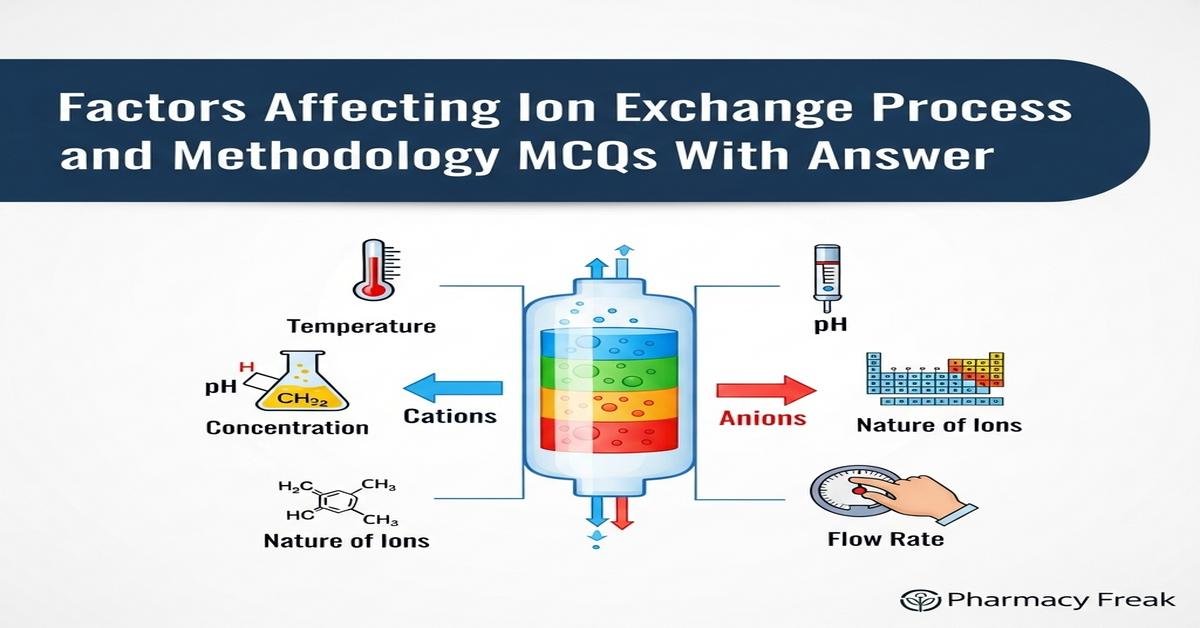
Introduction
Ion exchange is a vital separation technique in pharmaceutical analysis and formulation. Understanding factors affecting ion exchange — such as resin type, functional groups, exchange capacity, selectivity, pH, ionic strength, temperature, flow rate and bead porosity — helps B. Pharm students optimize the ion exchange process and methodology. Practical knowledge of column packing, regeneration, breakthrough curves, diffusion kinetics and competing ions ensures robust drug purification, excipient treatment and analytical assays. This concise guide emphasizes mechanism, operational parameters and troubleshooting to strengthen conceptual and applied skills in ion exchange for pharmaceutical applications. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What is the primary mechanism of ion exchange in a resin?
- Irreversible chemical reaction between resin and ion
- Physical adsorption without charge interaction
- Reversible replacement of counter-ions on charged functional groups
- Size-exclusion of molecules based on pore diameter
Correct Answer: Reversible replacement of counter-ions on charged functional groups
Q2. Which resin functional group is characteristic of a strong cation exchanger?
- Quaternary ammonium
- Sulfonic acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Hydroxyl
Correct Answer: Sulfonic acid
Q3. Which factor most strongly influences selectivity between two monovalent ions?
- Resin crosslinking only
- Hydrated ionic radius and charge density
- Ambient light intensity
- Column tubing material
Correct Answer: Hydrated ionic radius and charge density
Q4. Ion exchange capacity is usually expressed as which unit?
- mg/mL
- meq/g (milliequivalents per gram)
- mol/L
- percentage weight/weight
Correct Answer: meq/g (milliequivalents per gram)
Q5. How does increasing ionic strength of the solution affect ion exchange?
- Increases selectivity for trace ions
- Reduces resin swelling but has no effect on exchange
- Competes with analyte ions and decreases exchange efficiency
- Converts cation exchangers into anion exchangers
Correct Answer: Competes with analyte ions and decreases exchange efficiency
Q6. Which operational parameter most directly affects mass transfer kinetics in a packed ion-exchange column?
- Column color
- Flow rate
- Resin manufacturing brand
- Ambient humidity
Correct Answer: Flow rate
Q7. What is the effect of higher crosslink density in a resin?
- Increases resin porosity and diffusion rate
- Decreases mechanical strength
- Reduces pore size and slows intraparticle diffusion
- Eliminates functional groups
Correct Answer: Reduces pore size and slows intraparticle diffusion
Q8. For separation of divalent and monovalent cations, which property is exploited?
- Differences in solubility only
- Charge difference and selectivity coefficients
- Difference in molecular weight
- Optical activity
Correct Answer: Charge difference and selectivity coefficients
Q9. Which method is commonly used to determine total exchange capacity of a resin?
- UV-visible spectroscopy of blank resin
- Titration after exhaustive saturation with a standard ion
- Measuring resin color change under microscope
- Gravimetric drying at 25°C
Correct Answer: Titration after exhaustive saturation with a standard ion
Q10. pH affects ion exchange primarily by:
- Altering the resin bead size
- Changing the degree of ionization of the resin and analyte
- Changing the resin’s magnetic properties
- Converting covalent bonds in the polymer
Correct Answer: Changing the degree of ionization of the resin and analyte
Q11. What is a breakthrough curve?
- A plot of resin color versus time
- A plot of outlet concentration versus time showing when target ion appears
- The calibration curve for pH meter
- A thermal stability profile of resin
Correct Answer: A plot of outlet concentration versus time showing when target ion appears
Q12. Regeneration of a strong acid cation exchanger commonly uses which reagent?
- Alcohol
- Concentrated HCl or H2SO4
- Sodium hydroxide only
- Pure water at room temperature
Correct Answer: Concentrated HCl or H2SO4
Q13. In pharmaceutical water purification, ion exchange is often combined with which process to remove organics?
- Gel electrophoresis
- Activated carbon adsorption
- Dry heat sterilization
- Paper chromatography
Correct Answer: Activated carbon adsorption
Q14. Selectivity coefficient (K) in ion exchange quantifies:
- The resin’s porosity only
- Ratio of exchange affinities for two competing ions
- The mechanical strength of resin beads
- The flow rate at optimum performance
Correct Answer: Ratio of exchange affinities for two competing ions
Q15. Which diffusion step is usually rate-limiting in ion exchange columns?
- External film diffusion at very low flow rates
- Rapid bulk solution mixing
- Intraparticle (pore) diffusion into resin beads
- Gas-phase diffusion
Correct Answer: Intraparticle (pore) diffusion into resin beads
Q16. Fouling of ion exchange resin in pharma can be reduced by:
- Skipping regeneration cycles
- Pre-filtration and pre-treatment of feed
- Using ultrapure alcohol as feed
- Operating at very high temperatures only
Correct Answer: Pre-filtration and pre-treatment of feed
Q17. How does temperature generally affect ion exchange equilibria?
- Has no effect on equilibria or kinetics
- May change equilibrium constant and usually increases kinetics
- Always makes resin degrade chemically
- Converts resins to catalysts
Correct Answer: May change equilibrium constant and usually increases kinetics
Q18. What is the main difference between strong and weak ion exchangers?
- Strong exchangers have permanent ionizable groups independent of pH
- Weak exchangers are always synthetic, strong are natural only
- Strong exchangers dissolve in water
- Weak exchangers have higher mechanical strength
Correct Answer: Strong exchangers have permanent ionizable groups independent of pH
Q19. In mixed-bed ion exchange used in water deionization, what occurs?
- Cation and anion exchangers are mixed to produce high-purity water
- Only cation exchange happens
- Resins are dissolved for chemical reaction
- Magnetic separation of ions is performed
Correct Answer: Cation and anion exchangers are mixed to produce high-purity water
Q20. Which analytical technique can monitor concentration of eluted ions during column runs?
- Flame photometry or ion chromatography
- X-ray crystallography
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Polarimetry of resin beads
Correct Answer: Flame photometry or ion chromatography
Q21. What role does bead size play in ion exchange?
- Smaller beads increase surface area and reduce diffusion path length
- Bead size only affects color
- Larger beads always give higher capacity per gram
- Bead size converts resin into an anion exchanger
Correct Answer: Smaller beads increase surface area and reduce diffusion path length
Q22. When separating weakly ionized drugs, which parameter must be optimized?
- pH to ensure drug ionization and resin compatibility
- Column length only
- Ambient light conditions
- Resin manufacturer’s logo orientation
Correct Answer: pH to ensure drug ionization and resin compatibility
Q23. Which competing ion most strongly affects cation exchange of calcium?
- Chloride anion
- Magnesium (another divalent cation)
- Nitrogen gas
- Glucose molecule
Correct Answer: Magnesium (another divalent cation)
Q24. What is meant by “exhaustion” of an ion exchange resin?
- When all functional groups are permanently destroyed
- When resin has exchanged most available sites and breakthrough occurs
- When resin melts at high temperature
- When resin changes color under UV light
Correct Answer: When resin has exchanged most available sites and breakthrough occurs
Q25. In a pharmaceutical ion-exchange purification, leak of which impurity indicates incomplete regeneration?
- Residual regenerant counter-ion such as sodium or chloride
- Air bubbles only
- Ambient dust particles
- Resin polymer fragments that are invisible
Correct Answer: Residual regenerant counter-ion such as sodium or chloride
Q26. Which is a common method to characterize resin porosity and surface area?
- Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) adsorption analysis
- Paper pH strips
- Simple optical density at 660 nm
- Counting beads by eye
Correct Answer: Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) adsorption analysis
Q27. Why is column packing technique important in ion exchange columns?
- Poor packing causes channeling and non-uniform flow reducing efficiency
- Packing only affects aesthetic appearance
- Packing determines resin chemical identity
- Packing prevents pH from changing
Correct Answer: Poor packing causes channeling and non-uniform flow reducing efficiency
Q28. Which parameter is used to quantify rate of ion exchange in kinetic studies?
- Exchange rate constant or mass transfer coefficient
- Color intensity of resin
- Viscosity of resin beads
- Electrical power consumption of pump
Correct Answer: Exchange rate constant or mass transfer coefficient
Q29. How does fixed-charge density of a resin influence its performance?
- Higher fixed-charge density increases capacity and often selectivity for multivalent ions
- It only affects resin melting point
- Lower fixed-charge density always improves selectivity
- Fixed-charge density is unrelated to ion exchange
Correct Answer: Higher fixed-charge density increases capacity and often selectivity for multivalent ions
Q30. Best practice for validating an ion-exchange method in pharmaceutical analysis includes:
- Assessing specificity, capacity, reproducibility, and regeneration cycles
- Only checking the resin color after use
- Ignoring breakthrough curves
- Using unfiltered tap water as mobile phase
Correct Answer: Assessing specificity, capacity, reproducibility, and regeneration cycles

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com