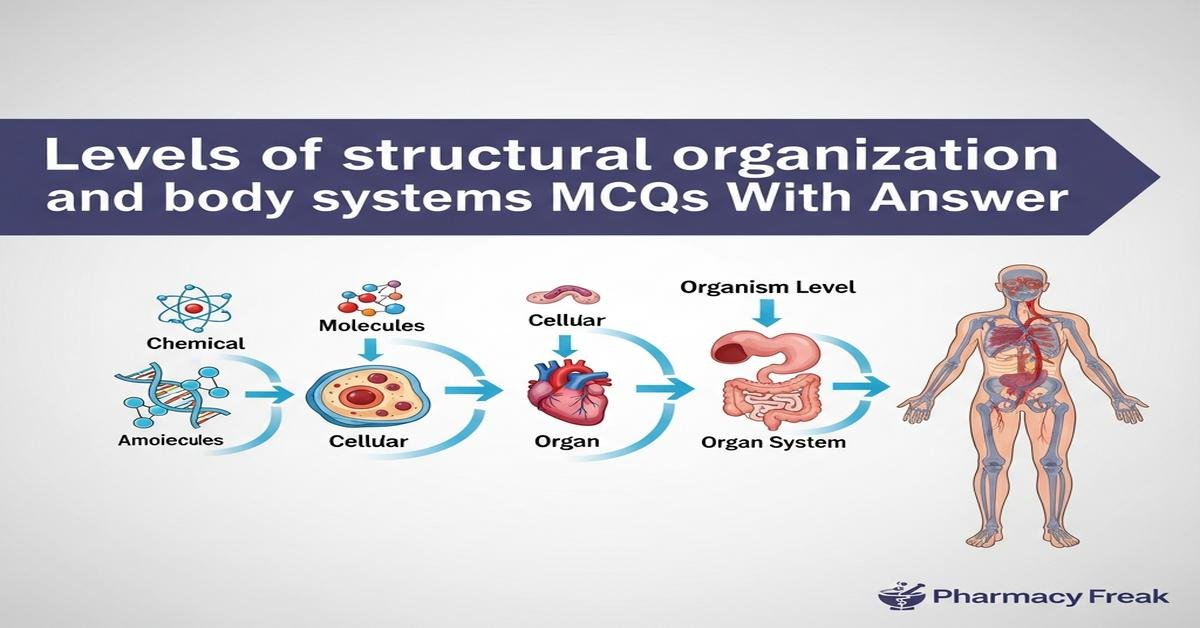
Understanding the levels of structural organization and body systems is essential for B.Pharm students who must link molecular action to organ-level drug effects. This concise introduction covers hierarchical levels — chemical/molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism — and explores major body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous, endocrine, hepatic, renal, immune) relevant to pharmacology, ADME, and toxicology. Emphasis on histology, homeostasis, inter-system communication, and organ-specific functions helps students predict drug targets, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. Clinical examples illustrate how structural organization determines therapeutic response and adverse effects. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which level of structural organization is directly above the chemical (molecular) level?
- Organ level
- Tissue level
- Cellular level
- Organ system level
Correct Answer: Cellular level
Q2. Which organelle is the primary site of ATP production and energy metabolism in most cells?
- Ribosome
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondrion
- Lysosome
Correct Answer: Mitochondrion
Q3. How many basic tissue types are recognized in human histology?
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Five
Correct Answer: Four
Q4. Which of the following is a primary function of epithelial tissue relevant to drug absorption?
- Contraction and force generation
- Support and extracellular matrix production
- Barrier, absorption and secretion
- Impulse conduction
Correct Answer: Barrier, absorption and secretion
Q5. Which components primarily make up connective tissue?
- Cells, extracellular matrix and fibers
- Thin sheets of cells only
- Contractile filaments and sarcomeres
- Neurons and synapses
Correct Answer: Cells, extracellular matrix and fibers
Q6. Which organ is a classical example composed of all four tissue types (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous)?
- Liver
- Heart
- Spleen
- Thyroid
Correct Answer: Heart
Q7. Which organ is most important for first-pass metabolism and biotransformation of drugs?
- Kidney
- Liver
- Lung
- Pancreas
Correct Answer: Liver
Q8. Which body system provides the most rapid communication for short-term regulation of physiological processes?
- Endocrine system
- Nervous system
- Immune system
- Lymphatic system
Correct Answer: Nervous system
Q9. Compared to the nervous system, endocrine signaling is generally:
- Faster and shorter in duration
- Slower and longer in duration
- Restricted to synaptic clefts only
- Independent of blood circulation
Correct Answer: Slower and longer in duration
Q10. The blood-brain barrier is primarily formed by which structural feature?
- Tight junctions between cerebral capillary endothelial cells
- Fenestrated capillaries in the brain
- Loose endothelial junctions and lymphatics
- Myelin sheath around neurons
Correct Answer: Tight junctions between cerebral capillary endothelial cells
Q11. Glomerular filtration in the kidney takes place in which anatomical structure?
- Loop of Henle
- Renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule)
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
Correct Answer: Renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule)
Q12. The spleen and lymph nodes are principal organs of which body system?
- Endocrine system
- Respiratory system
- Lymphatic/immune system
- Digestive system
Correct Answer: Lymphatic/immune system
Q13. Which tissue type is specialized for contraction and force generation?
- Nervous tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue
Correct Answer: Muscle tissue
Q14. What is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle?
- Myofibril
- Sarcomere
- Motor unit
- Sarcoplasm
Correct Answer: Sarcomere
Q15. Which neurotransmitter is released at the typical neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle?
- Glutamate
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- Acetylcholine
- Dopamine
Correct Answer: Acetylcholine
Q16. Most synaptic transmission in the peripheral nervous system is which type?
- Electrical via gap junctions
- Chemical via neurotransmitter release
- Direct cytoplasmic continuity
- Mechanical propagation
Correct Answer: Chemical via neurotransmitter release
Q17. The predominant cell type in the epidermis that produces keratin is called:
- Melanocyte
- Keratinocyte
- Fibroblast
- Langerhans cell
Correct Answer: Keratinocyte
Q18. Which organelle is specialized for synthesis of secreted and membrane proteins?
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondrion
- Lysosome
Correct Answer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Q19. In skeletal muscle cells, which structure stores and releases calcium for contraction?
- Golgi apparatus
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Microtubules
Correct Answer: Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Q20. Cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for many drug oxidations are primarily located in which cellular compartment of hepatocytes?
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (microsomal fraction)
- Lysosomal lumen
- Nuclear envelope
Correct Answer: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (microsomal fraction)
Q21. Which blood vessel type is the primary site for exchange of gases, nutrients, and drugs between blood and tissues?
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arterioles
Correct Answer: Capillaries
Q22. Which organ system is the main regulator of extracellular fluid volume, electrolyte balance, and excretion of water-soluble drug metabolites?
- Respiratory system
- Urinary system (kidneys)
- Endocrine system
- Integumentary system
Correct Answer: Urinary system (kidneys)
Q23. Where does most oral drug absorption occur due to large surface area and specialized epithelium?
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Esophagus
Correct Answer: Small intestine
Q24. Choose the correct order from smallest to largest in structural organization:
- Organ system → organ → tissue → cell
- Cell → tissue → organ → organ system
- Tissue → cell → organ → organ system
- Molecule → organ system → organ → tissue
Correct Answer: Cell → tissue → organ → organ system
Q25. Which receptor family is a common drug target that is a seven-transmembrane, GTP-binding protein-coupled receptor?
- Ligand-gated ion channel
- Receptor tyrosine kinase
- G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
- Nuclear hormone receptor
Correct Answer: G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
Q26. Which organ system contains bone marrow and is the primary site of hematopoiesis?
- Respiratory system
- Skeletal system
- Digestive system
- Endocrine system
Correct Answer: Skeletal system
Q27. Blood is classified histologically as which type of tissue?
- Epithelium
- Muscle tissue
- Connective tissue
- Nervous tissue
Correct Answer: Connective tissue
Q28. Which organ is primarily responsible for first-pass hepatic metabolism after oral drug administration?
- Stomach
- Liver
- Small intestine
- Kidney
Correct Answer: Liver
Q29. Lymph from most of the body drains into the venous circulation at which major structure?
- Right atrium
- Superior vena cava
- Thoracic duct into the left subclavian vein
- Hepatic portal vein
Correct Answer: Thoracic duct into the left subclavian vein
Q30. Which two body systems primarily cooperate to maintain homeostasis through rapid and long-term control?
- Respiratory and digestive systems
- Nervous and endocrine systems
- Cardiovascular and lymphatic systems
- Integumentary and skeletal systems
Correct Answer: Nervous and endocrine systems

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com