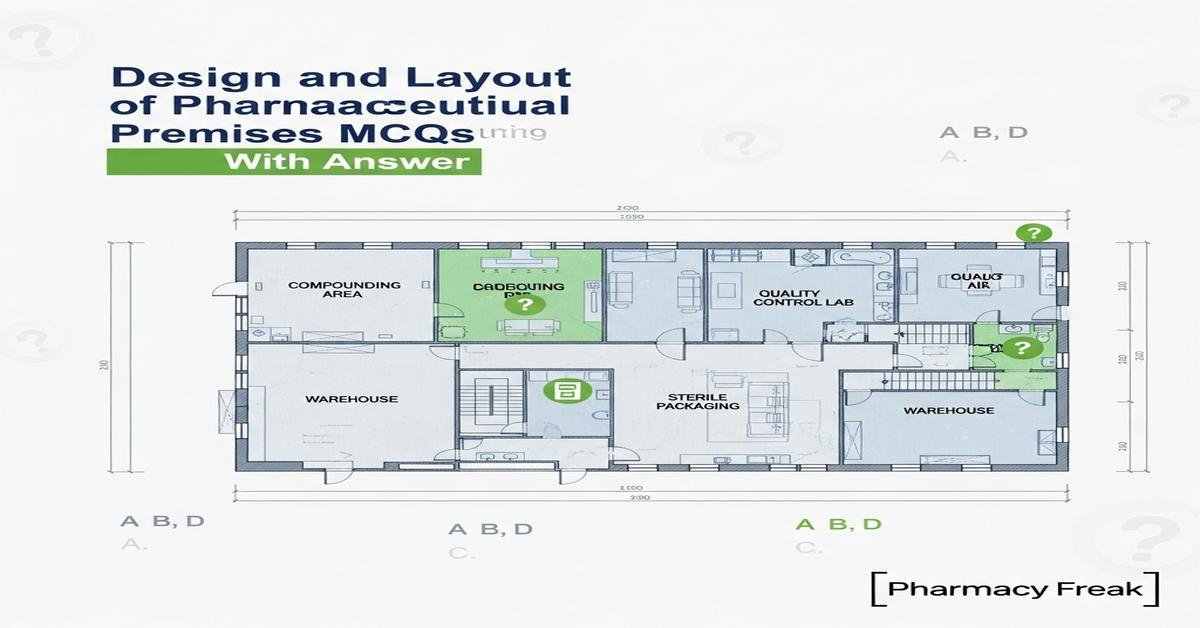
Introduction: The design and layout of pharmaceutical premises MCQs With Answer covers essential principles for safe, compliant drug production. This introduction explains key topics such as GMP-compliant cleanroom design, material and personnel flow, contamination control, HVAC and HEPA filtration, ISO classification, utilities (WFI, compressed air), containment for potent APIs, validation (IQ/OQ/PQ), and documentation. Students will learn how layout decisions—flooring, finishes, pressure differentials, pass‑throughs, gowning areas, and storage—reduce cross-contamination, ensure product quality, and enable regulatory compliance. Practical knowledge of risk assessment, monitoring and maintenance is emphasized to prepare for real-world pharmacy operations. ‘Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.’
Q1. What is the primary objective of pharmaceutical premises design and layout?
- To prevent contamination and cross-contamination through controlled material and personnel flow
- To maximize the number of production lines in minimum space
- To reduce employee travel time only
- To create visually appealing facilities for marketing
Correct Answer: To prevent contamination and cross-contamination through controlled material and personnel flow
Q2. Which of the following best describes segregation of raw materials and finished products?
- Locating them in the same room for convenience
- Storing together but labeling differently
- Physical separation to avoid mix-ups and cross-contamination
- Using temporary partitions without dedicated storage
Correct Answer: Physical separation to avoid mix-ups and cross-contamination
Q3. Which standard is commonly used to classify cleanroom air cleanliness by particle concentration?
- ISO 14644-1
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11
- ICH Q7
- OSHA 1910
Correct Answer: ISO 14644-1
Q4. A typical recommended positive pressure differential between a cleaner room and an adjacent less clean area is approximately:
- 5 Pascals
- Approximately 15 Pascals (positive)
- 50 Pascals
- 500 Pascals
Correct Answer: Approximately 15 Pascals (positive)
Q5. What is the principal function of HEPA filters in pharmaceutical HVAC systems?
- To remove odors from the air
- To trap particles ≥0.3 µm with high efficiency (~99.97%)
- To cool the air only
- To add humidity to dry air
Correct Answer: To trap particles ≥0.3 µm with high efficiency (~99.97%)
Q6. Which flooring is preferred in production areas for hygiene and cleanability?
- Carpet tiles
- Seamless, non-shedding epoxy or resin flooring
- Unsealed concrete
- Wooden planks
Correct Answer: Seamless, non-shedding epoxy or resin flooring
Q7. The main purpose of a gowning area is to:
- Provide rest space for staff
- Allow personnel to change into clean garments and reduce contamination
- Store finished products temporarily
- House HVAC equipment
Correct Answer: Allow personnel to change into clean garments and reduce contamination
Q8. Ideal flow of materials in a manufacturing layout should be:
- Unidirectional from raw materials to finished goods
- Bidirectional to save space
- Random according to convenience
- From finished goods to raw materials
Correct Answer: Unidirectional from raw materials to finished goods
Q9. What is a pass-through (pass box) used for?
- To transfer personnel between floors
- To transfer materials between controlled rooms while minimizing air exchange
- For storage of hazardous waste
- To house electrical panels
Correct Answer: To transfer materials between controlled rooms while minimizing air exchange
Q10. Which describes an appropriate drainage design for production areas?
- Open drains with no traps
- Indirect, closed drainage with trapped gullies and adequate slope to prevent pooling
- Drains that discharge directly onto the exterior floor
- No drainage to discourage water use
Correct Answer: Indirect, closed drainage with trapped gullies and adequate slope to prevent pooling
Q11. Fire safety in pharmaceutical premises should include:
- Single unlocked door for all exits
- Clearly marked evacuation routes, fire-rated compartments and suppression systems
- No fire alarms to prevent false alarms
- Using production rooms as shelter areas in case of fire
Correct Answer: Clearly marked evacuation routes, fire-rated compartments and suppression systems
Q12. Which ISO class is typically required for aseptic filling operations?
- ISO 8
- ISO 7
- ISO 5
- ISO 9
Correct Answer: ISO 5
Q13. Water for Injection (WFI) in premises design is most commonly used for:
- Cleaning office floors
- Final formulation and rinsing in parenteral production and sterilization tasks
- Cooling HVAC coils only
- Drinking water for staff
Correct Answer: Final formulation and rinsing in parenteral production and sterilization tasks
Q14. Compressed air used in direct contact with product must be:
- Oil-free, filtered and dried to appropriate quality standards
- Untreated ambient air
- Only cooled but not filtered
- Heavily lubricated to protect equipment
Correct Answer: Oil-free, filtered and dried to appropriate quality standards
Q15. The HVAC system in pharmaceutical areas is responsible for controlling:
- Temperature, humidity, pressure differentials and filtration
- Only temperature
- Only lighting levels
- Only personnel movement
Correct Answer: Temperature, humidity, pressure differentials and filtration
Q16. What is the role of a buffer room between a gowning area and a cleanroom?
- To act as a storage area for finished goods
- To provide an intermediate cleanliness zone and reduce contamination transfer
- To house heavy machinery
- To allow external deliveries directly into the cleanroom
Correct Answer: To provide an intermediate cleanliness zone and reduce contamination transfer
Q17. Good layout planning for personnel and material flow aims to:
- Combine all flows into a single corridor
- Separate and maintain unidirectional flows to minimize cross-contamination
- Allow personnel to cross material flow to improve access
- Ignore flows to maximize space usage
Correct Answer: Separate and maintain unidirectional flows to minimize cross-contamination
Q18. A pass box should ideally have which of the following features?
- Interlocking doors and easy-to-clean surfaces
- Open shelving for quick access
- Windows that open to the outside
- Porous wooden interior for cushioning
Correct Answer: Interlocking doors and easy-to-clean surfaces
Q19. Which sequence describes facility qualification stages?
- PQ → OQ → IQ
- IQ → OQ → PQ
- OQ → PQ → IQ
- Validation only, no stages required
Correct Answer: IQ → OQ → PQ
Q20. Effective pest prevention in premises design relies on:
- Leaving exterior doors open during business hours
- Sealed building envelope, screened vents and active pest control programs
- Storing food in production rooms
- Using plants inside cleanrooms
Correct Answer: Sealed building envelope, screened vents and active pest control programs
Q21. Sampling of raw materials should normally be conducted in:
- A controlled sampling area separate from bulk storage and production
- Directly inside the storage container without controls
- In the production line during processing
- At random outdoor locations
Correct Answer: A controlled sampling area separate from bulk storage and production
Q22. Preferred ceiling materials in cleanrooms are:
- Perforated and dusty materials
- Smooth, non-shedding panels with sealed joints
- Wooden slats
- Loose acoustic tiles
Correct Answer: Smooth, non-shedding panels with sealed joints
Q23. For handling potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), the layout should include:
- Shared general production areas for all APIs
- Dedicated containment rooms with negative pressure and separate HVAC
- Open benches near administrative offices
- Only procedural controls without physical segregation
Correct Answer: Dedicated containment rooms with negative pressure and separate HVAC
Q24. Recommended illumination level for visual inspection tasks in pharmaceutical control areas is approximately:
- 50 lux
- 200 lux
- 1000 lux
- 10 lux
Correct Answer: 1000 lux
Q25. Personnel movement pattern in a clean facility should generally be from:
- More clean to less clean areas to save time
- Less clean to more clean areas with proper gowning and unidirectional flow
- Random directions dictated by tasks
- Outside directly into sterile suites
Correct Answer: Less clean to more clean areas with proper gowning and unidirectional flow
Q26. Routine cleanroom monitoring should include:
- Only visual inspections
- Particle counting and viable (microbial) monitoring
- Only HVAC temperature checks
- Monitoring only during weekends
Correct Answer: Particle counting and viable (microbial) monitoring
Q27. Storage of flammable solvents requires:
- Storage in regular office cabinets
- Dedicated, fire-rated storage with ventilation and segregation from incompatible materials
- Mixing with water in storage rooms
- Placement near electrical panels for easy access
Correct Answer: Dedicated, fire-rated storage with ventilation and segregation from incompatible materials
Q28. A “dirty corridor” in a facility layout is intended for:
- Transporting raw materials into sterile areas
- Movement of waste, soiled materials and non-product items away from clean zones
- Storing finished products
- Public access and tours
Correct Answer: Movement of waste, soiled materials and non-product items away from clean zones
Q29. Why is HVAC redundancy important in critical pharmaceutical areas?
- It is not important and increases cost unnecessarily
- To maintain environmental controls and product safety during equipment failure
- Only to provide extra heating in winter
- To allow frequent shutdowns for maintenance
Correct Answer: To maintain environmental controls and product safety during equipment failure
Q30. Which documents are essential during design and layout validation of pharmaceutical premises?
- Only marketing brochures
- Layout drawings, utility schematics, risk assessments, SOPs and validation protocols
- Only purchase orders for equipment
- Informal notes from contractors
Correct Answer: Layout drawings, utility schematics, risk assessments, SOPs and validation protocols

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com