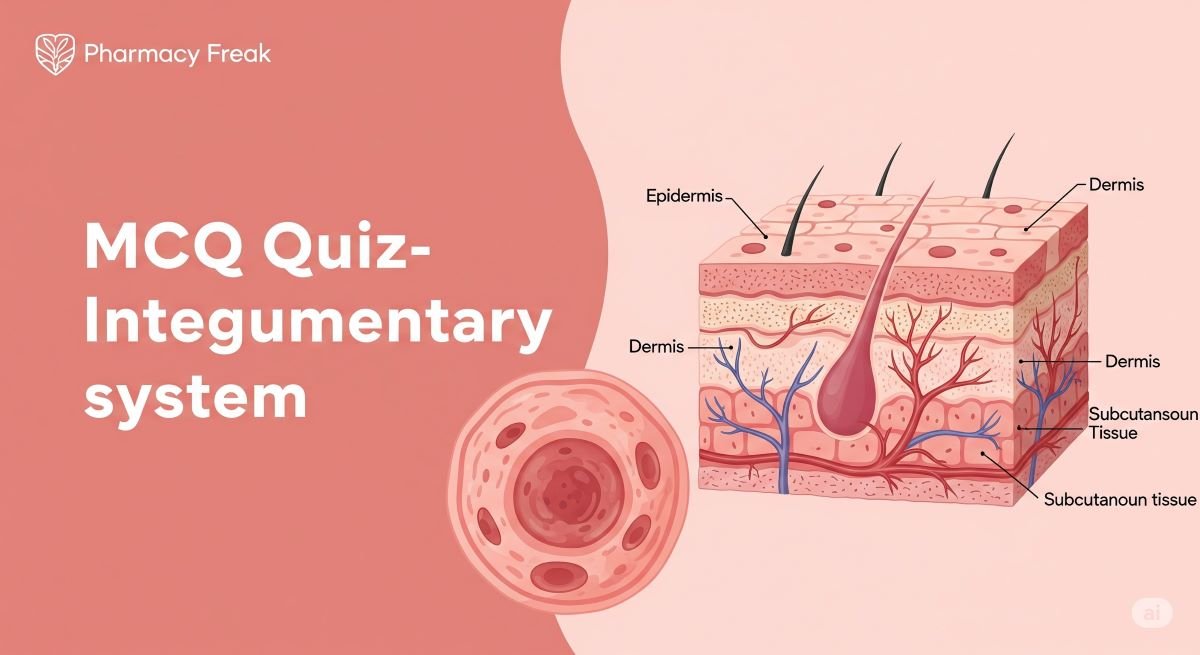
The integumentary system, primarily the skin, is the body’s first line of defense and a critical topic for B.Pharm students. Understanding its complex structure and diverse functions, from protection and temperature regulation to its role in sensation and vitamin D synthesis, is essential. This knowledge provides a vital foundation for comprehending transdermal drug delivery, topical medication effects, and various dermatological conditions you will encounter in your pharmaceutical studies.
- What is the outermost layer of the skin?
- Dermis
- Hypodermis
- Epidermis
- Subcutaneous layer
- Which of the following is the primary function of the skin?
- Production of blood cells
- Protection from environmental hazards
- Digestion of nutrients
- Regulation of heart rate
- The epidermis is composed of which type of epithelial tissue?
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Transitional epithelium
- Simple columnar epithelium
- Which layer of the epidermis is responsible for the continuous production of new cells?
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum basale
- Stratum lucidum
- The pigment responsible for skin and hair color is:
- Hemoglobin
- Keratin
- Melanin
- Collagen
- Which cells in the epidermis produce melanin?
- Keratinocytes
- Melanocytes
- Langerhans cells
- Merkel cells
- The dermis is primarily composed of which tissue type?
- Epithelial tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Nervous tissue
- Connective tissue
- Which structures are responsible for fingerprints?
- Dermal papillae
- Hair follicles
- Sebaceous glands
- Sweat glands
- What is the main protein found in skin, hair, and nails?
- Elastin
- Collagen
- Keratin
- Melanin
- Which glands are associated with hair follicles and produce sebum?
- Sudoriferous glands
- Apocrine glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Eccrine glands
- What is the primary function of sebum?
- To cool the skin
- To lubricate the skin and hair
- To produce pigment
- To detect sensory information
- The sweat glands that are widely distributed over the body and function in temperature regulation are called:
- Sebaceous glands
- Apocrine glands
- Eccrine glands
- Mammary glands
- Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels, nerves, and glands?
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Stratum corneum
- Hypodermis
- The subcutaneous layer or hypodermis primarily consists of:
- Epithelial tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Dense regular connective tissue
- Reticular tissue
- What is the function of the arrector pili muscle?
- To produce sweat
- To secrete sebum
- To make hair stand on end
- To detect touch
- Nails are modifications of which epidermal layer?
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum corneum
- The synthesis of which vitamin begins in the skin upon exposure to UV radiation?
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
- Which layer of the epidermis is present only in the thick skin of the palms and soles?
- Stratum basale
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum spinosum
- The cells in the epidermis that play a role in the immune response are:
- Melanocytes
- Keratinocytes
- Merkel cells
- Langerhans cells
- Which of the following is NOT a function of the integumentary system?
- Thermoregulation
- Protection
- Vitamin B synthesis
- Sensation
- The visible part of the hair that projects above the skin surface is the:
- Root
- Shaft
- Follicle
- Bulb
- What is the most numerous cell type in the epidermis?
- Melanocytes
- Keratinocytes
- Langerhans cells
- Merkel cells
- Body temperature regulation is primarily managed by:
- Sebaceous glands
- Sudoriferous glands
- Arrector pili muscles
- Hair follicles
- The “true skin” that contains the accessory structures is the:
- Epidermis
- Hypodermis
- Dermis
- Subcutaneous layer
- Which sensory receptors in the skin are responsible for detecting deep pressure?
- Meissner’s corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscles
- Merkel discs
- Free nerve endings
- What is the function of collagen fibers in the dermis?
- To provide elasticity
- To provide strength and toughness
- To store fat
- To produce pigment
- Apocrine sweat glands are most concentrated in which areas?
- Forehead and neck
- Palms and soles
- Axillary and genital regions
- Back and chest
- The nail body or plate rests on which part of the finger?
- Nail bed
- Lunula
- Cuticle
- Free edge
- Which of the following is a protective function of the skin?
- Preventing water loss
- Producing hormones
- Storing minerals
- Filtering blood
- The layer that separates the epidermis from the dermis is the:
- Subcutaneous layer
- Basement membrane
- Hypodermis
- Arrector pili
- What is the consequence of the epidermis being avascular?
- It cannot protect the body.
- It does not contain nerves.
- It relies on the dermis for nutrients and oxygen.
- It cannot produce new cells.
- The half-moon shaped white area at the base of the nail is called the:
- Cuticle
- Nail root
- Lunula
- Eponychium
- Which glands begin to function at puberty and are involved in producing body odor?
- Eccrine glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Apocrine glands
- Salivary glands
- The process of shedding the outer layer of dead skin cells is called:
- Keratinization
- Desquamation
- Melanization
- Vasodilation
- Tactile (Merkel) cells are associated with:
- The sense of pain
- The sense of temperature
- The sense of touch
- The sense of pressure
- The flexibility and elasticity of the skin are provided by:
- Keratin and melanin
- Collagen and elastic fibers
- Adipose and areolar tissue
- Sebaceous and sweat glands
- Which part of the hair contains the cells that undergo division and cause hair growth?
- Shaft
- Cortex
- Cuticle
- Hair matrix (in the bulb)
- How does the skin help in cooling the body?
- By shivering
- By producing sebum
- By evaporating sweat
- By constricting blood vessels
- Which skin condition is caused by the inflammation of sebaceous glands?
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Acne
- Rosacea
- The waterproof nature of the skin is primarily due to:
- Melanin in the epidermis
- Keratin and lipids in the stratum corneum
- Collagen in the dermis
- The abundant blood supply
- From deep to superficial, what are the main layers of the skin?
- Dermis, Hypodermis, Epidermis
- Hypodermis, Dermis, Epidermis
- Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
- Dermis, Epidermis, Hypodermis
- What is the medical term for the cuticle of a nail?
- Lunula
- Hyponychium
- Eponychium
- Nail matrix
- The skin’s ability to perceive stimuli like touch, pressure, temperature, and pain is known as:
- Absorption
- Excretion
- Cutaneous sensation
- Thermoregulation
- Which is the thickest layer of the epidermis?
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum corneum
- What is the primary role of the subcutaneous (hypodermis) layer?
- To produce new skin cells
- To provide insulation and anchor the skin
- To produce melanin
- To provide waterproofing
- Goosebumps are caused by the action of:
- Sudoriferous glands
- Pacinian corpuscles
- Arrector pili muscles
- Sebaceous glands
- The secretion from eccrine glands is composed mostly of:
- Sebum and dead cells
- Water, salts, and urea
- Lipids and proteins
- Melanin and keratin
- Which of the following best describes the dermis?
- Avascular and made of epithelial cells
- A strong, flexible connective tissue layer
- The deepest layer composed mainly of fat
- The most superficial, protective layer
- Hair, nails, and glands are known as ______ of the skin.
- layers
- accessory structures
- main components
- sensory receptors
- The loss of which type of fiber in the dermis contributes to wrinkling of the skin?
- Reticular fibers
- Keratin fibers
- Elastic and collagen fibers
- Fibrin fibers

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com