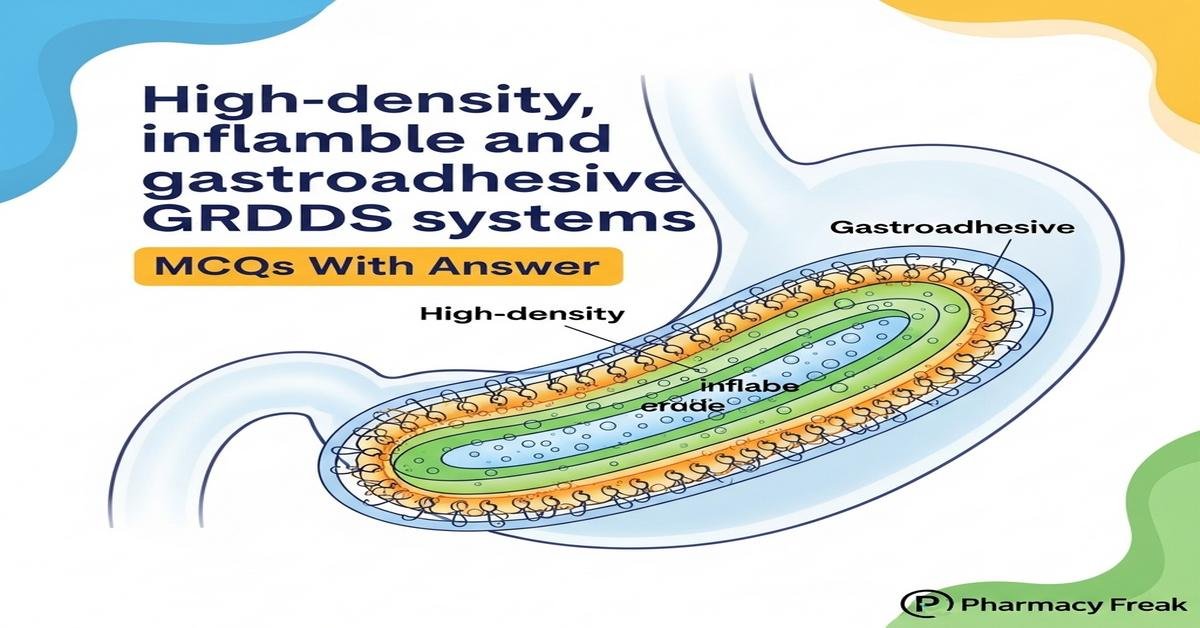
Introduction: High-density, inflatable, and gastroadhesive GRDDS (gastroretentive drug delivery systems) are specialized formulations designed to prolong gastric residence, enhance bioavailability, and target drugs to the stomach or proximal small intestine. High-density systems sink to the antrum, inflatable/expandable systems enlarge to prevent pyloric passage, and gastroadhesive (mucoadhesive) systems attach to the mucosal lining using polymers like Carbopol, chitosan, and HPMC. Key design considerations include density, buoyancy, expansion ratio, mucoadhesive strength, polymer selection, drug stability in acidic media, and in vitro/in vivo evaluation (e.g., buoyancy tests, gamma scintigraphy). These systems suit drugs with a narrow absorption window or local gastric action. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the primary retention mechanism of a high-density GRDDS?
- Sitting buoyantly on gastric contents
- Sinking and settling in the antrum
- Adhering to gastric mucosa
- Rapid disintegration and absorption
Correct Answer: Sinking and settling in the antrum
Q2. Which polymer is commonly used for gastroadhesive mucoadhesion due to carboxylic groups and high swelling?
- Ethylcellulose
- Carbopol (polyacrylic acid)
- Polylactic acid
- Sodium lauryl sulfate
Correct Answer: Carbopol (polyacrylic acid)
Q3. Inflatable or expandable GRDDS typically rely on which design feature to prevent passage through the pylorus?
- High-density core weight
- Rapid polymer erosion
- Large folded or inflated size after deployment
- Enteric coating dissolution in duodenum
Correct Answer: Large folded or inflated size after deployment
Q4. Which gas-generating excipient pair is commonly used to produce CO2 for floating/inflatable systems?
- Sodium chloride and potassium chloride
- Sodium bicarbonate and citric acid
- Magnesium stearate and talc
- Polyethylene glycol and glycerin
Correct Answer: Sodium bicarbonate and citric acid
Q5. Which characteristic most defines a drug suitable for gastroretentive delivery?
- Extensive absorption throughout the colon
- Low solubility in acidic pH only
- Narrow absorption window in the stomach or proximal small intestine
- High first-pass hepatic metabolism only
Correct Answer: Narrow absorption window in the stomach or proximal small intestine
Q6. What is the typical target relative density for a system intended to sink in gastric fluid?
- Less than 0.8 g/cm³
- Approximately equal to air density
- Greater than gastric fluid density (~1.004 g/cm³)
- Exactly 0.5 g/cm³
Correct Answer: Greater than gastric fluid density (~1.004 g/cm³)
Q7. Which in vivo imaging technique is considered a gold-standard for evaluating gastric residence time?
- UV-visible spectroscopy
- Gamma scintigraphy
- Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
- Thermogravimetric analysis
Correct Answer: Gamma scintigraphy
Q8. Which polymer is cationic and often used to enhance mucoadhesion by electrostatic interaction with mucin?
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG)
- Chitosan
- Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC)
- Polystyrene
Correct Answer: Chitosan
Q9. Which test measures the time required for a floating formulation to rise and remain buoyant on a dissolution medium?
- Floating lag time
- Burst pressure test
- Wash-off adhesion test
- Loss on drying
Correct Answer: Floating lag time
Q10. For mucoadhesive GRDDS, which mechanism contributes significantly to adhesive bond formation?
- Chain interpenetration and hydrogen bonding with mucin
- Enzymatic degradation of mucin
- Complete hydrophobic repulsion
- Rapid ionic precipitation
Correct Answer: Chain interpenetration and hydrogen bonding with mucin
Q11. Which material is commonly incorporated as a radio-opaque agent and density enhancer in high-density systems?
- Barium sulfate
- Microcrystalline cellulose
- Lactose monohydrate
- Sucrose
Correct Answer: Barium sulfate
Q12. Which polymer function best describes HPMC in many gastroretentive matrix systems?
- Hydrophobic matrix former causing immediate release
- Hydrophilic swellable polymer controlling diffusion and erosion
- Strong acid that neutralizes gastric pH
- Surfactant to increase solubility only
Correct Answer: Hydrophilic swellable polymer controlling diffusion and erosion
Q13. Which evaluation method is commonly used to quantify mucoadhesive strength in vitro?
- Tensile (detachment) test or wash-off test
- pH titration only
- Colorimetric assay for proteins
- Refractive index measurement
Correct Answer: Tensile (detachment) test or wash-off test
Q14. A potential safety concern unique to inflatable GRDDS is:
- Increased renal clearance of drug
- Gastric outlet obstruction if not degradable or deflatable
- Improved systemic bioavailability of all drugs
- Immediate disintegration in stomach acid
Correct Answer: Gastric outlet obstruction if not degradable or deflatable
Q15. Which factor most influences gastric residence time of floating systems?
- System density being much higher than gastric contents
- Fed versus fasted state of the patient
- Color of the dosage form
- Ambient room temperature
Correct Answer: Fed versus fasted state of the patient
Q16. Which instrument is ideal for measuring true particle or formulation density in GRDDS development?
- Pycnometer
- pH meter
- UV spectrophotometer
- Malvern particle size analyzer only
Correct Answer: Pycnometer
Q17. The primary rate-limiting step in the release from a typical mucoadhesive matrix is:
- Polymer hydration and drug diffusion through the swollen matrix
- Immediate enzymatic cleavage of polymer chains
- Volatilization of the active pharmaceutical ingredient
- Sublimation of excipients
Correct Answer: Polymer hydration and drug diffusion through the swollen matrix
Q18. Which polymeric material is frequently chosen for flexible inflatable membranes in controlled-expandable devices?
- Polyurethane
- Polystyrene foam
- Unplasticized PVC tubing
- Sugar glass
Correct Answer: Polyurethane
Q19. Which in vitro parameter assesses the mechanical integrity of an inflatable balloon-type GRDDS before in vivo use?
- Burst pressure or burst strength test
- Disintegration time in colon fluid
- Cloud point measurement
- Melting point determination
Correct Answer: Burst pressure or burst strength test
Q20. What is a common purpose of adding mucoadhesive polymers to a gastroretentive formulation besides adhesion?
- To reduce molecular weight of the drug
- To increase residence time and provide controlled release
- To enhance renal elimination
- To provoke rapid vomiting
Correct Answer: To increase residence time and provide controlled release
Q21. Which gastric region is favored for retention by high-density systems?
- Fundus
- Antrum
- Jejunum
- Colon
Correct Answer: Antrum
Q22. Which parameter best describes the time taken for a gastroretentive floating dosage form to begin buoyancy?
- Mucoadhesive strength
- Floating lag time
- Burst release time
- Intrinsic dissolution rate
Correct Answer: Floating lag time
Q23. Why are enteric coatings generally avoided for formulations intended to release drug in the stomach?
- They accelerate gastric release
- They prevent drug release in acidic stomach, counteracting gastroretention goals
- They increase mucoadhesion indiscriminately
- They make formulations immediately float
Correct Answer: They prevent drug release in acidic stomach, counteracting gastroretention goals
Q24. Which property of mucin facilitates mucoadhesion of negatively charged polymers like Carbopol?
- Complete hydrophobicity
- Presence of glycoprotein chains with hydrogen-bonding sites
- High crystalline order
- Metallic ionic centers
Correct Answer: Presence of glycoprotein chains with hydrogen-bonding sites
Q25. Which kinetic model is commonly used to describe diffusion-controlled drug release from matrix-type GRDDS?
- Higuchi model
- Arrhenius equation
- Michaelis-Menten kinetics
- Nernst equation
Correct Answer: Higuchi model
Q26. In designing an inflatable GRDDS, which gas-generation characteristic critically affects expansion kinetics and initial buoyancy?
- Color of the gas
- Rate of CO2 generation and retention within the chamber
- Electrical conductivity of gas
- pH of neutral buffers only
Correct Answer: Rate of CO2 generation and retention within the chamber
Q27. Which excipient can be used both as a mucoadhesive and to modulate matrix swelling in gastroretentive tablets?
- Magnesium stearate
- Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)
- Sorbitol
- Sodium chloride
Correct Answer: Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)
Q28. For in vivo tracking of a gastroretentive system by X-ray, which additive is appropriate to provide radiopacity?
- Barium sulfate
- Gelatin
- Lactose
- Cellulose acetate
Correct Answer: Barium sulfate
Q29. Which parameter is most important to minimize in a floating formulation to ensure rapid onset of buoyancy?
- Floating lag time
- Total drug load
- Polymer viscosity index
- Tablet hardness always
Correct Answer: Floating lag time
Q30. Which challenge is commonly associated with gastroadhesive systems in vivo?
- Excessive systemic clearance through lungs
- Continuous mucus turnover and gastric motility reducing adhesion
- Instantaneous droplet formation in stomach
- Permanent chemical bonding to epithelial DNA
Correct Answer: Continuous mucus turnover and gastric motility reducing adhesion

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com