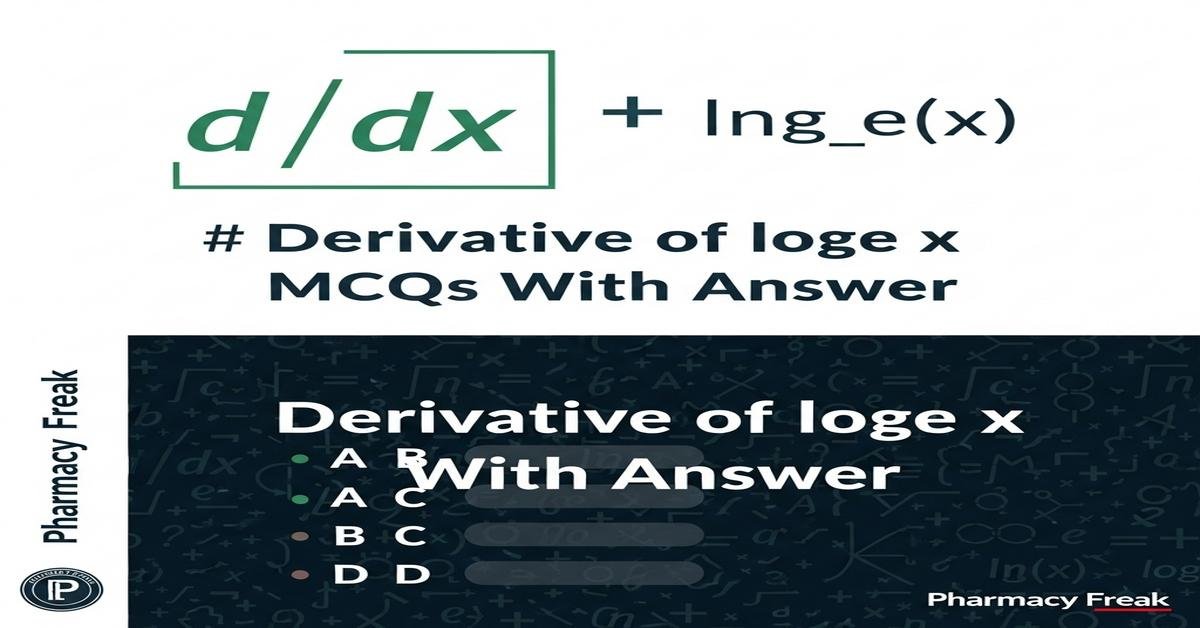Introduction: The derivative of loge x (ln x) is a fundamental concept for B.Pharm students studying pharmacokinetics, drug stability, and concentration–time modeling. Understanding d/dx ln x = 1/x (for x > 0) and the more general d/dx ln|x| = 1/x (x ≠ 0) helps analyze relative rates, half-life calculations, pH-related transformations, and exponential decay. This topic links calculus rules — chain rule, product rule, and implicit differentiation — to practical pharmaceutical problems. These MCQs with answers reinforce both theory and application, improving problem-solving for dosing, kinetics and lab calculations. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the derivative of loge x with respect to x for x > 0?
- 1/x
- ln x
- x ln x
- x
Correct Answer: 1/x
Q2. The derivative of ln|x| is valid for which values of x?
- All real x except x = 0
- Only x > 0
- Only x < 0
- All real x including x = 0
Correct Answer: All real x except x = 0
Q3. Using chain rule, what is d/dx [ln(u(x))]?
- u(x) / u'(x)
- u'(x) / u(x)
- ln u'(x)
- u'(x) * ln u(x)
Correct Answer: u'(x) / u(x)
Q4. What is d/dx [ln(3x^2 + 1)]?
- 6x / (3x^2 + 1)
- 3x^2 / (3x^2 + 1)
- 6x ln(3x^2 + 1)
- 1 / (3x^2 + 1)
Correct Answer: 6x / (3x^2 + 1)
Q5. What is d/dx [ln(ax)] where a is a positive constant?
- 1 / (ax)
- a / x
- 1 / x
- ln a / x
Correct Answer: 1 / x
Q6. What is the derivative of ln(x^2)?
- 2 / x
- 1 / x^2
- 2x / ln x
- ln x / x
Correct Answer: 2 / x
Q7. For y = ln(f(x)) where f(x) = e^{2x}, what is dy/dx?
- 2
- e^{2x}
- 2e^{2x}
- 1/2
Correct Answer: 2
Q8. d/dx [ln(x) + ln(y)] with x a function of t and y constant: which term remains?
- d/dx ln(y)
- 1/x
- 0
- ln y
Correct Answer: 1/x
Q9. What is d/dx [ln(1/x)]?
- -1 / x
- 1 / x
- -1 / x^2
- ln(1/x) / x
Correct Answer: -1 / x
Q10. Which expression equals d/dx [ln|x|] at x = -2?
- -1/2
- 1/2
- -2
- Undefined
Correct Answer: -1/2
Q11. The second derivative of ln x is:
- -1 / x^2
- 1 / x^2
- 0
- 1 / x
Correct Answer: -1 / x^2
Q12. d/dx [ln(sin x)] for 0 < x < π is:
- cos x / sin x
- sin x / cos x
- 1 / sin x
- ln(cos x)
Correct Answer: cos x / sin x
Q13. If C(t) = C0 e^{-kt}, what is d/dt [ln C(t)]?
- -k
- k
- -k C0
- e^{-kt}
Correct Answer: -k
Q14. Which rule is most directly used to differentiate ln(g(x))?
- Chain rule
- Product rule
- Integration by parts
- Quotient rule
Correct Answer: Chain rule
Q15. d/dx [ln(x) * x] requires which combination of rules?
- Product rule only
- Chain rule only
- Product rule and derivative of ln (1/x)
- Quotient rule and chain rule
Correct Answer: Product rule and derivative of ln (1/x)
Q16. What is d/dx [ln(x) / x]?
- (1 – ln x) / x^2
- (ln x – 1) / x^2
- 1 / x^2
- ln x / x
Correct Answer: (1 – ln x) / x^2
Q17. For y = ln(u) where u = x^n, dy/dx equals:
- n / x
- x^{n-1} / n
- ln x / n
Correct Answer: n / x
Q18. d/dx [log_a x] equals:
- 1 / (x ln a)
- ln a / x
- 1 / x
- ln x / a
Correct Answer: 1 / (x ln a)
Q19. If y = ln(x) and x = e^t, dy/dt =
- 1
- e^t
- t
- 1 / e^t
Correct Answer: 1
Q20. Differentiate y = ln(x+√(x^2+1)). dy/dx =
- 1 / √(x^2+1)
- x / √(x^2+1)
- 1 / (x+√(x^2+1))
- √(x^2+1)
Correct Answer: 1 / √(x^2+1)
Q21. For drug concentration C, instantaneous relative rate r = (1/C) dC/dt equals:
- d/dt [ln C]
- ln(dC/dt)
- C * dC/dt
- d/dt [1/C]
Correct Answer: d/dt [ln C]
Q22. Which is the derivative of ln(uv) where u and v are functions of x?
- u’ / u + v’ / v
- (uv)’ / uv
- ln u’ + ln v’
- u’v + uv’
Correct Answer: u’ / u + v’ / v
Q23. d/dx [ln(x^2 + 1)^{3}] simplifies to:
- 6x / (x^2 + 1)
- 3 / (x^2 + 1)
- 3 ln(x^2 + 1) / x
- 6x ln(x^2 + 1)
Correct Answer: 6x / (x^2 + 1)
Q24. Using logarithmic differentiation, d/dx [x^x] equals:
- x^x (ln x + 1)
- x^{x-1} (ln x + 1)
- x^x / x
- ln(x^x)
Correct Answer: x^x (ln x + 1)
Q25. For f(x) = ln|sin x|, where is f'(x) undefined?
- At x = nπ where n is integer
- At x = π/2
- At x = π/4
- Nowhere; always defined
Correct Answer: At x = nπ where n is integer
Q26. What is d/dx [ln( (x+1)/(x-1) )]?
- 2 / (x^2 – 1)
- 1 / (x+1) – 1 / (x-1)
- (x-1 – x-1) / (x^2-1)
- ln((x+1)/(x-1))’ = 0
Correct Answer: 2 / (x^2 – 1)
Q27. Which statement is true about ln x at x = 0?
- ln x is not defined at x = 0
- ln x has derivative 1 at x = 0
- ln x has a finite value at x = 0
- ln x is defined and differentiable at x = 0
Correct Answer: ln x is not defined at x = 0
Q28. If y = ln(g(x)) and g(a) = 1, what is y'(a)?
- g'(a)
- 0
- g'(a) / 1 = g'(a)
- 1
Correct Answer: g'(a) / 1 = g'(a)
Q29. Differentiate y = ln( e^{x} + e^{-x} ). y’ =
- (e^{x} – e^{-x}) / (e^{x} + e^{-x})
- 1
- e^{x} + e^{-x}
- (e^{x} + e^{-x}) / (e^{x} – e^{-x})
Correct Answer: (e^{x} – e^{-x}) / (e^{x} + e^{-x})
Q30. For concentration C(t) = A / (1 + Bt), what is d/dt [ln C]?
- -B / (1 + Bt)
- B / (1 + Bt)
- -A / (1 + Bt)^2
- 0
Correct Answer: -B / (1 + Bt)
Q31. The derivative of ln(x) at x = 1 is:
- 1
- 0
- -1
- Undefined
Correct Answer: 1
Q32. d/dx [ln(x) * ln(2x)] requires which simplification step?
- Use product rule and derivative 1/x and 1/x for ln terms
- Treat ln(2x) as constant
- Differentiate ln(x) only
- Use quotient rule only
Correct Answer: Use product rule and derivative 1/x and 1/x for ln terms
Q33. If f(x) = ln(g(x))/h(x), which rule is used to find f'(x)?
- Quotient rule combined with chain rule
- Simple chain rule only
- Product rule only
- Integration
Correct Answer: Quotient rule combined with chain rule
Q34. d/dx [ln(1 + e^{x})] equals:
- e^{x} / (1 + e^{x})
- 1 / (1 + e^{x})
- ln(1 + e^{x}) / x
- e^{x}
Correct Answer: e^{x} / (1 + e^{x})
Q35. For f(x) = ln( (x^3) ), f'(x) simplifies to:
- 3 / x
- 1 / x^3
- 3x^2 / x^3
- ln(x^3) / x
Correct Answer: 3 / x
Q36. Which identity helps convert differentiation of ln(a x^n) quickly?
- ln(a x^n) = ln a + n ln x
- ln(a x^n) = a + n x
- ln(a x^n) = a ln x^n
- ln(a x^n) = ln a * ln x^n
Correct Answer: ln(a x^n) = ln a + n ln x
Q37. If y = ln(u) and u = v^k, dy/dx =
- k v’ / v
- v’ / v^k
- k ln v
- v^k / v’
Correct Answer: k v’ / v
Q38. What is derivative of ln(1 – x) with respect to x?
- -1 / (1 – x)
- 1 / (1 – x)
- – (1 – x)
- ln(1 – x)’ = 0
Correct Answer: -1 / (1 – x)
Q39. For a dissolution rate proportional to concentration C, d/dt ln C = constant. This constant represents:
- The proportional rate constant
- Absolute change in concentration
- Half-life
- Initial concentration
Correct Answer: The proportional rate constant
Q40. d/dx [ln(x) + ln(2x)] equals:
- 1/x + 1/x
- 1/x + 1/(2x)
- ln(2x) / x
- 2 / x
Correct Answer: 1/x + 1/x
Q41. Evaluate derivative at x = 2: d/dx [ln(x^2 + x)] at x=2 equals:
- (2x + 1)/(x^2 + x) at x=2 = 5/6
- 1/2
- 2/(x^2 + x) at x=2 = 2/6
- ln(6)/2
Correct Answer: (2x + 1)/(x^2 + x) at x=2 = 5/6
Q42. d/dx [ln|x|] equals 1/x. This implies the slope sign changes at:
- Across x = 0, slope goes from negative to positive depending on sign of x
- x = 1 only
- Never; slope is constant
- x = -1 only
Correct Answer: Across x = 0, slope goes from negative to positive depending on sign of x
Q43. If pH = -log10[H+], express dpH/d[H+] using natural log relation. dpH/d[H+] =
- -1 / ([H+] ln 10)
- -ln 10 / [H+]
- 1 / ([H+] ln 10)
- -1 / [H+]
Correct Answer: -1 / ([H+] ln 10)
Q44. Differentiate y = ln(√x). y’ equals:
- 1 / (2x)
- 1 / x
- 1 / (√x)
- ln √x / x
Correct Answer: 1 / (2x)
Q45. For y = ln( (x^2 + 1)^{1/2} ), y’ simplifies to:
- x / (x^2 + 1)
- 1 / (2 √(x^2 + 1))
- x / √(x^2 + 1)
- ln(x^2 + 1) / 2
Correct Answer: x / (x^2 + 1)
Q46. Using logarithmic differentiation for f(x) = (x+1)^{x}, f'(x) includes which main term?
- (x+1)^{x} (ln(x+1) + x/(x+1))
- (x+1)^{x} ln x
- x (x+1)^{x-1}
- ln((x+1)^{x})’
Correct Answer: (x+1)^{x} (ln(x+1) + x/(x+1))
Q47. The derivative of ln x approaches what value as x → ∞?
- 0
- 1
- ∞
- -∞
Correct Answer: 0
Q48. Differentiate y = ln( (x^2 – 1) ) for x > 1. y’ equals:
- 2x / (x^2 – 1)
- 1 / (x^2 – 1)
- ln(x^2 – 1)’ = 0
- 2 / (x – 1)
Correct Answer: 2x / (x^2 – 1)
Q49. If concentration follows C = C0 t^{-n}, ln C = ln C0 – n ln t. d/dt ln C equals:
- -n / t
- n / t
- -n t^{n-1}
- 0
Correct Answer: -n / t
Q50. Which practical interpretation is correct: d/dt [ln(concentration)] gives
- Instantaneous fractional (relative) rate of change of concentration
- Absolute concentration change per unit time
- Half-life directly
- Initial concentration
Correct Answer: Instantaneous fractional (relative) rate of change of concentration

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com