Table of Contents
Introduction
Clopidogrel is a widely used oral antiplatelet drug belonging to the thienopyridine class. It plays a critical role in preventing thrombotic events such as myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemic stroke, especially in patients with coronary artery disease or those undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
This drug is essential to understand for students preparing for USMLE, NCLEX, NAPLEX, GPAT, and NEET-PG — particularly in pharmacology of platelet physiology, antithrombotic agents, and cardiovascular pharmacotherapy.
Mechanism of Action of Clopidogrel: Step-by-Step
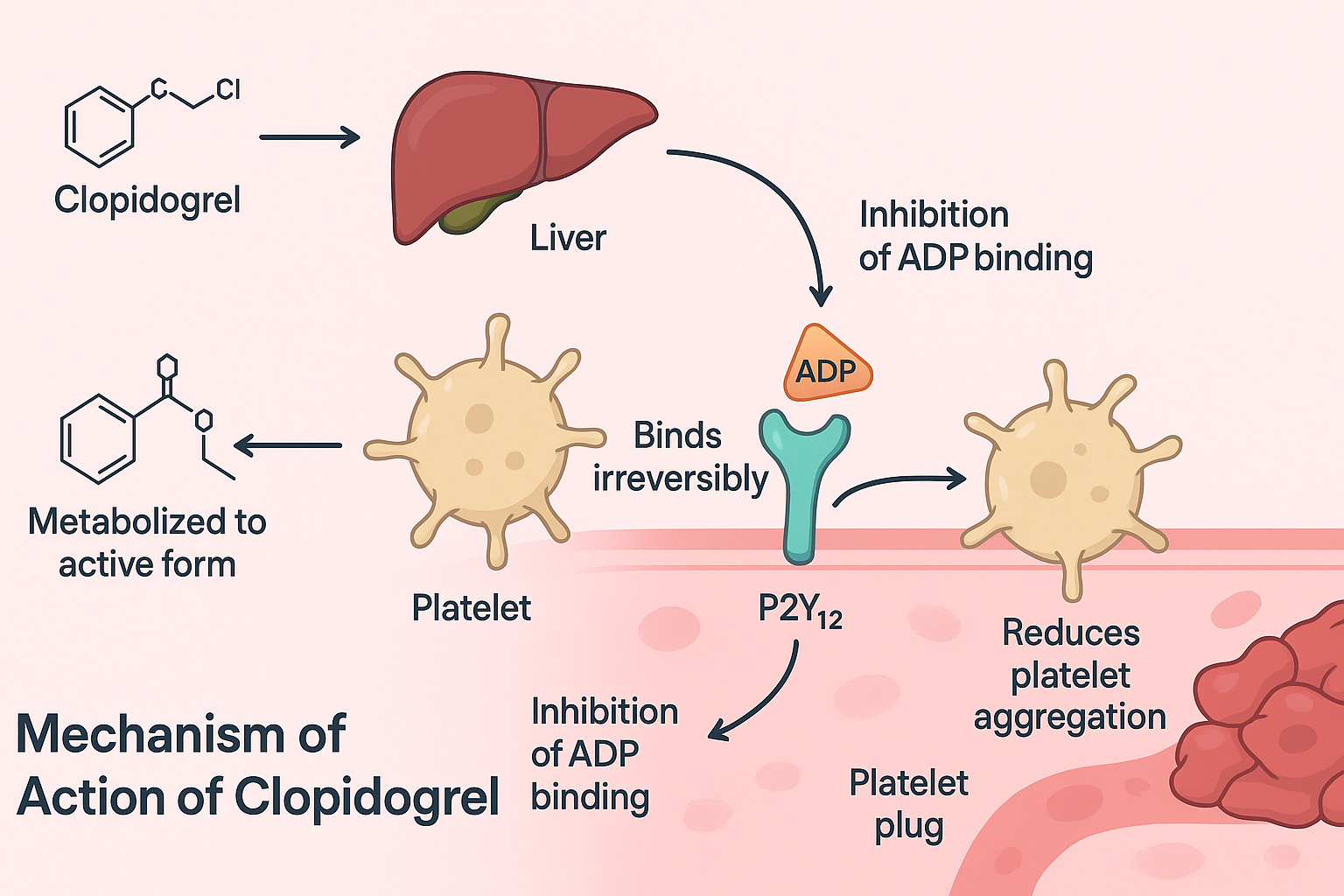
- Administration as a prodrug
Clopidogrel is administered orally and is inactive in its original form. - Hepatic biotransformation
It undergoes oxidative activation in the liver, primarily by CYP2C19, to form its active thiol metabolite. - Irreversible binding to P2Y12 receptor
The active metabolite irreversibly binds to the P2Y12 subtype of ADP receptors on platelet surfaces. - Inhibition of ADP-mediated platelet activation
This blocks ADP from activating the GPIIb/IIIa complex, essential for platelet aggregation. - Result: Antiplatelet effect
Platelets become less sticky, reducing clot formation. Because of irreversible receptor binding, the effect lasts for the entire lifespan of the platelet (~7–10 days).
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Clopidogrel
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | ~50% (due to first-pass metabolism) |
| Half-life | ~6 hours (effect lasts longer) |
| Protein binding | ~98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C19-dependent activation) |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| Onset of action | 2 hours; full effect in 3–7 days |
Clinical Uses of Clopidogrel
- Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
- Myocardial infarction (MI) prophylaxis
- Stroke prophylaxis
- Post-stenting (PCI)
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Alternative to aspirin in intolerance
Adverse Effects of Clopidogrel
- Bleeding (most common)
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Rash and pruritus
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) (rare)
- Neutropenia (rare)
- Drug resistance due to CYP2C19 polymorphism
Comparative Analysis: Clopidogrel vs Aspirin
| Feature | Clopidogrel | Aspirin |
|---|---|---|
| Target | P2Y12 ADP receptor | COX-1 enzyme |
| Effect on platelets | Blocks ADP pathway | Blocks thromboxane A₂ |
| Binding | Irreversible | Irreversible |
| Onset of action | Slower (~3–5 days) | Faster (within hours) |
| Use in aspirin allergy | Preferred | Contraindicated |
| Risk of GI bleeding | Lower than aspirin | Higher |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Clopidogrel belongs to which drug class?
a. COX inhibitors
b. Thienopyridines ✅
c. Direct thrombin inhibitors
d. Nitrates
Q2. What is the mechanism of action of clopidogrel?
a. Inhibits thrombin
b. Blocks thromboxane A₂
c. Irreversibly inhibits P2Y12 ADP receptor ✅
d. Inhibits phosphodiesterase
Q3. Clopidogrel must be activated by which enzyme?
a. CYP3A4
b. CYP2C19 ✅
c. CYP1A2
d. CYP2D6
Q4. Which condition may reduce clopidogrel’s efficacy?
a. Asthma
b. CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism ✅
c. Hypokalemia
d. Diabetes
Q5. The antiplatelet effect of clopidogrel lasts for:
a. 1–2 days
b. 3 days
c. 7–10 days ✅
d. 24 hours
Q6. Which is a serious but rare side effect of clopidogrel?
a. TTP ✅
b. MI
c. Hypertension
d. Angioedema
Q7. Clopidogrel is preferred over aspirin when:
a. Cost is a concern
b. There is aspirin allergy ✅
c. Aspirin is more potent
d. Bleeding is required
Q8. How does clopidogrel differ from ticagrelor?
a. Clopidogrel is reversible
b. Ticagrelor is a prodrug
c. Clopidogrel requires CYP activation ✅
d. Both act on COX enzyme
Q9. Clopidogrel prevents:
a. Arterial thrombosis ✅
b. Venous thrombosis
c. Hemophilia
d. DIC
Q10. Onset of action of clopidogrel is:
a. Immediate
b. 1–2 hours
c. 2–3 days ✅
d. 7–10 days
FAQs
Q1: Is clopidogrel safe in pregnancy?
Generally not recommended, unless benefits outweigh risks. Consult prescriber.
Q2: Can clopidogrel be stopped before surgery?
Yes, usually 5–7 days prior, to allow for platelet regeneration.
Q3: What if a patient is a poor CYP2C19 metabolizer?
Alternative agents like prasugrel or ticagrelor may be more effective.
Q4: Can clopidogrel be used with aspirin?
Yes — dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is common post-stent or in ACS.
Q5: Is clopidogrel used for DVT?
No. It’s used for arterial thrombotic prevention, not venous.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Sparsh Gupta – Review of Pharmacology
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538507/
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com