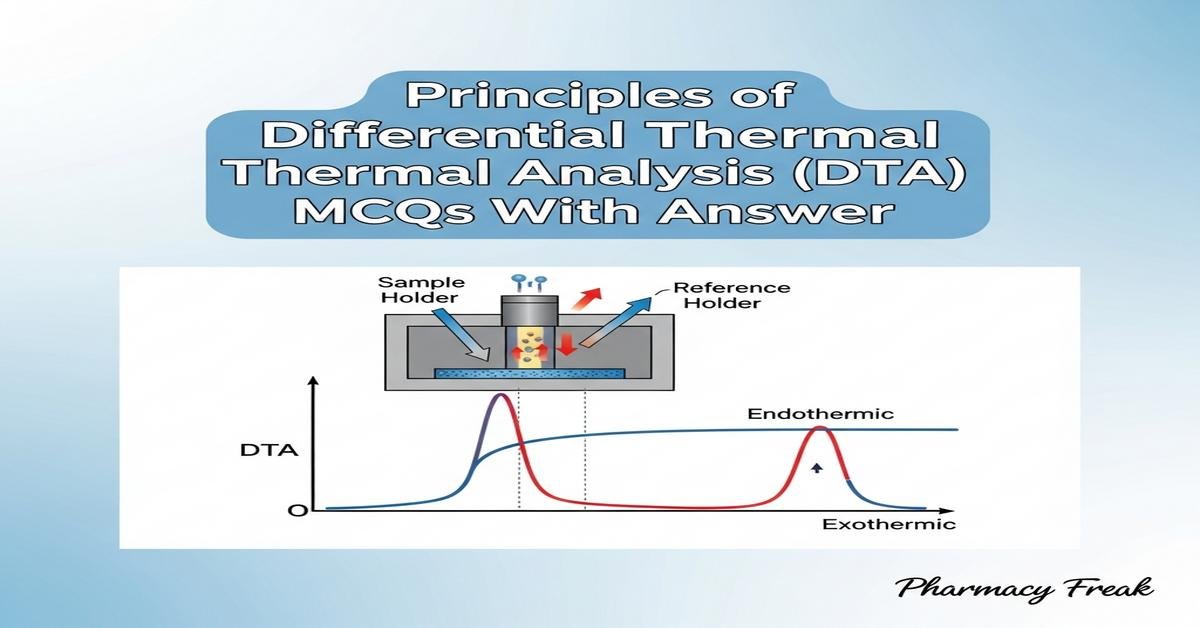
Principles of Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) MCQs With Answer is a focused review for B. Pharm students covering core concepts of thermal analysis. DTA measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference during controlled heating, producing thermograms that reveal phase transitions, melting points, polymorphism, and decomposition. Key principles include heat flow, enthalpy changes, baseline calibration, heating rate effects, crucible selection, and atmospheric conditions. Understanding instrument components, peak interpretation, sensitivity, and applications in drug stability, compatibility testing, and formulation development is essential for pharmaceutical analysis. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the fundamental principle of Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA)?
- Measuring temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference during controlled heating
- Measuring mass loss of a sample as temperature increases
- Measuring the refractive index change with temperature
- Measuring electrical conductivity variations with temperature
Correct Answer: Measuring temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference during controlled heating
Q2. A DTA thermogram typically plots which parameter against temperature?
- Temperature difference (ΔT) between sample and reference vs temperature
- Mass loss (%) vs temperature
- Heat flow (mW) vs time
- Pressure vs temperature
Correct Answer: Temperature difference (ΔT) between sample and reference vs temperature
Q3. In DTA, an exothermic event is indicated by which of the following?
- A peak corresponding to release of heat from the sample
- A decrease in sample mass without a peak
- A steady baseline with no signal
- An immediate sample ignition signal only
Correct Answer: A peak corresponding to release of heat from the sample
Q4. Which DTA feature is most directly related to the enthalpy change of a thermal event?
- Area under the DTA peak
- Peak onset temperature only
- Baseline noise level
- Crucible color change
Correct Answer: Area under the DTA peak
Q5. What is the primary difference between DTA and DSC?
- DTA measures temperature difference while DSC measures heat flow directly
- DTA measures mass loss while DSC measures refractive index
- DTA is only for liquids and DSC only for solids
- DTA requires vacuum but DSC does not
Correct Answer: DTA measures temperature difference while DSC measures heat flow directly
Q6. Which material is commonly used as an inert reference in DTA experiments?
- Alumina (Al2O3)
- Calcium carbonate
- Sodium chloride
- Glass wool
Correct Answer: Alumina (Al2O3)
Q7. Which type of crucible is commonly used in pharmaceutical DTA for reliability and inertness?
- Platinum crucibles
- Cardboard cups
- Wooden dishes
- Paint-coated metal pans
Correct Answer: Platinum crucibles
Q8. How does increasing the heating rate generally affect DTA peaks?
- Shifts peaks to higher temperatures and can broaden them, reducing resolution
- Makes peaks appear at lower temperatures with sharper shapes
- Eliminates peaks completely
- Has no effect on peak position or shape
Correct Answer: Shifts peaks to higher temperatures and can broaden them, reducing resolution
Q9. What does a drifting baseline in a DTA thermogram usually indicate?
- Instrumental drift, heat capacity mismatch, or poor thermal contact
- Perfectly stable instrument performance
- A guaranteed exothermic decomposition event
- That the sample is inert at all temperatures
Correct Answer: Instrumental drift, heat capacity mismatch, or poor thermal contact
Q10. Which standard material is commonly used to calibrate temperature in DTA instruments?
- Indium (melting point standard)
- Potassium nitrate
- Carbon black
- Sand
Correct Answer: Indium (melting point standard)
Q11. In DTA analysis, what does the onset temperature of a peak represent?
- The beginning of the thermal transition or reaction
- The moment the instrument is switched on
- The time the sample was prepared
- The maximum temperature the furnace can reach
Correct Answer: The beginning of the thermal transition or reaction
Q12. Which practice improves DTA sensitivity and reproducibility for small thermal events?
- Using a small, well-contacted sample and optimizing heating rate
- Using a very large, unevenly packed sample
- Turning off the reference sensor
- Heating the sample in direct sunlight
Correct Answer: Using a small, well-contacted sample and optimizing heating rate
Q13. One key pharmaceutical application of DTA is:
- Detecting polymorphism and phase transitions in drug substances
- Measuring microbial contamination directly
- Determining tablet dissolution rate in vivo
- Measuring optical clarity of formulations
Correct Answer: Detecting polymorphism and phase transitions in drug substances
Q14. Which purge gas is typically used for inert atmosphere DTA to prevent oxidation?
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Chlorine
- Hydrogen peroxide vapor
Correct Answer: Nitrogen
Q15. How is melting usually represented on a DTA thermogram for a pharmaceutical compound?
- As an endothermic peak indicating heat absorption at the melting point
- As an immediate mass increase on the curve
- As a decrease in baseline noise only
- As a constant plateau with no signal
Correct Answer: As an endothermic peak indicating heat absorption at the melting point
Q16. What advantage does simultaneous DTA–TGA provide for pharmaceutical samples?
- It provides thermal event information and mass loss data at the same time
- It eliminates the need for calibration standards
- It increases sample throughput by 1000% automatically
- It measures color changes during heating
Correct Answer: It provides thermal event information and mass loss data at the same time
Q17. Which factors commonly cause peak broadening in DTA thermograms?
- Thermal lag, large sample size, and sample heterogeneity
- Using perfect single crystals and ultra-thin samples
- Operating at absolute zero temperature
- Using a monochromatic light source instead of heat
Correct Answer: Thermal lag, large sample size, and sample heterogeneity
Q18. The detection limit for a thermal event in DTA mainly depends on:
- Instrument sensitivity, baseline noise, and sample mass
- Color of the sample only
- Room humidity alone regardless of instrument
- Age of the operator
Correct Answer: Instrument sensitivity, baseline noise, and sample mass
Q19. The primary role of the reference material in DTA is to:
- Provide a baseline for measuring temperature difference relative to the sample
- React chemically with the sample to enhance signals
- Absorb moisture from the furnace atmosphere
- Change color to indicate peak areas
Correct Answer: Provide a baseline for measuring temperature difference relative to the sample
Q20. Which parameter is NOT directly obtained from a standalone DTA experiment?
- Mass loss (%)
- Peak onset temperature
- Peak shape/position
- Relative thermal event enthalpy (with calibration)
Correct Answer: Mass loss (%)
Q21. How can DTA be used to detect different polymorphs of a drug?
- Different polymorphs show distinct thermal events (different transition/melting temperatures)
- Polymorphs always have identical thermograms
- DTA measures solubility directly, which differentiates polymorphs
- DTA cannot detect polymorphism under any circumstances
Correct Answer: Different polymorphs show distinct thermal events (different transition/melting temperatures)
Q22. The quantitative estimation of enthalpy from a DTA peak requires:
- Calibration with standards to relate peak area to energy
- Only the peak height without calibration
- Counting the number of peaks irrespective of area
- Using room temperature as the energy reference always
Correct Answer: Calibration with standards to relate peak area to energy
Q23. What is the desirable characteristic of a sample pan/crucible in DTA for accurate results?
- Thin-walled and chemically inert to the sample
- Thick, porous, and reactive with the sample
- Made of paper or cardboard
- Coated with organic dyes to improve heat absorption
Correct Answer: Thin-walled and chemically inert to the sample
Q24. Poor thermal contact between sample and sensor in DTA most likely results in:
- Peak shift and distorted or noisy signals
- Improved resolution and sharper peaks
- Complete elimination of baseline drift forever
- Instantaneous sample cooling below room temperature
Correct Answer: Peak shift and distorted or noisy signals
Q25. To resolve two closely overlapping thermal events in DTA, the best approach is to:
- Reduce heating rate or apply mathematical deconvolution/curve-fitting
- Increase sample mass drastically and heat faster
- Ignore one event and report only the dominant peak
- Change the sample color to separate peaks
Correct Answer: Reduce heating rate or apply mathematical deconvolution/curve-fitting
Q26. A zero baseline in a DTA experiment indicates:
- No temperature difference between sample and reference under those conditions
- The sample is exploding
- The instrument is turned off
- The sample has infinite heat capacity
Correct Answer: No temperature difference between sample and reference under those conditions
Q27. Why is it important to calibrate both temperature and enthalpy scales in DTA?
- To ensure accurate measurement of transition temperatures and energy changes
- To make the instrument heavier and more stable
- To reduce the cost of consumables only
- To allow use of any random reference material
Correct Answer: To ensure accurate measurement of transition temperatures and energy changes
Q28. DTA is useful for drug–excipient compatibility studies because it can:
- Detect new or shifted thermal events indicating interactions
- Directly measure bacterial growth between components
- Replace clinical trials for stability assessment
- Measure pH changes of the solid mixture
Correct Answer: Detect new or shifted thermal events indicating interactions
Q29. A pronounced negative peak on a DTA trace most likely corresponds to:
- An endothermic transition representing heat absorption
- An exothermic decomposition releasing heat
- Mass gain due to oxidation only
- An electrical short circuit in the instrument
Correct Answer: An endothermic transition representing heat absorption
Q30. Compared to DTA, DSC provides which analytical advantage for enthalpy measurements?
- DSC measures heat flow directly and is generally more quantitative for enthalpy without extensive calibration
- DSC measures color change which correlates with enthalpy directly
- DTA is always more quantitative than DSC for enthalpy
- DSC cannot measure enthalpy at all
Correct Answer: DSC measures heat flow directly and is generally more quantitative for enthalpy without extensive calibration

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com