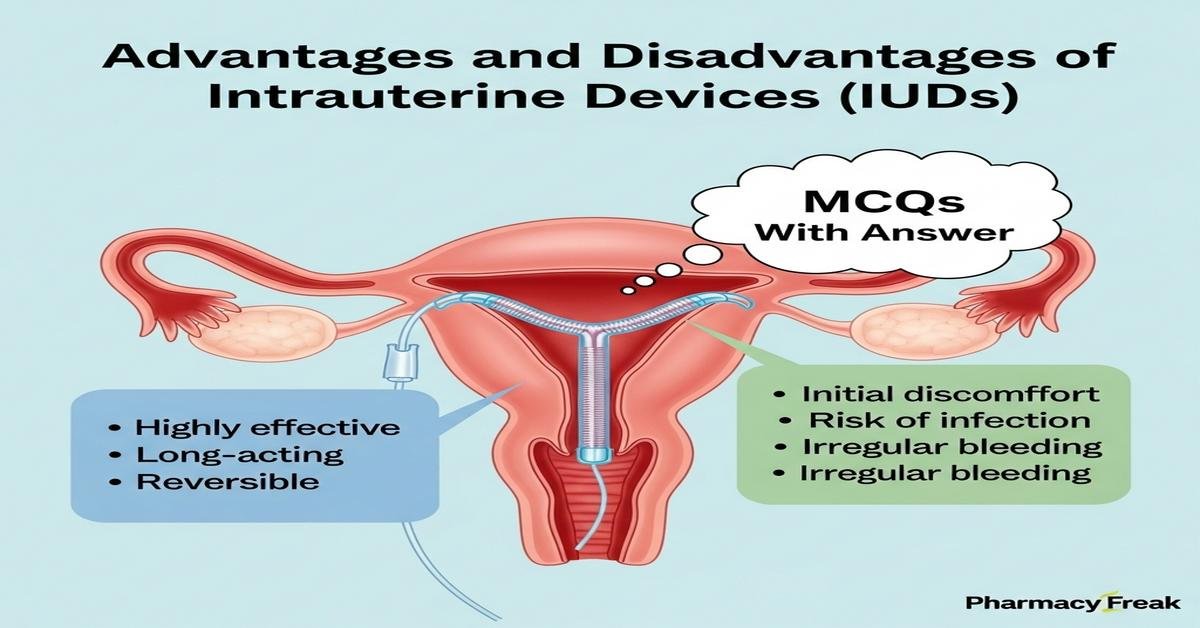
Introduction: Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are long-acting reversible contraceptives widely used in clinical practice. This introduction reviews advantages and disadvantages of intrauterine devices, including copper IUDs and levonorgestrel intrauterine systems (LNG-IUS). Key topics cover mechanisms of action, efficacy (failure rates <1%), duration of use, side effects such as heavy bleeding or amenorrhea, insertion and removal considerations, contraindications (e.g., active pelvic infection, copper-related disorders), complications like expulsion and uterine perforation, and counseling points for B.Pharm students. Understanding pharmacology, device types (Cu-IUD, LNG-IUS), and clinical implications enhances patient counselling and safe use. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which primary mechanism best describes how a copper IUD prevents pregnancy?
- Systemic ovulation suppression via hormonal feedback
- Copper-induced local inflammatory reaction toxic to sperm and ova
- Thickening of cervical mucus to block sperm entry
- Endometrial decidualization preventing implantation
Correct Answer: Copper-induced local inflammatory reaction toxic to sperm and ova
Q2. Which mechanism is most characteristic of levonorgestrel intrauterine systems (LNG-IUS)?
- Systemic estrogen replacement
- Local progestin effect causing endometrial atrophy and thickened cervical mucus
- Release of copper ions causing spermicidal action
- Mechanical barrier preventing sperm transport
Correct Answer: Local progestin effect causing endometrial atrophy and thickened cervical mucus
Q3. Which of the following is a major advantage of IUDs compared with short-acting methods?
- Higher daily adherence requirements
- Long-term reversible contraception with low maintenance
- Immediate immunity to STIs
- Guaranteed prevention of all ectopic pregnancies
Correct Answer: Long-term reversible contraception with low maintenance
Q4. Which is a common disadvantage specifically associated with copper IUDs?
- Decreased menstrual bleeding
- Increased menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea
- Significant systemic hormonal side effects
- High risk of breast tenderness
Correct Answer: Increased menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea
Q5. What is the approximate typical-use failure rate of modern IUDs?
- 10–15% per year
- 5–7% per year
- Less than 1% per year
- 20–25% per year
Correct Answer: Less than 1% per year
Q6. Which patient condition is a contraindication to copper IUD use?
- History of cesarean section
- Wilson’s disease or copper allergy
- Nulliparity in young women
- Controlled hypertension
Correct Answer: Wilson’s disease or copper allergy
Q7. Which of the following is a recognized benefit of LNG-IUS beyond contraception?
- Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Reliable prevention of urinary tract infections
- Permanent sterilization
- Prevention of osteoporosis
Correct Answer: Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
Q8. Which complication, though rare, is a serious risk during IUD insertion?
- Uterine perforation
- Systemic hormonal thrombosis
- Immediate pregnancy in all cases
- Chronic kidney disease
Correct Answer: Uterine perforation
Q9. Which factor increases the risk of IUD expulsion?
- Insertion >6 weeks postpartum
- Nulliparity only
- Heavy menses and younger age
- Using LNG-IUS rather than copper
Correct Answer: Heavy menses and younger age
Q10. How does LNG-IUS primarily reduce menstrual bleeding?
- Systemic suppression of ovarian estrogen production
- Local endometrial suppression and glandular atrophy
- Mechanical entrapment of blood in the uterine cavity
- Induction of hyperplasia to stabilize endometrium
Correct Answer: Local endometrial suppression and glandular atrophy
Q11. Which IUD is commonly known by the brand name ParaGard?
- Levonorgestrel IUS (Mirena)
- Copper T 380A
- Progesterone-only oral pill
- Combined hormonal ring
Correct Answer: Copper T 380A
Q12. For emergency contraception, which IUD is recommended when immediate long-term contraception is desired?
- Copper IUD inserted within 5 days after unprotected intercourse
- LNG-IUS inserted one month later
- Combined oral contraceptive emergency regimen only
- No IUD is effective as emergency contraception
Correct Answer: Copper IUD inserted within 5 days after unprotected intercourse
Q13. Which statement about IUD-related pelvic infection (PID) risk is correct?
- IUDs cause chronic PID in all users
- PID risk is highest in the first 20 days after insertion
- Infection risk is unrelated to STI exposure
- Once an IUD is in place, PID risk is permanently elevated
Correct Answer: PID risk is highest in the first 20 days after insertion
Q14. Which is a systemic effect typically associated with LNG-IUS?
- High plasma levonorgestrel levels causing acne in most users
- Minimal systemic hormonal effects due to local release
- Significant suppression of bone mineral density
- Systemic estrogenic side effects
Correct Answer: Minimal systemic hormonal effects due to local release
Q15. Which patient counseling point is essential before IUD insertion?
- No need to screen for STI history
- Inform about signs of infection, expulsion, and when to seek care
- Assure the IUD prevents all sexually transmitted infections
- Advise that fertility will be permanently lost
Correct Answer: Inform about signs of infection, expulsion, and when to seek care
Q16. Which IUD would be most appropriate for a woman seeking contraception plus treatment for heavy bleeding?
- Copper T 380A
- Combined oral contraceptive pill
- Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS)
- Condoms only
Correct Answer: Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS)
Q17. Which is a recognized disadvantage of LNG-IUS in the initial months after insertion?
- Immediate permanent amenorrhea in all users
- Irregular spotting and unpredictable bleeding
- Severe systemic estrogen excess
- Guaranteed infertility for 2 years
Correct Answer: Irregular spotting and unpredictable bleeding
Q18. Which laboratory or clinical condition is a contraindication for LNG-IUS?
- Current pregnancy and untreated pelvic infection
- Well-controlled hypothyroidism
- Desire for future fertility within 1 month
- Previous uncomplicated vaginal delivery
Correct Answer: Current pregnancy and untreated pelvic infection
Q19. Regarding fertility after IUD removal, which statement is accurate?
- Fertility remains impaired for several years after removal
- Fertility typically returns quickly after IUD removal
- Pregnancy is impossible after removal of LNG-IUS
- Removal always requires surgical intervention under general anesthesia
Correct Answer: Fertility typically returns quickly after IUD removal
Q20. What is a pharmacological reason copper IUDs are effective without hormones?
- Copper provides systemic contraceptive hormone levels
- Copper ions create a spermicidal environment in the uterus
- Copper physically blocks the cervical os
- Copper stimulates ovulation inhibition centrally
Correct Answer: Copper ions create a spermicidal environment in the uterus
Q21. Which of the following is TRUE about IUD use in breastfeeding women?
- LNG-IUS is contraindicated during breastfeeding
- Copper IUD can generally be used and LNG-IUS is acceptable after immediate postpartum period per guidelines
- IUDs cause failure of lactation in all cases
- IUDs must be avoided for at least 2 years postpartum
Correct Answer: Copper IUD can generally be used and LNG-IUS is acceptable after immediate postpartum period per guidelines
Q22. Which effect is relatively more associated with copper IUDs than with LNG-IUS?
- Reduction in menstrual blood loss
- Increased menstrual bleeding and cramping
- Endometrial thinning
- Therapeutic effect on menorrhagia
Correct Answer: Increased menstrual bleeding and cramping
Q23. What is the recommended action if an IUD string is not palpable and pregnancy is suspected?
- Assume device is fine and start oral contraceptives
- Perform pregnancy test and pelvic ultrasound to locate device
- Immediately insert a second IUD without evaluation
- Wait six months and reassess
Correct Answer: Perform pregnancy test and pelvic ultrasound to locate device
Q24. Which is a pharmacoeconomic advantage of IUDs?
- High ongoing medication costs making them unaffordable
- Cost-effectiveness due to long duration and low failure rates
- Require daily pharmacy visits increasing costs
- Not covered by health systems due to short-term use
Correct Answer: Cost-effectiveness due to long duration and low failure rates
Q25. Which adverse outcome is more commonly associated with pregnancy while using an IUD?
- Increased likelihood of normal intrauterine pregnancy without complications
- Higher relative risk of ectopic pregnancy among pregnancies that occur
- Guaranteed miscarriage in all cases
- No risk of infection
Correct Answer: Higher relative risk of ectopic pregnancy among pregnancies that occur
Q26. Which feature differentiates hormonal IUS (LNG-IUS) from copper IUD in systemic hormone exposure?
- LNG-IUS provides high systemic estrogen levels
- LNG-IUS releases low-dose progestin locally with minimal systemic exposure
- Copper IUD delivers systemic levonorgestrel
- Both devices deliver identical systemic hormone levels
Correct Answer: LNG-IUS releases low-dose progestin locally with minimal systemic exposure
Q27. When counseling adolescents about IUDs, which statement is correct?
- IUDs are unsuitable for nulliparous adolescents
- IUDs can be a safe, effective option for adolescents with appropriate counseling
- IUD insertion is always contraindicated under age 21
- IUDs invariably cause infertility in adolescents
Correct Answer: IUDs can be a safe, effective option for adolescents with appropriate counseling
Q28. Which monitoring or follow-up is typically advised after IUD insertion?
- No follow-up is ever needed
- Check strings at 4–6 weeks and seek care if pain, fever, or abnormal bleeding occur
- Hospitalization for one week post-insertion
- Repeat insertion every month
Correct Answer: Check strings at 4–6 weeks and seek care if pain, fever, or abnormal bleeding occur
Q29. Which statement about drug interactions with LNG-IUS is most accurate?
- CYP inducers significantly reduce the local efficacy of LNG-IUS in the uterus
- Systemic drug interactions are minimal due to low systemic levonorgestrel levels
- Antibiotics always render LNG-IUS ineffective
- All enzyme-inducing drugs completely negate IUD function
Correct Answer: Systemic drug interactions are minimal due to low systemic levonorgestrel levels
Q30. Which is an appropriate reason to remove an IUD promptly?
- New desire for long-term contraception continuation
- Confirmed intrauterine pregnancy or severe pelvic infection
- Mild spotting in the first week after insertion
- Routine change of IUD color
Correct Answer: Confirmed intrauterine pregnancy or severe pelvic infection

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com