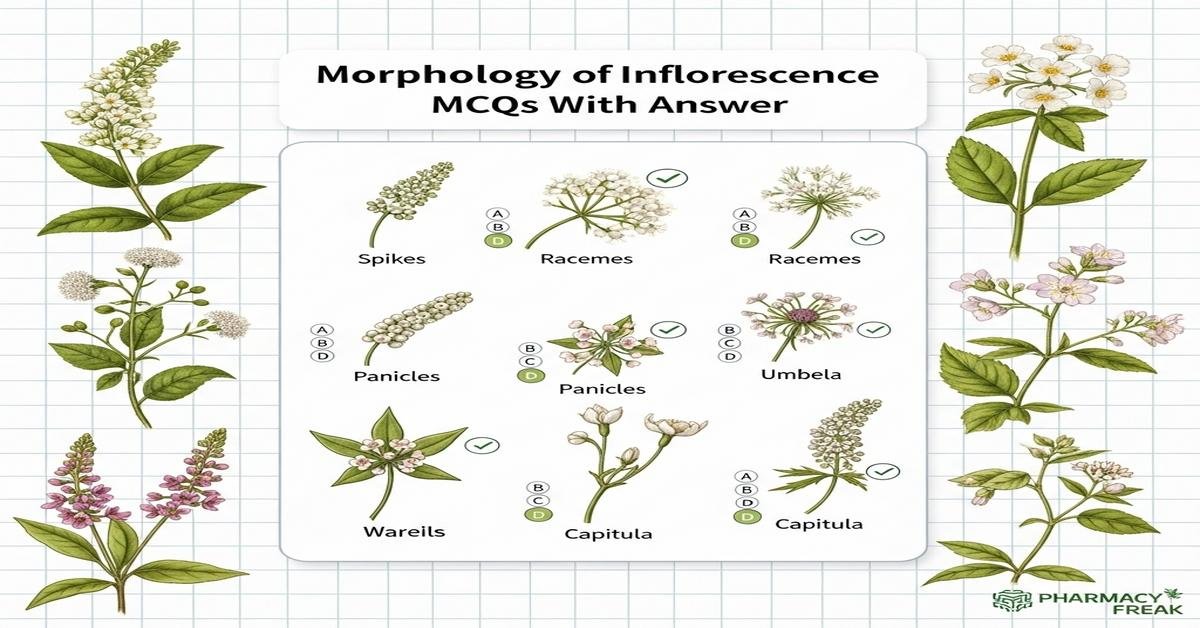
Morphology of inflorescence MCQs With Answer is an essential topic for B. Pharm students studying pharmacognosy and medicinal plant identification. This concise guide explores structural features—peduncle, pedicel, bracts, rachis—and key inflorescence types such as racemose, cymose, umbel, panicle, spike, capitulum and spadix. Understanding these forms aids accurate botanical identification, quality control of herbal drugs, and interpretation of taxonomic keys. Questions focus on diagnostic characters, developmental patterns (determinate vs indeterminate), and practical examples from medicinal plants, preparing you for exams and lab work. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is an inflorescence?
- A single flower on a stem
- A cluster or arrangement of flowers on a plant
- A type of root modification
- A vegetative branching pattern
Correct Answer: A cluster or arrangement of flowers on a plant
Q2. What is the peduncle in an inflorescence?
- The main stalk supporting the entire inflorescence
- An individual flower stalk within the inflorescence
- A small bract subtending a flower
- The axis bearing ovules
Correct Answer: The main stalk supporting the entire inflorescence
Q3. What is a pedicel?
- The stalk of the whole inflorescence
- The stalk supporting an individual flower within an inflorescence
- The central axis of a compound leaf
- A modified root
Correct Answer: The stalk supporting an individual flower within an inflorescence
Q4. Which statement correctly distinguishes racemose from cymose inflorescence?
- Racemose is determinate; cymose is indeterminate
- Racemose is indeterminate; cymose is determinate
- Both are always terminal on the shoot
- Both have pedicellate flowers only
Correct Answer: Racemose is indeterminate; cymose is determinate
Q5. Which of the following is a typical example of a raceme?
- Wheat (Triticum)
- Mustard (Brassica)
- Sunflower (Helianthus)
- Arum (Arum)
Correct Answer: Mustard (Brassica)
Q6. Which feature best describes a spike?
- Flowers on long pedicels
- Flowers sessile (without pedicels) on a central axis
- A single terminal flower
- Compound umbel of umbels
Correct Answer: Flowers sessile (without pedicels) on a central axis
Q7. Which plant shows a spike inflorescence?
- Rice (Oryza sativa)
- Wheat (Triticum)
- Coriander (Coriandrum sativum)
- Sunflower (Helianthus)
Correct Answer: Wheat (Triticum)
Q8. How is a panicle defined?
- A simple unbranched inflorescence with sessile flowers
- A branched indeterminate inflorescence; a compound raceme
- A determinate single-flowered inflorescence
- A group of flowers arising from one point
Correct Answer: A branched indeterminate inflorescence; a compound raceme
Q9. Which crop has a panicle type inflorescence?
- Wheat (Triticum)
- Rice (Oryza sativa)
- Sunflower (Helianthus)
- Mustard (Brassica)
Correct Answer: Rice (Oryza sativa)
Q10. What characterizes an umbel?
- Flowers arranged along a spike with sessile flowers
- Pedicels of almost equal length arising from a common point
- Branched raceme with alternating branches
- A single large flower with many petals
Correct Answer: Pedicels of almost equal length arising from a common point
Q11. Which plant exemplifies an umbel inflorescence?
- Coriander (Coriandrum sativum)
- Arum (Arum)
- Sunflower (Helianthus)
- Wheat (Triticum)
Correct Answer: Coriander (Coriandrum sativum)
Q12. What is a capitulum (head) inflorescence?
- A loose raceme with long pedicels
- A compact structure of many small sessile florets on a common receptacle
- An underground floral structure
- A single flower with fused petals
Correct Answer: A compact structure of many small sessile florets on a common receptacle
Q13. Which family is typically associated with the capitulum?
- Poaceae
- Asteraceae
- Fabaceae
- Apiaceae
Correct Answer: Asteraceae
Q14. Which statement describes a corymb?
- Flowers borne on a common point like an umbrella
- Outer flowers have longer pedicels so the inflorescence appears flat-topped
- All flowers are sessile on a swollen receptacle
- Inflorescence is strictly single-flowered
Correct Answer: Outer flowers have longer pedicels so the inflorescence appears flat-topped
Q15. What is a spadix?
- A solitary large petal in orchids
- A fleshy, thickened axis bearing small flowers, often enclosed by a spathe
- A type of raceme with long pedicels
- An underground inflorescence of bulbs
Correct Answer: A fleshy, thickened axis bearing small flowers, often enclosed by a spathe
Q16. What is an involucre?
- A type of seed coat
- A whorl or cluster of bracts subtending an inflorescence such as a capitulum
- An accessory root
- The ovary wall
Correct Answer: A whorl or cluster of bracts subtending an inflorescence such as a capitulum
Q17. Which inflorescence type is described as a catkin (ament)?
- A compact head with involucral bracts
- A pendulous or erect unisexual spike, often wind-pollinated
- A flat-topped cluster of pedicellate flowers
- A single terminal flower with showy petals
Correct Answer: A pendulous or erect unisexual spike, often wind-pollinated
Q18. What defines a monochasial cyme?
- Two lateral branches develop at each node
- One lateral branch continues growth at each node forming a zig-zag or helix
- All branches are equally developed to form a flat top
- Flowers are produced only at the base of the plant
Correct Answer: One lateral branch continues growth at each node forming a zig-zag or helix
Q19. What characterizes a dichasial cyme?
- Terminal flower opens last
- Two lateral branches develop from the node, each ending in a flower
- Flowers are always sessile
- Inflorescence is always indeterminate
Correct Answer: Two lateral branches develop from the node, each ending in a flower
Q20. What is a glomerule?
- A single large flower at the tip of a stem
- A dense cluster of sessile or subsessile flowers forming a ball-like head
- A long spike with spaced flowers
- An underground reproductive structure
Correct Answer: A dense cluster of sessile or subsessile flowers forming a ball-like head
Q21. Which inflorescence has pedicellate flowers along a central axis?
- Spike
- Raceme
- Capitulum
- Spadix
Correct Answer: Raceme
Q22. Which term correctly describes an indeterminate inflorescence?
- Terminal flower opens first, stopping axis growth
- Axial growth continues and terminal bud does not form a flower initially
- Flowers develop only below the soil
- All flowers open simultaneously and axis dies
Correct Answer: Axial growth continues and terminal bud does not form a flower initially
Q23. In determinate inflorescence which flower opens first?
- Basal flower
- Middle flower
- Terminal flower
- Topmost vegetative bud
Correct Answer: Terminal flower
Q24. What is a thyrse?
- A simple unbranched raceme with sessile flowers
- A mixed inflorescence with an indeterminate main axis and determinate lateral cymes
- A single large petaloid bract
- A compound umbel of umbels only
Correct Answer: A mixed inflorescence with an indeterminate main axis and determinate lateral cymes
Q25. What is a spathe?
- A bract or pair of bracts that encloses or subtends a spadix
- A floral nectary on the petals
- A modified root storing water
- The fruiting body of grasses
Correct Answer: A bract or pair of bracts that encloses or subtends a spadix
Q26. What is the role of the receptacle in an inflorescence?
- It bears and supports the floral organs and florets in composite heads
- It is the protective seed coat
- It produces pollen grains only
- It stores starch in underground stems
Correct Answer: It bears and supports the floral organs and florets in composite heads
Q27. Where is a bracteole located?
- At the base of the main stem
- On the pedicel near the flower, often subtending the flower
- Inside the ovary surrounding the ovule
- At the tip of the root
Correct Answer: On the pedicel near the flower, often subtending the flower
Q28. How does a rachis differ from a peduncle?
- Rachis is the main axis of a compound leaf; peduncle is a floral stalk only
- Rachis is the main axis of an inflorescence above the peduncle; peduncle is the stalk supporting the whole inflorescence
- Rachis is a root modification; peduncle is a leaf base
- They are synonymous botanical terms
Correct Answer: Rachis is the main axis of an inflorescence above the peduncle; peduncle is the stalk supporting the whole inflorescence
Q29. Which flowering sequence is typical of racemose (indeterminate) inflorescences?
- Basipetal (upper to lower)
- Acropetal (lower to upper)
- Random opening without order
- All flowers open simultaneously
Correct Answer: Acropetal (lower to upper)
Q30. Which flowering sequence is typical of cymose (determinate) inflorescences?
- Acropetal (lower to upper)
- Basipetal (upper to lower)
- Simultaneous opening from centre outward
- Flowers do not open in cymose types
Correct Answer: Basipetal (upper to lower)
Q31. What is a compound umbel?
- An umbel where each primary ray ends in a secondary umbel (umbellule)
- An umbel with only two flowers
- A spike condensed into a head
- A single flower with an umbrella-shaped bract
Correct Answer: An umbel where each primary ray ends in a secondary umbel (umbellule)
Q32. What term is used for the small individual flowers found in a capitulum?
- Peduncles
- Florets
- Strobili
- Catkins
Correct Answer: Florets
Q33. Which cyme type produces flowers in a helix on one side of the axis?
- Dichasial cyme
- Helicoid (a form of monochasial) cyme
- Compound umbel
- Panicle
Correct Answer: Helicoid (a form of monochasial) cyme
Q34. What is a scorpioid cyme?
- A cyme with opposite branches forming a zig-zag or scorpion tail pattern
- A single unbranched spike
- A dense head of sessile flowers
- A branched indeterminate raceme
Correct Answer: A cyme with opposite branches forming a zig-zag or scorpion tail pattern
Q35. What does “sessile flower” mean?
- Flower with a long conspicuous pedicel
- Flower without a pedicel, attached directly to the axis
- Flower located underground
- Flower that does not produce pollen
Correct Answer: Flower without a pedicel, attached directly to the axis
Q36. Why are bracts important in inflorescences?
- They are photosynthetic roots
- They often protect flower buds, attract pollinators, or form involucres
- They always contain nectar-producing glands
- They convert flowers into fruits
Correct Answer: They often protect flower buds, attract pollinators, or form involucres
Q37. Which structure subtends an individual flower?
- Rachis
- Bract
- Spathe
- Receptacle
Correct Answer: Bract
Q38. Which statement about indeterminate inflorescences is true?
- The terminal bud becomes a flower and stops growth immediately
- The terminal bud remains vegetative and axis growth may continue while flowers develop laterally
- Flowers open only once at the base
- They never bear more than three flowers
Correct Answer: The terminal bud remains vegetative and axis growth may continue while flowers develop laterally
Q39. Which inflorescence type is determinate?
- Racemose
- Cymose
- Panicle
- Spike
Correct Answer: Cymose
Q40. In Asteraceae, what separates the ray and disc florets?
- They are the same; no distinction exists
- Ray florets are peripheral and zygomorphic; disc florets are central and actinomorphic
- Ray florets are underground; disc florets are above ground
- Ray florets are male only and disc florets female only in all species
Correct Answer: Ray florets are peripheral and zygomorphic; disc florets are central and actinomorphic
Q41. Which description fits a capitulum’s floral arrangement?
- Single large tubular flower
- Many small, often sessile florets arranged on an expanded receptacle
- A long spike of alternate flowers on pedicels
- Flowers arranged in a regular spiral on bulbs
Correct Answer: Many small, often sessile florets arranged on an expanded receptacle
Q42. How does a panicle differ from a thyrse?
- Panicle has determinate laterals; thyrse has all indeterminate branches
- Panicle is a compound indeterminate inflorescence; thyrse has an indeterminate main axis with determinate lateral cymes
- They are identical terms for the same structure
- Thyrse is always single-flowered while panicle is compound
Correct Answer: Panicle is a compound indeterminate inflorescence; thyrse has an indeterminate main axis with determinate lateral cymes
Q43. What is a fascicle in inflorescence terminology?
- A small, tight cluster of flowers or leaves arising closely together
- A long pedunculate raceme
- An underground tuberous inflorescence
- A single terminal stamen
Correct Answer: A small, tight cluster of flowers or leaves arising closely together
Q44. Which of the following is a correct classification of cymose types?
- Racemose, racemoid, spike
- Dichasial, monochasial, polychasial
- Umbel, panicle, spike
- Pseudanthium, spadix, capitulum
Correct Answer: Dichasial, monochasial, polychasial
Q45. Which inflorescence is most commonly enclosed by a spathe?
- Capitulum
- Spadix
- Panicle
- Umbel
Correct Answer: Spadix
Q46. Which inflorescence term refers to flowers attached directly to a highly condensed axis forming a head?
- Raceme
- Capitulum
- Spikelet
- Rachilla
Correct Answer: Capitulum
Q47. Why is knowledge of inflorescence morphology important for B. Pharm students?
- It is irrelevant to pharmacognosy and drug standardization
- It aids in correct identification of medicinal plants, quality control and taxonomic keys for herbal drugs
- It only helps in animal anatomy studies
- It replaces the need to study phytochemistry
Correct Answer: It aids in correct identification of medicinal plants, quality control and taxonomic keys for herbal drugs
Q48. Which inflorescence type is particularly adapted to attract pollinators by forming a single large display?
- Spike
- Capitulum
- Simple raceme
- Sessile solitary flower
Correct Answer: Capitulum
Q49. What term describes a condensed raceme with sessile flowers forming a dense axis?
- Corymb
- Spike
- Compound umbel
- Monochasial cyme
Correct Answer: Spike
Q50. Which contrast correctly pairs flowering sequence with inflorescence type?
- Racemose—basipetal; Cymose—acropetal
- Racemose—acropetal; Cymose—basipetal
- Both racemose and cymose show simultaneous flowering only
- Neither shows any predictable flowering sequence
Correct Answer: Racemose—acropetal; Cymose—basipetal

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com