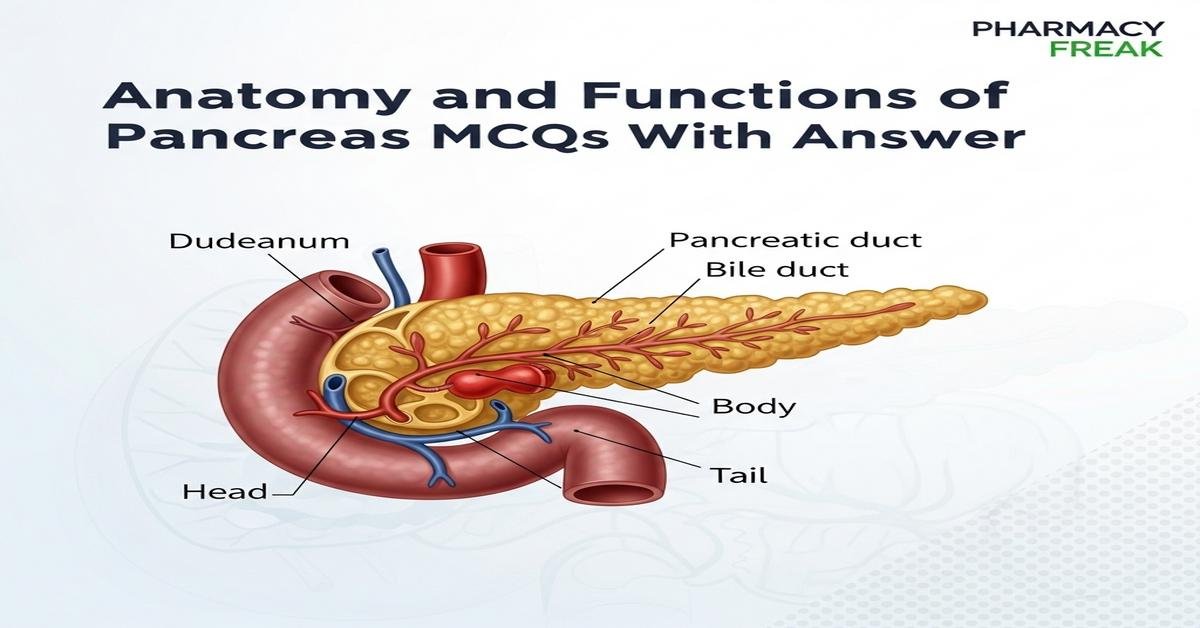
Anatomy and functions of pancreas MCQs With Answer
This concise introduction covers the anatomy of pancreas, histology, exocrine and endocrine functions, pancreatic hormones, and clinical correlations tailored for B.Pharm students. Learn key concepts such as pancreatic lobular structure, ducts (Wirsung and Santorini), blood supply, islets of Langerhans, acinar cells, pancreatic enzymes (amylase, lipase, proteases), bicarbonate secretion, and hormonal regulation by insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. Emphasis is on drug-related physiology, enzyme activation (trypsinogen), diagnostic markers and common pathologies like pancreatitis and diabetes. This focused primer uses high-yield keywords for exam prep and pharmacy practice. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which embryologic origin gives rise to the pancreas?
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Ectoderm
- Neural crest
Correct Answer: Endoderm
Q2. The main pancreatic duct that drains most of the pancreas is called:
- Wirsung duct
- Santorini duct
- Cystic duct
- Common hepatic duct
Correct Answer: Wirsung duct
Q3. Which artery primarily supplies the body and tail of the pancreas?
- Splenic artery
- Gastroduodenal artery
- Superior mesenteric artery
- Proper hepatic artery
Correct Answer: Splenic artery
Q4. The exocrine pancreas secretes pancreatic juice rich in which of the following?
- Digestive enzymes and bicarbonate
- Insulin and glucagon
- Cholecystokinin and secretin
- Hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor
Correct Answer: Digestive enzymes and bicarbonate
Q5. Which cells in the pancreas are responsible for producing insulin?
- Beta cells of islets
- Alpha cells of islets
- Acinar cells
- Ductal epithelial cells
Correct Answer: Beta cells of islets
Q6. Trypsinogen is activated to trypsin by which intestinal enzyme?
- Enterokinase (enteropeptidase)
- Amylase
- Lipase
- Pepsin
Correct Answer: Enterokinase (enteropeptidase)
Q7. What is the primary physiologic stimulus for bicarbonate release from pancreatic ductal cells?
- Secretin
- Cholecystokinin (CCK)
- Gastrin
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
Correct Answer: Secretin
Q8. The majority cell type in pancreatic acini that synthesizes digestive enzymes is called:
- Acinar cell
- Ductal cell
- Alpha cell
- Stellate cell
Correct Answer: Acinar cell
Q9. Which pancreatic hormone raises blood glucose concentration?
- Glucagon
- Insulin
- Somatostatin
- Pancreatic polypeptide
Correct Answer: Glucagon
Q10. Centroacinar cells are located in which part of the pancreas?
- Pancreatic duct near the acinus
- Within islets of Langerhans
- Surface capsule of pancreas
- Tail lymphatic tissue
Correct Answer: Pancreatic duct near the acinus
Q11. Which enzyme is most specific and sensitive for diagnosing acute pancreatitis?
- Lipase
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Elastase
Correct Answer: Lipase
Q12. Pancreatic islets are highly vascularized mainly to facilitate:
- Rapid hormone release into bloodstream
- Secretion of digestive enzymes into ducts
- Immune surveillance only
- Lymph formation within the gland
Correct Answer: Rapid hormone release into bloodstream
Q13. Which cell type within islets secretes somatostatin?
- Delta cells
- Beta cells
- Alpha cells
- PP cells
Correct Answer: Delta cells
Q14. Pancreatic polypeptide primarily affects:
- Gastrointestinal motility and exocrine secretion
- Glucose uptake in muscle
- Renal sodium reabsorption
- Thyroid hormone release
Correct Answer: Gastrointestinal motility and exocrine secretion
Q15. Which duct is an accessory pancreatic duct that may drain into the minor duodenal papilla?
- Santorini duct
- Wirsung duct
- Cystic duct
- Hepatopancreatic ampulla
Correct Answer: Santorini duct
Q16. Activation of pancreatic zymogens within the pancreas leads to which condition?
- Acute pancreatitis
- Chronic hepatitis
- Gallstones
- Peptic ulcer disease
Correct Answer: Acute pancreatitis
Q17. SPINK1 is a pancreatic trypsin inhibitor important for:
- Preventing premature trypsin activation
- Stimulating insulin secretion
- Enhancing lipase activity
- Transporting bicarbonate
Correct Answer: Preventing premature trypsin activation
Q18. Which nerve provides parasympathetic stimulation to pancreatic secretion?
- Vagus nerve
- Phrenic nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
Correct Answer: Vagus nerve
Q19. The exocrine secretion of pancreatic enzymes is primarily stimulated by which hormone?
- Cholecystokinin (CCK)
- Insulin
- Secretin
- Glucagon
Correct Answer: Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Q20. Which of the following enzymes is secreted in active form from the pancreas?
- Lipase
- Trypsinogen
- Chymotrypsinogen
- Proelastase
Correct Answer: Lipase
Q21. The islets of Langerhans compose approximately what percentage of pancreatic mass?
- 1–2%
- 20–25%
- 50–60%
- 10–15%
Correct Answer: 1–2%
Q22. Which pancreatic enzyme digests triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids?
- Pancreatic lipase
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Carboxypeptidase
Correct Answer: Pancreatic lipase
Q23. Fecal elastase is used clinically to assess:
- Exocrine pancreatic function
- Endocrine pancreatic function
- Hepatic synthetic function
- Renal filtration rate
Correct Answer: Exocrine pancreatic function
Q24. Which of the following is a zymogen produced by the pancreas?
- Trypsinogen
- Amylase (active)
- Lipase (active)
- Insulin
Correct Answer: Trypsinogen
Q25. The hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater) is formed by union of the common bile duct and:
- Main pancreatic duct (Wirsung)
- Accessory pancreatic duct (Santorini)
- Cystic duct
- Hepatic artery
Correct Answer: Main pancreatic duct (Wirsung)
Q26. Which cell type in islets secretes glucagon?
- Alpha cells
- Beta cells
- Delta cells
- Acinar cells
Correct Answer: Alpha cells
Q27. Chronic pancreatitis commonly leads to which long-term consequence?
- Exocrine insufficiency and malabsorption
- Hyperthyroidism
- Increased bile production
- Enhanced insulin secretion
Correct Answer: Exocrine insufficiency and malabsorption
Q28. Which diagnostic imaging technique visualizes pancreatic ducts noninvasively?
- MRCP (Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography)
- Plain abdominal X-ray
- DEXA scan
- Bone scintigraphy
Correct Answer: MRCP (Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography)
Q29. Insulin promotes which of the following actions in peripheral tissues?
- Glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis
- Gluconeogenesis in the liver
- Lipolysis in adipose tissue
- Protein catabolism
Correct Answer: Glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis
Q30. Which cells form the majority of the exocrine pancreas?
- Acinar cells
- Alpha cells
- Beta cells
- Delta cells
Correct Answer: Acinar cells
Q31. Activation of trypsin in the small intestine primarily occurs at which duodenal structure?
- Brush border via enteropeptidase
- Major duodenal papilla secretion
- Pancreatic ductal epithelium
- Gastric antrum
Correct Answer: Brush border via enteropeptidase
Q32. Which pancreatic hormone inhibits both insulin and glucagon secretion?
- Somatostatin
- Pancreatic polypeptide
- Ghrelin
- Secretin
Correct Answer: Somatostatin
Q33. The tail of the pancreas commonly lies adjacent to which organ?
- Spleen
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Left kidney
Correct Answer: Spleen
Q34. Which blood test is most likely to remain elevated longer after acute pancreatitis?
- Lipase
- Amylase
- AST
- ALT
Correct Answer: Lipase
Q35. The bicarbonate-rich component of pancreatic juice helps to:
- Neutralize gastric acid in the duodenum
- Activate pancreatic zymogens
- Stimulate bile secretion
- Bind iron for absorption
Correct Answer: Neutralize gastric acid in the duodenum
Q36. In cystic fibrosis, pancreatic exocrine insufficiency occurs primarily due to:
- Thick secretions obstructing ducts
- Autoimmune destruction of islets
- Excess insulin production
- Hyperplasia of acinar cells
Correct Answer: Thick secretions obstructing ducts
Q37. Which enzyme class secreted by pancreas assists in starch digestion?
- Amylase
- Lipase
- Peptidase
- Nuclease
Correct Answer: Amylase
Q38. Pancreatic ductal cells secrete bicarbonate in exchange for which ion via transporters?
- Chloride (Cl–)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Potassium (K+)
- Calcium (Ca2+)
Correct Answer: Chloride (Cl–)
Q39. Which pancreatic enzyme hydrolyzes peptide bonds at the carboxyl terminus of proteins?
- Carboxypeptidase
- Trypsin
- Amylase
- Lipase
Correct Answer: Carboxypeptidase
Q40. The endocrine portion of pancreas mainly regulates:
- Glucose and metabolic homeostasis
- Bile acid synthesis
- Gastric acid secretion
- Renal blood flow
Correct Answer: Glucose and metabolic homeostasis
Q41. What is the anatomical relation of the pancreas to the peritoneum?
- Retroperitoneal (except tail)
- Intraperitoneal entirely
- Subperitoneal
- Supraperitoneal only
Correct Answer: Retroperitoneal (except tail)
Q42. Which of the following is NOT typically secreted by pancreatic acinar cells?
- Insulin
- Amylase
- Trypsinogen
- Lipase
Correct Answer: Insulin
Q43. The main mechanism by which CCK stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion is via:
- CCK receptors on acinar cells and vagal pathways
- Direct stimulation of ductal bicarbonate secretion only
- Binding to insulin receptors
- Inhibiting secretin release
Correct Answer: CCK receptors on acinar cells and vagal pathways
Q44. Which protein-storage organelle in acinar cells contains digestive zymogens?
- Zymogen granules
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes only
- Ribosomes
Correct Answer: Zymogen granules
Q45. Pancreatic carcinoma most commonly arises from which cells?
- Ductal epithelial cells (adenocarcinoma)
- Islet beta cells
- Acinar cells (most common)
- Stromal fibroblasts
Correct Answer: Ductal epithelial cells (adenocarcinoma)
Q46. The regulatory peptide that stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion in response to fats and proteins in the duodenum is:
- Cholecystokinin (CCK)
- Secretin
- Gastrin
- Motilin
Correct Answer: Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Q47. Which laboratory value is more specific for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency than serum amylase?
- Fecal elastase
- Serum bilirubin
- Serum albumin
- Urine ketones
Correct Answer: Fecal elastase
Q48. Which ion channel activity in ductal cells is essential for bicarbonate secretion?
- CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator)
- Voltage-gated calcium channel
- Sodium channel ENaC
- Proton pump H+/K+ ATPase
Correct Answer: CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator)
Q49. Which statement best describes pancreatic blood drainage?
- Pancreatic veins drain into the portal vein via tributaries
- Pancreatic veins drain directly to the systemic circulation bypassing the liver
- Pancreas has no venous drainage
- Pancreatic lymph drains into renal veins
Correct Answer: Pancreatic veins drain into the portal vein via tributaries
Q50. Which therapeutic enzyme replacement is used for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in clinical practice?
- Pancrelipase
- Insulin glargine
- Metformin
- Somatostatin analog
Correct Answer: Pancrelipase

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com