Table of Contents
Introduction
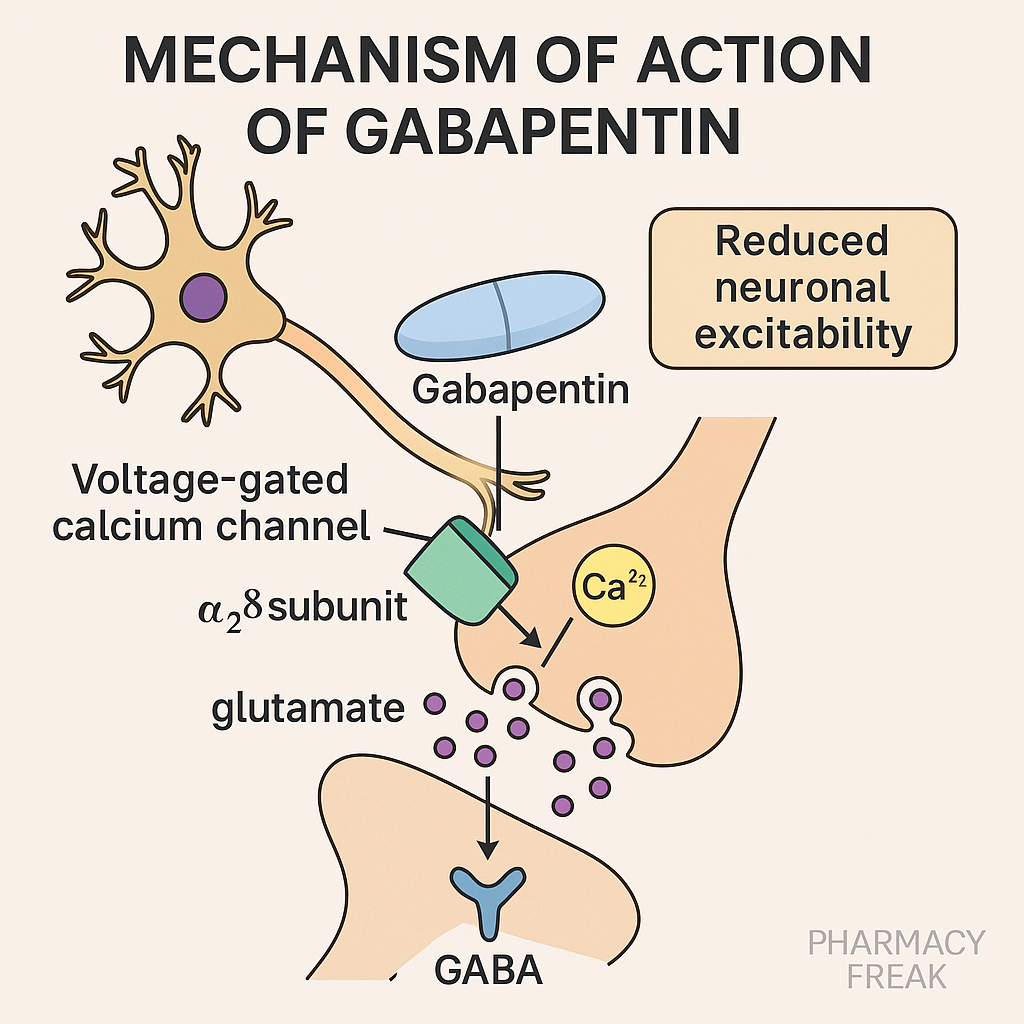
Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug and one of the most widely prescribed medications for neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial seizures. Originally developed as a GABA analog, it surprisingly does not act directly on GABA receptors. Instead, it binds to voltage-gated calcium channels, altering neurotransmitter release. It is also used off-label for conditions like anxiety, fibromyalgia, and hot flashes.
Gabapentin is a favorite topic in USMLE, NCLEX, GPAT, and NEET-PG due to its dual role in epilepsy and pain management.
Stepwise Mechanism of Action of Gabapentin
- Binding to α2δ subunit of voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels
Gabapentin binds to the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the CNS, particularly in presynaptic neurons. - Reduction in calcium influx
This reduces Ca²⁺ entry into neurons upon depolarization, thereby limiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters like glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P. - Decreased excitatory transmission
The inhibition of neurotransmitter release leads to dampened neuronal hyperexcitability, especially in epileptic foci and pain pathways. - No direct action on GABA receptors
Although structurally similar to GABA, it does not bind to GABA-A or GABA-B receptors, nor does it affect GABA synthesis or uptake.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Gabapentin
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | Decreases with dose (non-linear, 60–30%) |
| Half-life | 5–7 hours |
| Metabolism | Not metabolized |
| Excretion | Renal (unchanged drug) |
| Protein binding | Negligible |
| Therapeutic range | Not routinely monitored |
Clinical Uses of Gabapentin
- Partial seizures (adjunct therapy)
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Fibromyalgia
- Generalized anxiety disorder (off-label)
- Restless legs syndrome (off-label)
- Hot flashes (off-label)
Adverse Effects of Gabapentin
- Sedation and drowsiness
- Dizziness and ataxia
- Fatigue
- Peripheral edema
- Weight gain
- Tremor
- Behavioral changes (children)
- Rare: Suicidal ideation, mood swings
⚠️ Dose adjustment is required in renal impairment due to renal clearance.
Comparative Analysis: Gabapentin vs Pregabalin
| Feature | Gabapentin | Pregabalin |
|---|---|---|
| Ca²⁺ channel target | α2δ-1 subunit | α2δ-1 subunit |
| GABA receptor binding | No | No |
| Bioavailability | Variable, non-linear | High, linear |
| Onset of action | Slower | Faster |
| Indications | Similar, with more off-label use | Approved for more indications |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Gabapentin exerts its action by binding to:
a. GABA-A receptor
b. Sodium channels
c. α2δ subunit of calcium channels ✅
d. NMDA receptor
Q2. What is the effect of gabapentin on calcium influx?
a. Increases Ca²⁺ influx
b. No effect
c. Reduces Ca²⁺ influx ✅
d. Blocks calcium reuptake
Q3. Gabapentin is structurally similar to:
a. Glycine
b. GABA ✅
c. Glutamate
d. Serotonin
Q4. Gabapentin is most commonly used for:
a. Myoclonic seizures
b. Status epilepticus
c. Neuropathic pain ✅
d. Absence seizures
Q5. Which neurotransmitter’s release is reduced by gabapentin?
a. Dopamine
b. Acetylcholine
c. Glutamate ✅
d. Serotonin
Q6. Gabapentin metabolism occurs in:
a. Liver
b. Kidney
c. Brain
d. Not metabolized ✅
Q7. Protein binding of gabapentin is:
a. High
b. Moderate
c. Negligible ✅
d. Variable
Q8. Which condition is gabapentin ineffective in?
a. Neuropathic pain
b. Tonic-clonic seizures ✅
c. Anxiety
d. Diabetic neuropathy
Q9. What is a common side effect of gabapentin?
a. Hyperthermia
b. Peripheral edema ✅
c. Hypoglycemia
d. Insomnia
Q10. In renal failure, gabapentin dose should be:
a. Increased
b. Doubled
c. Reduced ✅
d. Unchanged
FAQs
Q1: Is gabapentin a GABA agonist?
No, it does not act on GABA receptors despite its structural similarity.
Q2: Is gabapentin a controlled substance?
In the US, it is not federally controlled, but some states regulate it.
Q3: Can gabapentin be used as monotherapy in epilepsy?
It is not preferred as monotherapy, used mainly as adjunctive therapy.
Q4: How is gabapentin eliminated?
Unchanged by the kidneys, requiring dose adjustment in renal impairment.
Q5: Does gabapentin interact with other drugs?
Minimal drug interactions, since it is not metabolized by the liver.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Sparsh Gupta – Review of Pharmacology
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459127/
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com