Table of Contents
Introduction
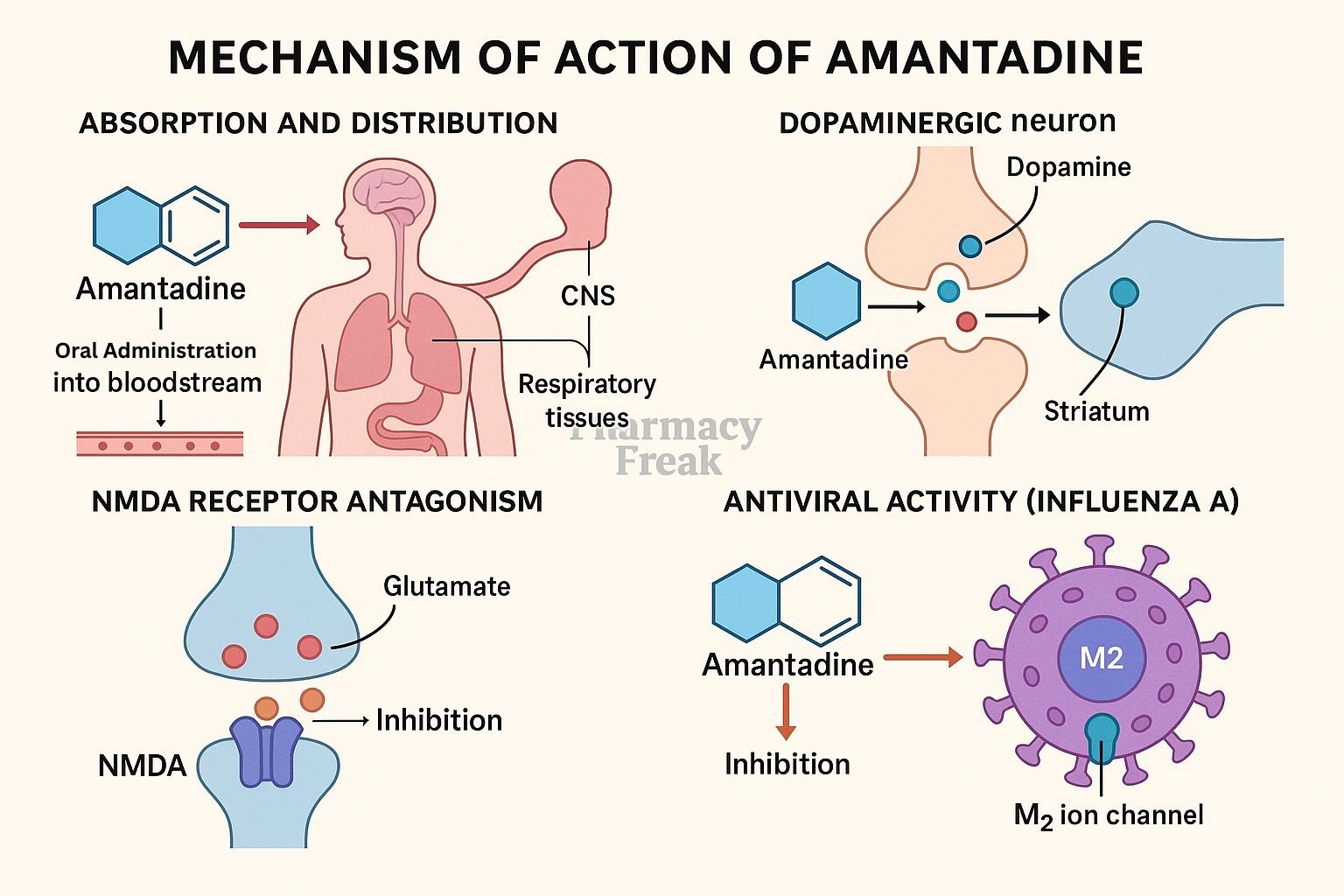
Amantadine is an antiviral agent and antiparkinsonian medication. Initially used for influenza A, it also treats drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms and Parkinson’s disease. Its mechanism combines viral M2 ion channel inhibition and enhancement of dopaminergic neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Inhibition of influenza A M2 ion channel
Amantadine binds to the M2 protein of influenza A virus, blocking proton ion transport and inhibiting uncoating and viral replication. - Enhancement of dopamine release
In the brain, it increases presynaptic dopamine release in striatal neurons, improving neurotransmission. - Inhibition of dopamine reuptake
It modestly blocks dopamine transporter, prolonging dopamine availability in synaptic clefts. - NMDA receptor antagonism
Amantadine acts as a weak NMDA receptor antagonist, which may help reduce dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. - Indirect cholinergic modulation
Through dopaminergic enhancement, it aids in balancing acetylcholine and dopamine in basal ganglia circuits.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Oral (capsule, syrup) |
| Bioavailability | ~86% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | ~2–4 hours |
| Protein Binding | ~67% |
| Metabolism | Minimal hepatic |
| Half-life | ~10–17 hours (renal impairment prolongs) |
| Excretion | Primarily unchanged in urine |
Clinical Uses
- Treatment of early Parkinson’s disease
- Management of drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms
- As influenza A antiviral (limited use due to resistance)
Adverse Effects
- CNS: dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, hallucinations
- GI: nausea, constipation
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Anticholinergic-like effects: dry mouth, peripheral edema
- Rare: livedo reticularis (skin mottling)
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Mechanism Components | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Amantadine | M2 channel blocker, dopaminergic effects, NMDA antagonism | Influenza A, Parkinson’s, EPS |
| Rimantadine | M2 channel blocker only | Influenza A only |
| Levodopa | Dopamine precursor | Parkinson’s disease |
| Memantine | NMDA receptor antagonist | Alzheimer’s disease |
MCQs
- Amantadine blocks which viral structure?
a) Hemagglutinin b) M2 ion channel c) Neuraminidase d) RNA polymerase
Answer: b) M2 ion channel - In Parkinson’s disease, it increases:
a) GABA levels b) Dopamine release c) Serotonin uptake d) Acetylcholine release
Answer: b) Dopamine release - Which receptor does amantadine antagonize?
a) GABA_A b) NMDA c) Muscarinic d) GABA_B
Answer: b) NMDA - Primary excretion route is:
a) Biliary b) Renal unchanged c) Hepatic metabolite d) Pulmonary excretion
Answer: b) Renal unchanged - A common CNS side effect is:
a) Bradycardia b) Dizziness c) Lethargy d) Hypoglycemia
Answer: b) Dizziness - Which antiviral effect is limited now?
a) Influenza B b) RSV c) Influenza A d) Rhinovirus
Answer: c) Influenza A - Protein binding is roughly:
a) 30% b) 50% c) 67% d) 90%
Answer: c) 67% - Compared to rimantadine, amantadine additionally:
a) Blocks NMDA b) Blocks M2 only c) Is injectable d) Is antiviral only
Answer: a) Blocks NMDA - Onset of effect in Parkinson’s disease is:
a) Minutes b) Hours to days c) Months d) Years
Answer: b) Hours to days - Livedo reticularis is a side effect of:
a) Levodopa b) Amantadine c) Rimantadine d) Memantine
Answer: b) Amantadine
FAQs
1. Is amantadine still used for influenza A?
Its antiviral use is limited due to high resistance rates.
2. How does it help in Parkinson’s disease?
By enhancing dopamine release and blocking NMDA receptors, which may reduce symptoms and dyskinesia.
3. Can it worsen psychiatric symptoms?
Yes—it may cause hallucinations or confusion, especially in older patients.
4. Is dose adjustment needed in renal impairment?
Yes—dose should be reduced when renal function is impaired.
5. Can it be combined with levodopa?
Yes—combination therapy may augment motor control and reduce dyskinesia.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13ᵗʰ Edition
- KD Tripathi. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 8ᵗʰ Edition
- DrugBank: Amantadine summary
- StatPearls: Amantadine in Parkinson’s and influenza
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com