Table of Contents
Introduction
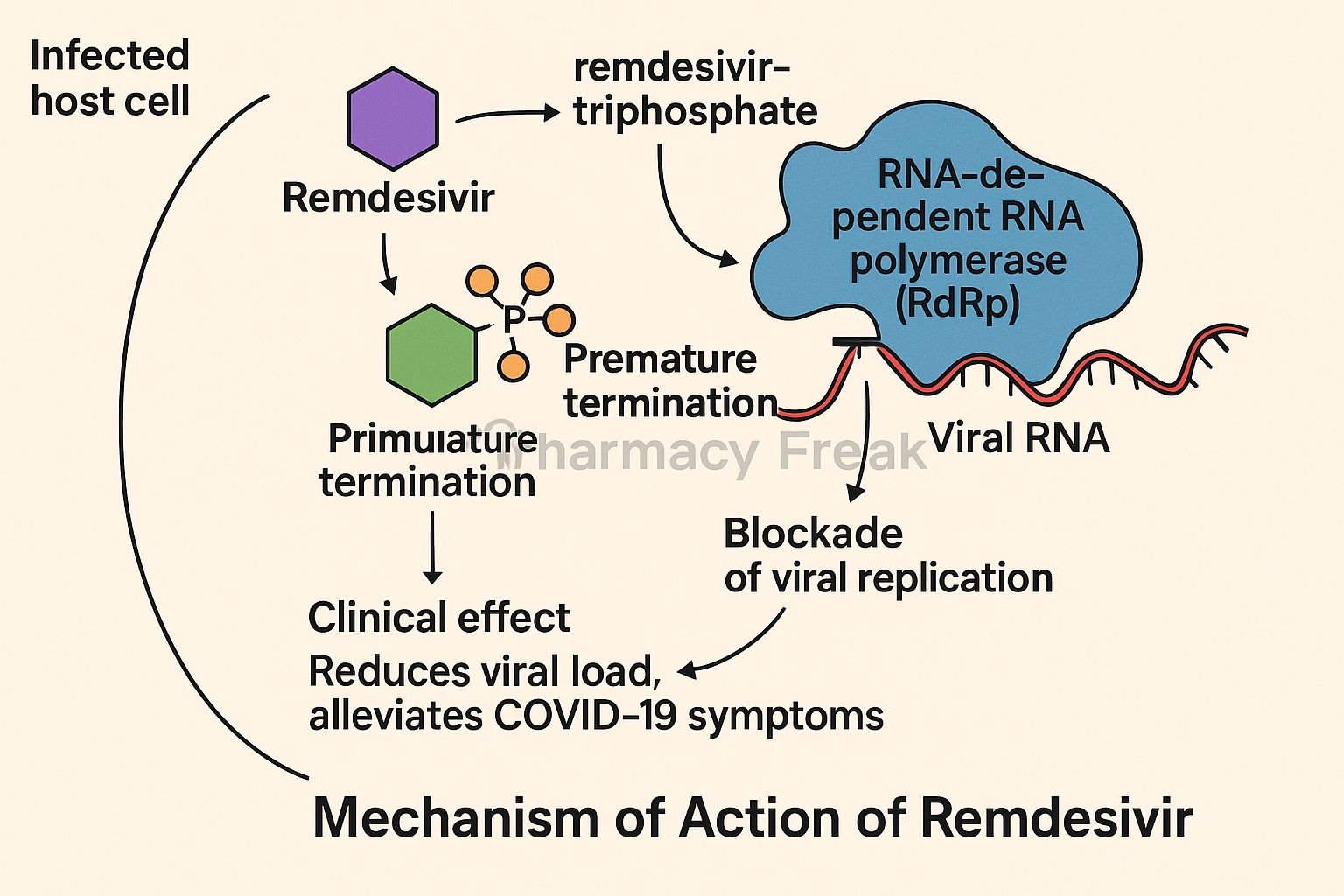
Remdesivir is an intravenous antiviral prodrug that inhibits viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Originally developed for Ebola, it is approved for COVID-19 in hospitalized and non-hospitalized high-risk patients. It also shows activity against several RNA viruses.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Cellular uptake and metabolism
Remdesivir enters infected host cells and is metabolized to its active triphosphate form. - Competitive incorporation into viral RNA
The active nucleoside analog competes with ATP as a substrate for viral RdRp. - Chain termination
Once incorporated, it causes delayed RNA chain termination, halting viral replication after adding a few more nucleotides. - Inhibition of viral replication
Blocked RNA synthesis reduces production of viral progeny, limiting infection spread within the host. - Increased viral clearance
Reduced viral load supports recovery and improved clinical outcomes.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Intravenous infusion (single or multiple doses) |
| Distribution | Extensive tissue uptake, including lungs |
| Half-life (parent) | ~1 hour |
| Half-life (metabolite) | ~20–25 hours |
| Metabolism | Intracellular conversion to active triphosphate |
| Excretion | Renal (~74%) and fecal (~18%) metabolites |
Clinical Uses
- Treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19
- Use in non-hospitalized high-risk patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19
- Investigational use in other RNA viral infections under study
Adverse Effects
- Infusion-related reactions: nausea, hypersensitivity
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Rare kidney tubular toxicity (use with caution in renal impairment)
- Possible effects on kidney function in patients with low GFR
Comparative Analysis
| Drug | Mechanism | Route | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir | RdRp inhibitor; delayed chain termination | IV infusion | COVID-19 |
| Molnupiravir | Promotes viral RNA mutagenesis | Oral tablet | Mild-to-moderate COVID-19 |
| Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) | Protease inhibitor | Oral tablet | Early COVID-19 |
MCQs
- Remdesivir is a prodrug that targets:
a) Viral protease b) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase c) Spike protein d) Viral helicase
Answer: b) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase - Its active form is a:
a) Monophosphate b) Diphosphate c) Triphosphate d) Nucleoside
Answer: c) Triphosphate - It terminates viral RNA strand by:
a) Immediate termination b) Delayed termination c) Proteolytic cleavage d) Methylation
Answer: b) Delayed termination - Route of administration is:
a) Oral b) IV infusion c) Subcutaneous d) Intramuscular
Answer: b) IV infusion - Which is a significant adverse effect?
a) QT prolongation b) Elevated liver enzymes c) Hypoglycemia d) Hypertension
Answer: b) Elevated liver enzymes - Which antiviral is taken orally for COVID-19?
a) Remdesivir b) Molnupiravir c) Veklury d) Ribavirin
Answer: b) Molnupiravir - The main elimination route is:
a) Pulmonary excretion b) Renal metabolites c) Bile d) Sweat
Answer: b) Renal metabolites - Remdesivir primarily helps by:
a) Blocking entry of virus b) Preventing viral RNA synthesis c) Neutralizing spike protein d) Activating host cell apoptosis
Answer: b) Preventing viral RNA synthesis - Its half-life in circulation is approximately:
a) 5 minutes b) 1 hour c) 6 hours d) 24 hours
Answer: b) 1 hour - A key cellular process required is:
a) Hepatic biotransformation b) Intracellular phosphorylation c) Direct proteolysis d) HDL-binding
Answer: b) Intracellular phosphorylation
FAQs
1. Is remdesivir safe in renal impairment?
Use with caution in patients with GFR <30; monitor renal function.
2. When should it be administered for best results?
Early in disease—ideally within 7–10 days of symptom onset.
3. Does remdesivir shorten hospital stay?
Yes—clinical trials show faster recovery in hospitalized patients.
4. Is combination therapy used?
Often used with dexamethasone or other immunomodulators in severe cases.
5. Can it be used in other viral infections?
Research is ongoing for viruses like RSV, Ebola variants, and others.
References
- FDA Label: Remdesivir (Veklury)
- PubMed Review: Remdesivir antiviral mechanism
- DrugBank: Remdesivir Detailed Summary
- StatPearls: Remdesivir in COVID-19
- PubMed Central: RNA polymerase inhibition data
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com