Table of Contents
Introduction
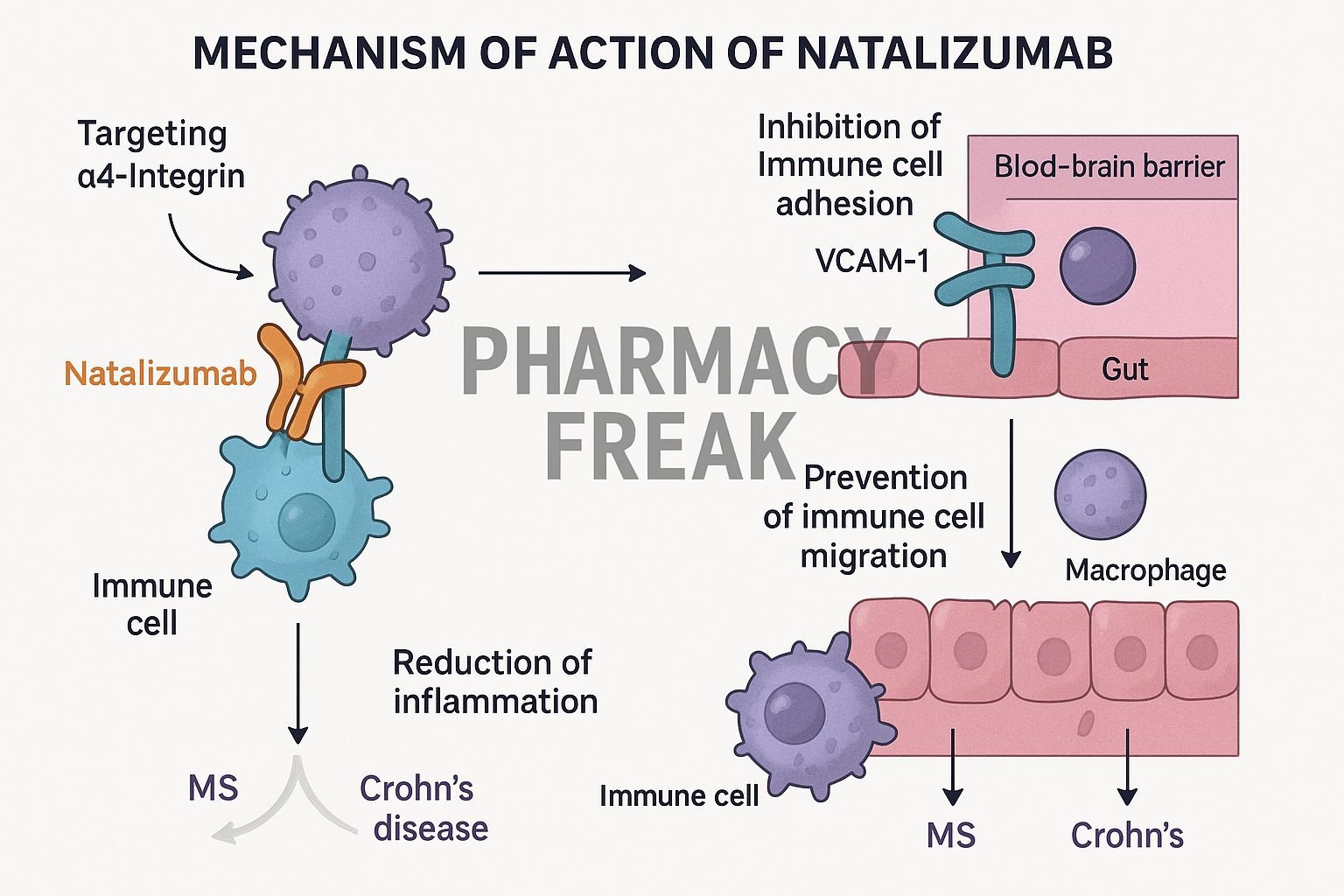
Natalizumab is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody targeting the α4 integrin subunit. It’s approved for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and moderate to severe Crohn’s disease. By blocking leukocyte adhesion, it prevents immune cell migration into the brain and gut.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Binding to α4 integrin
Natalizumab binds to the α4 subunit on leukocytes, including lymphocytes and monocytes. - Blocking α4β1 and α4β7 integrins
It prevents α4β1 interactions with VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule–1) in the CNS and α4β7 interactions with MAdCAM-1 in the GI tract. - Inhibition of leukocyte adhesion and migration
Leukocytes are unable to cross endothelial barriers in the brain and gut, reducing inflammation in MS and Crohn’s disease. - Decreased inflammatory damage
Preventing immune cell infiltration leads to decreased demyelination in MS and mucosal inflammation in the gut. - Modulation of immune activity
Peripheral lymphocytes remain functional, maintaining overall immune system competence outside target tissues.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Intravenous infusion |
| Half-life | ~11 days |
| Distribution | Primarily vascular and extracellular fluid |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic catabolism |
| Excretion | Catabolized into peptides and amino acids |
Clinical Uses
- Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS)
- Moderate to severe Crohn’s disease (after conventional therapy failure)
Adverse Effects
- Infusion-related reactions
- Increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Infections (e.g., herpes, respiratory)
- Rare hepatotoxicity or hypersensitivity reactions
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Target Integrins | PML Risk | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natalizumab | α4β1 & α4β7 | High | MS, Crohn’s |
| Vedolizumab | α4β7 only | Low | Ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s |
| Etrolizumab | β7 integrins | Low | Under investigation |
MCQs
- Natalizumab primarily binds to which integrin subunit?
a) β2 b) α4 c) β7 d) αEβ7
Answer: b) α4 - In MS, blockade of α4β1/VCAM-1 prevents leukocyte migration into the:
a) Liver b) Gut c) Brain d) Skin
Answer: c) Brain - In Crohn’s disease, blocking α4β7 prevents leukocyte migration into the:
a) Brain b) Lungs c) Gut d) Pancreas
Answer: c) Gut - A concerning adverse effect is:
a) Diabetes b) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy c) Hypothyroidism d) Hyperlipidemia
Answer: b) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy - Natalizumab differs from vedolizumab in that it blocks:
a) α4β7 only b) α4β1 and α4β7 c) TNF‑α d) IL‑6R
Answer: b) α4β1 and α4β7 - Its typical half-life is approximately:
a) 3 days b) 11 days c) 30 days d) 1 day
Answer: b) 11 days - Which route is used for administration?
a) Oral b) Intravenous c) Subcutaneous d) Intramuscular
Answer: b) Intravenous - Which infection risk is most associated with natalizumab?
a) Tuberculosis b) PML (JC virus) c) CMV colitis d) Candida
Answer: b) PML (JC virus) - Compared to etrolizumab, natalizumab blocks integrins:
a) α4β1 & α4β7 b) Only β7 c) Only α4 d) αLβ2
Answer: a) α4β1 & α4β7 - Why does natalizumab preserve systemic immunity?
a) It targets only B cells b) It blocks migration into specific tissues only c) It depletes leukocytes d) It’s short acting
Answer: b) It blocks migration into specific tissues only
FAQs
1. Why is there a PML risk with natalizumab?
Blocking immune cell entry into the CNS reduces surveillance for JC virus, raising PML risk.
2. How often is natalizumab given?
Standard dosing is every 4 weeks via IV infusion.
3. Is JC virus testing required?
Yes—patients must be monitored regularly for JC virus antibodies and MRI changes.
4. Can it be used with TNF inhibitors?
No—combined immunosuppression significantly increases infection risk.
5. Can therapy be paused?
Interrupting treatment may lead to disease rebound; decisions must be made carefully.
References
- Prescribing Information: Natalizumab (Tysabri)
- PubMed: Natalizumab mechanism in MS and Crohn’s
- DrugBank: Natalizumab Summary
- StatPearls: Natalizumab in MS
- PubMed Central: Mechanism of leukocyte trafficking inhibition
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com