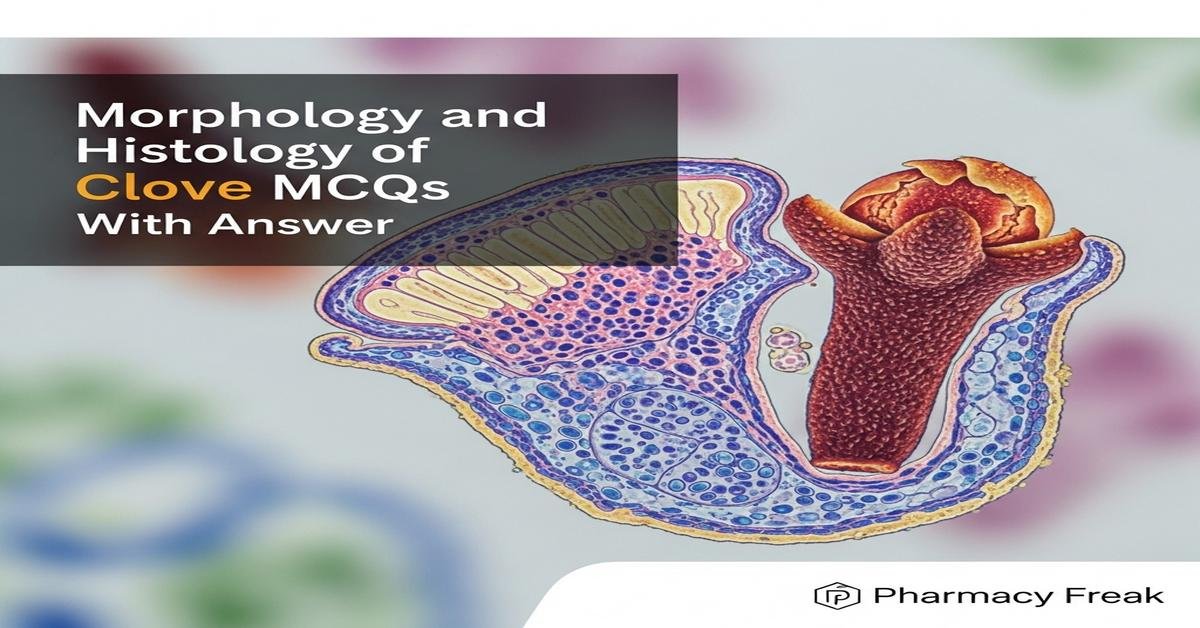
Introduction: Clove, the dried unopened flower bud of Syzygium aromaticum, is an essential pharmacognostic drug for B. Pharm students studying morphology and histology. This concise guide emphasizes macroscopic identification (bud shape, stalk, calyx), histological features (epidermis, oil cells/idioblasts, parenchyma with tannins, sclerenchyma, vascular bundles) and phytochemical relevance (major constituent eugenol and essential oil). Mastery of tissue arrangement, gland distribution, powder microscopy, extraction (steam distillation) and instrumental assays (GC) is crucial for quality control, detection of adulteration, formulation and drug development. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which plant part is the commercial drug ‘clove’ derived from?
- Dried root
- Dried leaf
- Dried flower bud
- Dried fruit
Correct Answer: Dried flower bud
Q2. What is the accepted botanical name of clove used in pharmacognosy?
- Eugenia caryophyllata
- Syzygium aromaticum
- Piper nigrum
- Cinnamomum verum
Correct Answer: Syzygium aromaticum
Q3. To which family does clove belong?
- Lauraceae
- Myrtaceae
- Rutaceae
- Zingiberaceae
Correct Answer: Myrtaceae
Q4. Which major bioactive compound is primarily responsible for clove’s analgesic and antiseptic properties?
- Menthol
- Eugenol
- Cineole
- Cinnamaldehyde
Correct Answer: Eugenol
Q5. Which macroscopic feature is characteristic of clove buds?
- Flattened disk-like head
- Long slender spike with many flowers
- Globular head with a long stalk
- Fleshy berry-like structure
Correct Answer: Globular head with a long stalk
Q6. In microscopic examination, which structures indicate the presence of essential oil in clove?
- Stone cells only
- Idioblasts or oil cells containing oil globules
- Sieve tube elements
- Calcium oxalate crystals exclusively
Correct Answer: Idioblasts or oil cells containing oil globules
Q7. Which tissue type often contains tannin deposits in clove histology?
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma fibers
- Parenchyma of cortex
- Phloem companion cells
Correct Answer: Parenchyma of cortex
Q8. What is the preferred method for extracting clove essential oil in the laboratory?
- Cold maceration
- Steam distillation
- Soxhlet extraction with hexane only
- Supercritical CO2 extraction exclusively
Correct Answer: Steam distillation
Q9. Which instrumental technique is commonly used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of eugenol in clove oil?
- UV-Visible spectrophotometry only
- Gas chromatography (GC) or GC-MS
- Polarimetry
- Colorimetry with iodine
Correct Answer: Gas chromatography (GC) or GC-MS
Q10. Which microscopic preparation is most informative for studying internal arrangement of clove bud tissues?
- Whole mount of powder
- Transverse section of the bud
- Smear of essential oil
- Chromatographic spot on TLC plate
Correct Answer: Transverse section of the bud
Q11. Which cell type contributes to the hardness and gritty texture sometimes seen in clove powder?
- Sclereids (stone cells)
- Sieve tube elements
- Cortex parenchyma only
- Tracheids exclusively
Correct Answer: Sclereids (stone cells)
Q12. Which histological stain combination is commonly used to differentiate lignified and non-lignified tissues in plant sections?
- Gram stain
- Safranin and fast green
- Methylene blue only
- Hematoxylin and eosin (routine animal stain)
Correct Answer: Safranin and fast green
Q13. Which of the following is a reliable powder microscopy feature of clove?
- Abundant oil globules and fragments of epidermis
- Predominance of starch grains
- Numerous pollen grains only
- Exclusively unicellular hairs
Correct Answer: Abundant oil globules and fragments of epidermis
Q14. Which statement about clove oil composition is correct?
- It contains a high proportion of eugenol, a phenylpropanoid
- It is rich in alkaloids as major constituents
- It is composed mainly of fatty acids
- It lacks phenolic compounds
Correct Answer: It contains a high proportion of eugenol, a phenylpropanoid
Q15. Which quality control parameter is essential in official monographs for clove?
- Moisture content only
- Eugenol content assay (or essential oil content)
- Optical rotation solely
- Color of powdered sample exclusively
Correct Answer: Eugenol content assay (or essential oil content)
Q16. Where are oil-containing idioblasts typically located in clove bud histology?
- Only in vascular bundles
- In ground parenchyma and cortex tissues
- Restricted to epidermal cuticle only
- Exclusively in stomatal guard cells
Correct Answer: In ground parenchyma and cortex tissues
Q17. What role do sclerenchyma fibers and sclereids play in clove morphology?
- Assist in photosynthesis
- Provide mechanical strength and contribute to hardness
- Act as primary sites for oil biosynthesis
- Function as sugar-storage cells
Correct Answer: Provide mechanical strength and contribute to hardness
Q18. Which simple microscopic observation suggests adulteration of clove powder?
- Excessive presence of oil globules
- Absence or very low number of characteristic oil cells/idioblasts
- Presence of trichomes typical of the bud
- Detection of eugenol by GC
Correct Answer: Absence or very low number of characteristic oil cells/idioblasts
Q19. Which pharmacological property is commonly associated with clove and its main constituent eugenol?
- Antimicrobial and local anesthetic effects
- Hypoglycemic action only
- Purely antihypertensive effect
- Exclusive diuretic action
Correct Answer: Antimicrobial and local anesthetic effects
Q20. Which country or region is clove (originally) native to?
- Amazon basin
- Maluku Islands (Moluccas), Indonesia
- Western Europe
- Central Africa
Correct Answer: Maluku Islands (Moluccas), Indonesia
Q21. Which laboratory technique is most appropriate for quantitative estimation of eugenol in clove oil?
- Thin layer chromatography (qualitative)
- Gas chromatography with suitable detector
- Paper chromatography only
- Simple refractive index measurement
Correct Answer: Gas chromatography with suitable detector
Q22. Which vascular arrangement is expected in the pedicel or axis of a dicotyledonous clove flower bud?
- Scattered vascular bundles as in monocots
- Collateral vascular bundles typical of dicots
- Concentric vascular bundles with phloem surround xylem only
- No vascular tissue present
Correct Answer: Collateral vascular bundles typical of dicots
Q23. For microscopic study of clove powder, which mounting medium is commonly used to visualize oil globules?
- Distilled water only
- Glycerin or glycerin-water mixtures
- Alcoholic iodine exclusively
- Petroleum ether as mountant
Correct Answer: Glycerin or glycerin-water mixtures
Q24. Which of the following best describes an idioblast in plant histology?
- A vascular mother cell
- A specialized cell differing from neighboring cells, often storing oils or crystals
- A type of stomatal complex
- A fungal spore adhered to tissue
Correct Answer: A specialized cell differing from neighboring cells, often storing oils or crystals
Q25. Which feature observed under microscope distinguishes clove from many other spice powders?
- High frequency of starch grains like cereals
- Characteristic oil cells and lignified sclereids
- Abundant pollen grains as main component
- Predominantly cutinized hairs only
Correct Answer: Characteristic oil cells and lignified sclereids
Q26. Which handling/storage practice helps preserve clove oil content in crude drug preparations?
- Exposure to sunlight to keep dry
- Storage in airtight, dark containers at cool temperature
- Storing in damp conditions to prevent brittleness
- Frequent grinding and exposure to air
Correct Answer: Storage in airtight, dark containers at cool temperature
Q27. Which chemical class does eugenol belong to?
- Alkaloid
- Phenylpropanoid (phenolic ether)
- Terpenoid hydrocarbon
- Saponin glycoside
Correct Answer: Phenylpropanoid (phenolic ether)
Q28. Which pharmaceutical preparation is classically produced from clove for medicinal use?
- Clove oil (essential oil)
- Clove aqueous syrup only
- Clove protein concentrate
- Clove metal chelate
Correct Answer: Clove oil (essential oil)
Q29. Which microscopic observation best indicates mature, intact clove buds rather than broken fragments?
- Predominance of isolated starch granules
- Presence of intact glandular idioblasts and organized tissue layers
- Only amorphous powder without cell structures
- Exclusive occurrence of leaf trichomes
Correct Answer: Presence of intact glandular idioblasts and organized tissue layers
Q30. Which statement about clove histology is FALSE?
- Clove buds show abundant oil-bearing idioblasts in ground tissue
- Parenchyma may contain tannin deposits visible microscopically
- Vascular bundles are entirely absent in the pedicel and bud
- Sclerenchyma elements contribute to the gritty texture of powder
Correct Answer: Vascular bundles are entirely absent in the pedicel and bud

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com