation
- It converts drugs into inactive forms
Correct Answer: It supplies bioavailable nitrogen for microbial production of antibiotics and amino-acid-derived drugs
Q25. Which compound is produced when soil microbes reduce nitrate but denitrification is incomplete?
- Ammonia
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Urea
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
Correct Answer: Nitrous oxide (N2O)
Q26. Which microbial process converts organic nitrogen in dead biomass into ammonium?
- Ammonification (mineralization)
- Denitrification
- Assimilation
- Nitrification
Correct Answer: Ammonification (mineralization)
Q27. Which form of nitrogen is directly assimilable by most plants for amino acid synthesis?
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
- Nitrate (NO3−) and ammonium (NH4+)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Molecular ammonia gas
Correct Answer: Nitrate (NO3−) and ammonium (NH4+)
Q28. Which bacterial group oxidizes nitrite to nitrate in soil?
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
Correct Answer: Nitrobacter
Q29. Which parameter in aquifers is most often monitored to assess agricultural nitrogen contamination?
- Ammonium levels only
- Nitrate concentration
- Pheromone concentration
- Oxygen saturation
Correct Answer: Nitrate concentration
Q30. Which metabolic condition favors denitrification in soils and sediments?
- High oxygen and low organic carbon
- Anoxic conditions with available organic carbon
- Very acidic and dry conditions
- High light intensity
Correct Answer: Anoxic conditions with available organic carbon
Q31. Which chemical form increases risk of forming carcinogenic nitrosamines in food or water?
- High ammonium concentrations
- High nitrite concentrations
- Nitrogen gas presence
- Urea residues
Correct Answer: High nitrite concentrations
Q32. Which bacterial enzyme reduces nitrite to nitric oxide during denitrification?
- Nitrite reductase
- Nitrogenase
- Nitrate reductase
- Ammonia monooxygenase
Correct Answer: Nitrite reductase
Q33. Which practice reduces nitrate leaching from agricultural fields?
- Excessive irrigation
- Use of cover crops and timing fertilizer application
- Continuous fallow periods
- Applying nitrate at high rates before rains
Correct Answer: Use of cover crops and timing fertilizer application
Q34. Which microbial genus is a well-known aerobic denitrifier sometimes used in bioremediation?
- Pseudomonas
- Rhizobium
- Nitrosococcus
- Bacillus
Correct Answer: Pseudomonas
Q35. In pharmaceutical fermentation, nitrogen limitation most directly affects production of:
- Secondary metabolites like antibiotics and amino acids
- Cell wall polysaccharides only
- Inorganic salts
- Vitamin C exclusively
Correct Answer: Secondary metabolites like antibiotics and amino acids
Q36. Which analytical method is commonly used to quantify nitrate in environmental and lab samples?
- Gas chromatography for nitrogen gas
- Colorimetric assays or ion chromatography
- Western blotting
- PCR amplification
Correct Answer: Colorimetric assays or ion chromatography
Q37. Which condition enhances biological nitrogen fixation in legume crops?
- High soil nitrate concentration
- Presence of compatible Rhizobium strains and adequate phosphorus
- Low phosphorus and high salinity
- Excessive fungicide application
Correct Answer: Presence of compatible Rhizobium strains and adequate phosphorus
Q38. Which molecule donates electrons to nitrogenase in many diazotrophs?
- Oxygen
- Reduced ferredoxin or flavodoxin
- Nitrate
- ATP only
Correct Answer: Reduced ferredoxin or flavodoxin
Q39. Which statement describes heterotrophic nitrification?
- Nitrification carried out solely by autotrophic bacteria
- Nitrification performed by heterotrophic microbes often coupled to organic carbon oxidation
- Reduction of nitrate to ammonia
- Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms
Correct Answer: Nitrification performed by heterotrophic microbes often coupled to organic carbon oxidation
Q40. Which nitrogen species is most likely to participate in microbial anaerobic respiration as a terminal electron acceptor?
- Nitrate (NO3−)
- Ammonium (NH4+)
- Atmospheric nitrogen (N2)
- Urea
Correct Answer: Nitrate (NO3−)
Q41. Which agricultural input significantly increases reactive nitrogen entering ecosystems?
- Phosphate fertilizers
- Nitrogen-containing fertilizers (synthetic or manure)
- Sulfur amendments
- Micronutrient foliar sprays
Correct Answer: Nitrogen-containing fertilizers (synthetic or manure)
Q42. Which microbial genus is associated with nitrite oxidation in marine environments?
- Prochlorococcus
- Nitrospina
- Escherichia
- Clostridium
Correct Answer: Nitrospina
Q43. During nitrification, what happens to soil pH locally and why?
- pH increases due to ammonium accumulation
- pH decreases due to production of protons during ammonia oxidation
- pH remains unchanged
- pH becomes highly alkaline due to nitrate production
Correct Answer: pH decreases due to production of protons during ammonia oxidation
Q44. Which monitoring parameter helps evaluate denitrification rates in soil microcosms?
- Oxygen production
- N2O emissions and nitrate depletion
- Chloride concentration
- Soil color only
Correct Answer: N2O emissions and nitrate depletion
Q45. Which class of drugs or formulations could be affected by nitrogenous impurities arising from processing water contaminated with nitrate/nitrite?
- Topical creams only
- Oxygen masks
- Oral drugs prone to nitrosation forming nitrosamines
- Inert tablets with no organic functionality
Correct Answer: Oral drugs prone to nitrosation forming nitrosamines
Q46. What role do cyanobacteria play in the nitrogen cycle?
- They oxidize nitrite to nitrate exclusively
- They are photosynthetic nitrogen fixers in aquatic systems
- They perform denitrification in sediments
- They mineralize ammonium to organic nitrogen
Correct Answer: They are photosynthetic nitrogen fixers in aquatic systems
Q47. Which environmental consequence is directly linked to increased nitrate runoff from fields?
- Decreased algal growth in water bodies
- Eutrophication and algal blooms
- Ozone formation at ground level
- Increased soil nitrogen retention
Correct Answer: Eutrophication and algal blooms
Q48. Which biochemical cofactor is commonly required for nitrate reductase activity in plants?
- NADH or NADPH
- FAD only
- Cytochrome c exclusively
- Biotin
Correct Answer: NADH or NADPH
Q49. How does temperature generally affect the rate of microbial nitrification?
- Rate increases with temperature up to an optimum, then declines
- Rate is independent of temperature
- Rate decreases as temperature rises
- Rate only depends on light
Correct Answer: Rate increases with temperature up to an optimum, then declines
Q50. Which practice in pharmaceutical wastewater treatment helps reduce nitrogen loads before discharge?
- Direct discharge without treatment
- Biological treatment with nitrification-denitrification or anammox reactors
- Addition of inorganic nitrate to wastewater
- Heating to boiling and release
Correct Answer: Biological treatment with nitrification-denitrification or anammox reactors

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com