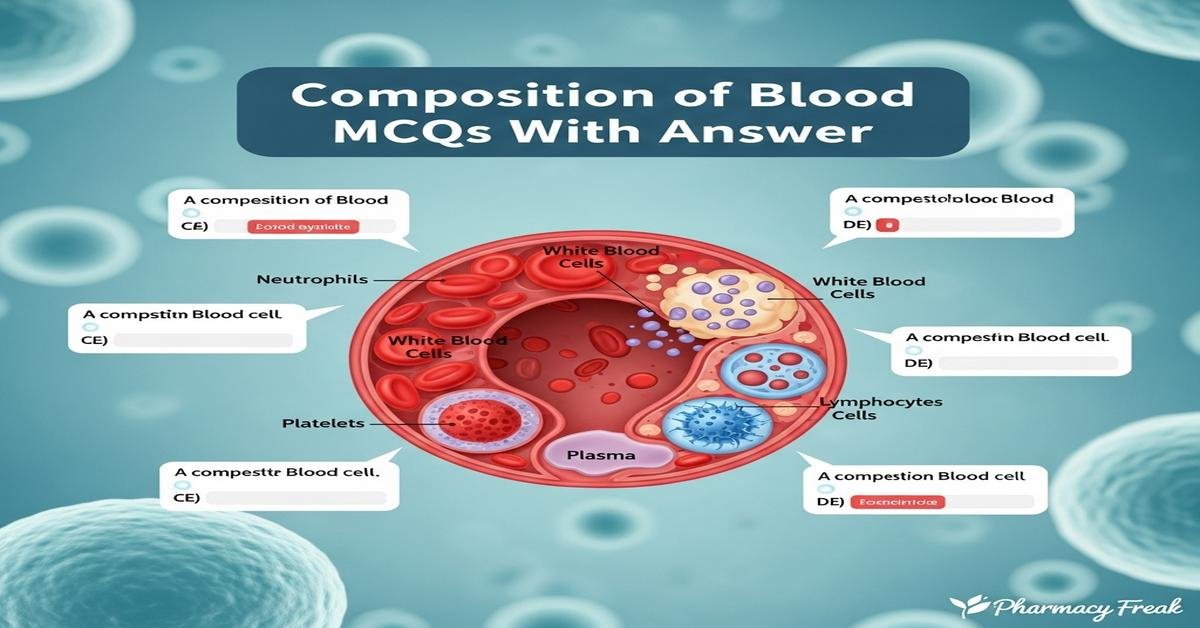
Introduction: The “Composition of blood MCQs With Answer” is an essential revision tool for B. Pharm students preparing for exams in physiology, pharmacology, and clinical lab sciences. This concise guide covers plasma components, formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), plasma proteins, electrolytes, hemoglobin structure, blood groups, and clinically relevant parameters like hematocrit, MCV, and ESR. Emphasis on pharmacological relevance—such as drug binding to albumin, anticoagulants used in labs, and transfusion basics—helps bridge theory with practice. Clear MCQs with explanations improve recall and exam readiness. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What percentage of total blood volume is normally occupied by red blood cells (hematocrit) in healthy adult males?
- 20–30%
- 35–45%
- 40–54%
- 60–70%
Correct Answer: 40–54%
Q2. Which plasma protein is primarily responsible for maintaining colloid oncotic pressure and binding many drugs?
- Fibrinogen
- Albumin
- Gamma globulin
- Transferrin
Correct Answer: Albumin
Q3. Which of the following is NOT a formed element of blood?
- Erythrocyte
- Leukocyte
- Platelet
- Glucose
Correct Answer: Glucose
Q4. Plasma differs from serum in that plasma contains which component that serum lacks?
- Electrolytes
- Fibrinogen
- Albumin
- Glucose
Correct Answer: Fibrinogen
Q5. Which cell type is the most abundant white blood cell in normal peripheral blood?
- Lymphocyte
- Monocyte
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
Correct Answer: Neutrophil
Q6. Hemoglobin molecule includes which prosthetic group responsible for oxygen binding?
- Porphyrin ring of bilirubin
- Heme
- Globulin peptide chain
- Ferritin core
Correct Answer: Heme
Q7. Which form represents the majority of carbon dioxide transport in blood?
- Dissolved CO2 in plasma
- Carbaminohemoglobin
- Bicarbonate (HCO3−)
- Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Correct Answer: Bicarbonate (HCO3−)
Q8. Which anticoagulant chelates calcium and is commonly used for complete blood counts (CBC)?
- Heparin
- EDTA
- Sodium citrate
- Warfarin
Correct Answer: EDTA
Q9. Albumin is synthesized mainly in which organ?
- Spleen
- Liver
- Bone marrow
- Kidney
Correct Answer: Liver
Q10. Normal adult hemoglobin A (HbA) composition consists of which globin chains?
- α2β2
- α2γ2
- α2δ2
- β4
Correct Answer: α2β2
Q11. Which plasma protein plays a central role in blood clot formation?
- Albumin
- Fibrinogen
- Transferrin
- Complement C3
Correct Answer: Fibrinogen
Q12. The buffy coat in centrifuged blood primarily contains which components?
- Plasma proteins
- Erythrocytes
- Leukocytes and platelets
- Serum and fibrin
Correct Answer: Leukocytes and platelets
Q13. Which electrolyte is most abundant in plasma and is critical for extracellular osmolarity?
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Sodium
- Magnesium
Correct Answer: Sodium
Q14. Erythropoietin primarily stimulates which process?
- Leukocyte differentiation
- Platelet aggregation
- Red blood cell production (erythropoiesis)
- Plasma protein synthesis
Correct Answer: Red blood cell production (erythropoiesis)
Q15. Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) helps classify anemia by indicating:
- Average hemoglobin concentration per RBC
- Average RBC size
- Platelet size distribution
- Plasma viscosity
Correct Answer: Average RBC size
Q16. Which white blood cell is primarily associated with allergic responses and parasitic infections?
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
- Lymphocyte
Correct Answer: Eosinophil
Q17. In adult humans, active hematopoiesis in bone marrow occurs mainly in:
- Long bone diaphyses
- Flat bones like pelvis and vertebrae
- Cartilage
- Spleen
Correct Answer: Flat bones like pelvis and vertebrae
Q18. Which laboratory test assesses the extrinsic coagulation pathway?
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
- Prothrombin time (PT)
- Bleeding time
- Thrombin time (TT)
Correct Answer: Prothrombin time (PT)
Q19. Which blood group antigen presence defines Rh positive status?
- Antigen A
- Antigen B
- Rh D antigen
- H antigen
Correct Answer: Rh D antigen
Q20. A common clinical consequence of hypoalbuminemia is:
- Increased oncotic pressure
- Edema due to decreased colloid oncotic pressure
- Hyperviscosity syndrome
- Enhanced clotting
Correct Answer: Edema due to decreased colloid oncotic pressure
Q21. Which molecule accelerates conversion of CO2 and water to bicarbonate in red blood cells?
- Hemoglobin
- Carbonic anhydrase
- Phosphofructokinase
- Aldolase
Correct Answer: Carbonic anhydrase
Q22. Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) reflects:
- Average hemoglobin per red cell
- Average red cell volume
- Hemoglobin concentration per unit volume of packed RBCs
- Total plasma hemoglobin
Correct Answer: Hemoglobin concentration per unit volume of packed RBCs
Q23. Which leukocyte matures into macrophages in tissues?
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- Monocyte
- Neutrophil
Correct Answer: Monocyte
Q24. Which plasma protein fraction contains most immunoglobulins?
- Albumin fraction
- Gamma globulin fraction
- Alpha-1 globulin fraction
- Fibrinogen fraction
Correct Answer: Gamma globulin fraction
Q25. Platelet primary function in hemostasis is to:
- Form enzymatic clotting factors
- Initiate the fibrinolytic system
- Adhere to damaged endothelium and form primary plug
- Carry oxygen
Correct Answer: Adhere to damaged endothelium and form primary plug
Q26. Which of the following conditions would increase erythropoietin secretion?
- Hyperoxia
- Anemia or hypoxia
- High plasma albumin
Correct Answer: Anemia or hypoxia
Q27. The ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is increased primarily by higher levels of which plasma proteins?
- Albumin
- Acute phase proteins like fibrinogen
- Transferrin
- Lipoproteins
Correct Answer: Acute phase proteins like fibrinogen
Q28. Which parameter is most directly measured by a hemocytometer or automated analyzer for red cell count?
- Hemoglobin concentration
- Number of RBCs per unit volume
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
- Reticulocyte count percentage
Correct Answer: Number of RBCs per unit volume
Q29. Which ion is primarily located intracellularly and critical for membrane potential?
- Sodium (Na+)
- Chloride (Cl−)
- Potassium (K+)
- Calcium (Ca2+)
Correct Answer: Potassium (K+)
Q30. In blood typing, a person with type O blood has which antigens on RBCs?
- A antigen only
- B antigen only
- Both A and B antigens
- Neither A nor B antigens
Correct Answer: Neither A nor B antigens
Q31. Which of the following is the normal approximate platelet count range in healthy adults?
- 10,000–50,000/mm3
- 150,000–450,000/mm3
- 500,000–1,000,000/mm3
- 1,000–5,000/mm3
Correct Answer: 150,000–450,000/mm3
Q32. Which protein transports iron in plasma?
- Ferritin
- Hemosiderin
- Transferrin
- Albumin
Correct Answer: Transferrin
Q33. Which factor is a major determinant of blood viscosity?
- Plasma sodium concentration
- Hematocrit
- Plasma glucose only
- Body temperature alone
Correct Answer: Hematocrit
Q34. A reticulocyte count is useful to assess which clinical process?
- Liver synthetic function
- Bone marrow red cell production (response to anemia)
- Platelet aggregation
- White cell differential
Correct Answer: Bone marrow red cell production (response to anemia)
Q35. Which laboratory anticoagulant is commonly used for coagulation studies like PT and aPTT?
- EDTA
- Heparin
- Sodium citrate
- Formalin
Correct Answer: Sodium citrate
Q36. The Bohr effect describes how which factor affects hemoglobin oxygen affinity?
- Increased pH increases O2 release
- Increased CO2 and decreased pH reduce O2 affinity
- Higher temperature increases O2 affinity
- Presence of 2,3-BPG increases O2 affinity
Correct Answer: Increased CO2 and decreased pH reduce O2 affinity
Q37. Which leukocyte is the major producer of antibodies?
- Neutrophil
- B-lymphocyte (plasma cell)
- Monocyte
- Eosinophil
Correct Answer: B-lymphocyte (plasma cell)
Q38. Which measurement is directly decreased in iron deficiency anemia?
- Platelet count
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
- Serum potassium
- Serum sodium
Correct Answer: Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Q39. Hemolytic transfusion reactions are most commonly due to incompatibility of which blood group system?
- MN system
- ABO system
- Kell system only
- Duffy system only
Correct Answer: ABO system
Q40. Which plasma protein fraction is increased during chronic inflammation and includes C-reactive protein?
- Albumin
- Acute phase proteins in alpha and beta globulin fractions
- Gamma globulins only
- Fibrinogen only
Correct Answer: Acute phase proteins in alpha and beta globulin fractions
Q41. Which component of hemoglobin contains the central iron atom?
- Globin chain
- Heme
- Polypeptide tail
- Carboxyl terminal
Correct Answer: Heme
Q42. Which test is prolonged in vitamin K deficiency or warfarin therapy?
- aPTT
- Bleeding time
- Prothrombin time (PT)
- Platelet count
Correct Answer: Prothrombin time (PT)
Q43. What is the principal effect of increased 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) in red blood cells?
- Increases hemoglobin affinity for oxygen
- Decreases hemoglobin affinity for oxygen promoting O2 release
- Converts hemoglobin to methemoglobin
- Inhibits erythropoiesis
Correct Answer: Decreases hemoglobin affinity for oxygen promoting O2 release
Q44. Which white blood cell contains histamine and is involved in immediate hypersensitivity reactions?
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
- Monocyte
Correct Answer: Basophil
Q45. Which parameter best reflects oxygen-carrying capacity of blood?
- Plasma sodium concentration
- Serum albumin level
- Hemoglobin concentration
- Total leukocyte count
Correct Answer: Hemoglobin concentration
Q46. Which molecule serves as the major intracellular buffer in red blood cells?
- Plasma albumin
- Hemoglobin
- Transferrin
- Fibrinogen
Correct Answer: Hemoglobin
Q47. Which lab parameter assesses platelet function rather than platelet number?
- Platelet count
- Bleeding time
- Prothrombin time
- Plasma fibrinogen concentration
Correct Answer: Bleeding time
Q48. Which molecule is the acute oxygen-binding form found in fetal blood with higher O2 affinity than adult HbA?
- HbA2
- HbF (fetal hemoglobin)
- Methemoglobin
- Sickle hemoglobin (HbS)
Correct Answer: HbF (fetal hemoglobin)
Q49. In clinical pharmacology, hypoalbuminemia can alter drug action primarily by affecting:
- Renal secretion of drugs
- Extent of drug binding and free drug concentration
- Drug pH only
- Hepatic metabolism exclusively
Correct Answer: Extent of drug binding and free drug concentration
Q50. Which process removes fibrin clots and restores vessel patency?
- Coagulation cascade
- Platelet aggregation
- Fibrinolysis mediated by plasmin
- Formation of thromboxane A2
Correct Answer: Fibrinolysis mediated by plasmin

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com