Table of Contents
Introduction
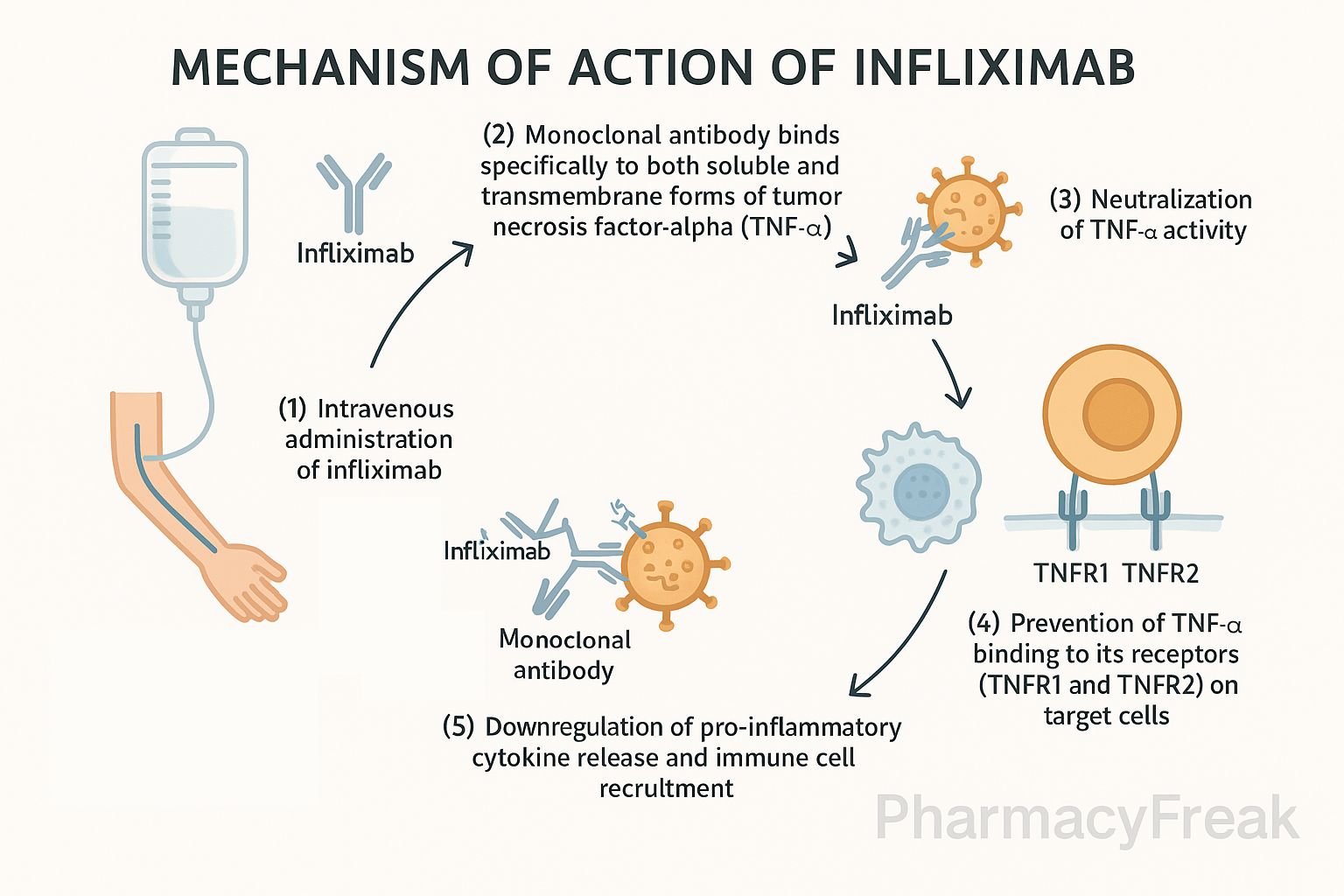
Infliximab is a chimeric (murine-human) IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets tumor necrosis factor‑α (TNF‑α). It is used to treat a range of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Binding to TNF‑α
Infliximab binds with high affinity to both soluble and transmembrane forms of TNF‑α. - Neutralization of TNF‑α
This prevents TNF‑α from interacting with TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) on target cells. - Inhibition of downstream signaling
Blocking TNF‑α suppresses activation of NF‑κB and MAPK signaling pathways, reducing inflammatory responses. - Fc-mediated effects
Infliximab can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) against TNF‑α–expressing cells. - Suppression of immune activation
Results in lowered production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL‑1, IL‑6), reduced recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reversal of disease activity.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Intravenous infusion |
| Half-life | ~8–10 days |
| Distribution | ~4–6 L |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic degradation |
| Excretion | Catabolized to peptides and amino acids |
Clinical Uses
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Plaque psoriasis
Adverse Effects
- Risk of serious infections (e.g., reactivation of latent tuberculosis)
- Infusion reactions (e.g., fever, chills, hypotension)
- Development of anti-drug antibodies, reducing efficacy
- Lupus-like syndrome, demyelinating disease (rare)
- Increased risk of certain malignancies, e.g., lymphoma
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Type | TNF Target | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infliximab | Chimeric mAb | TNF‑α | IV infusion; potential immunogenicity |
| Adalimumab | Fully human mAb | TNF‑α | Subcutaneous injection; lower immunogenicity |
| Etanercept | Soluble receptor fusion | TNF‑α/β | Receptor decoy; limited to TNF neutralization |
MCQs
- Infliximab is classified as a:
a) Fully human antibody b) Chimeric antibody c) Poorest choice d) Receptor antagonist
Answer: b) Chimeric antibody - It primarily neutralizes:
a) IL‑6 b) TNF‑α c) IL‑1 d) IFN‑γ
Answer: b) TNF‑α - Fc-mediated functions of infliximab include:
a) Inhibition of proteases b) ADCC and CDC c) CYP450 induction d) Renin release
Answer: b) ADCC and CDC - Its half-life is approximately:
a) 1–2 days b) 8–10 days c) 20–30 days d) 12 hours
Answer: b) 8–10 days - A safety concern before initiation includes screening for:
a) Diabetes b) Tuberculosis c) Hyperlipidemia d) Hypothyroidism
Answer: b) Tuberculosis - Compared to adalimumab, infliximab is:
a) Fully human b) Chimeric c) Oral tablet d) Fusion protein
Answer: b) Chimeric - Infliximab may trigger production of:
a) Anti-drug antibodies b) Insulin c) IL‑10 d) Vitamin D
Answer: a) Anti-drug antibodies - Infusion reactions are characterized by:
a) Hypoglycemia b) Fever and hypotension c) Hypertension d) Diarrhea
Answer: b) Fever and hypotension - The main downstream signaling pathways include NF‑κB and:
a) JAK‑STAT b) MAPK c) cAMP d) PI3K
Answer: b) MAPK - Compared to etanercept, infliximab:
a) Is given orally b) Induces less ADCC c) Has higher immunogenicity d) Only targets TNF‑β
Answer: c) Has higher immunogenicity
FAQs
1. Why is TB screening essential before starting infliximab?
Because TNF‑α inhibition can reactivate latent tuberculosis.
2. What is the route of administration?
Administered via intravenous infusion, typically every 6–8 weeks after induction dosing.
3. Can patients develop resistance?
Yes—formation of anti-drug antibodies can reduce drug effectiveness and cause infusion reactions.
4. Are vaccines safe during therapy?
Live vaccines are contraindicated during treatment with infliximab.
5. How long are the effects sustained?
Due to its long half-life, effects can last several weeks between doses.
References
- FDA Label: Infliximab (Remicade)
- DrugBank: Infliximab summary
- StatPearls: Infliximab clinical uses and pharmacology
- PubMed: Antibody-mediated cytotoxicity of infliximab
- PMC: Mechanism of action in autoimmune disease
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com