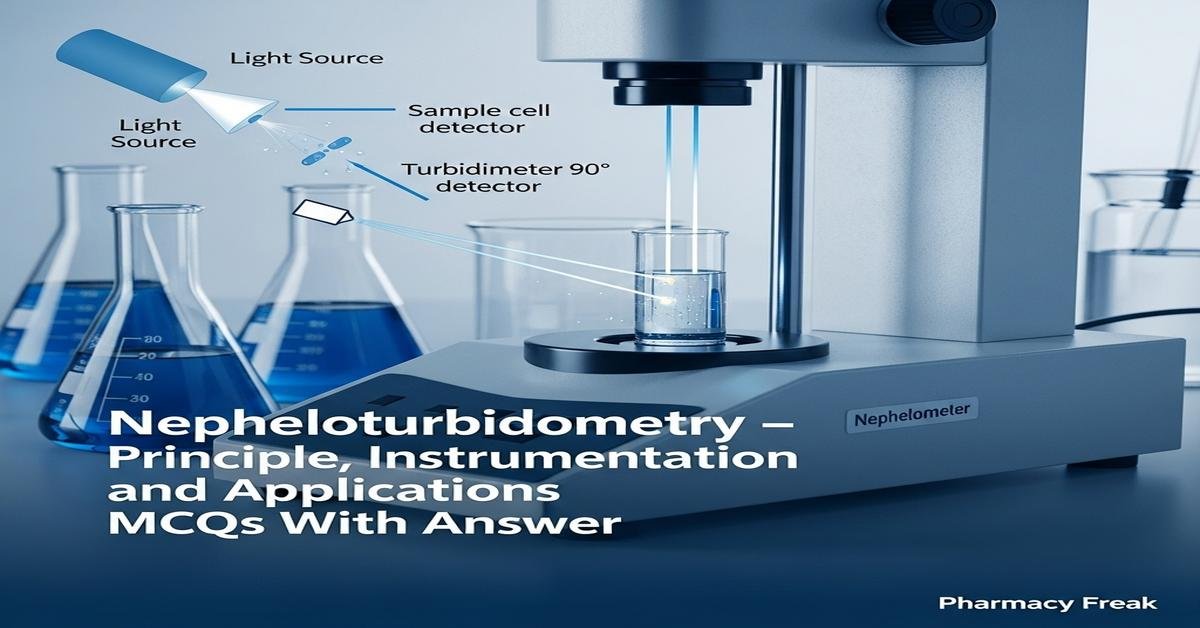
Nepheloturbidometry combines nephelometry and turbidimetry to quantify suspended particles by measuring light scattering and loss of transmitted light. The principle relies on light scattering phenomena (Rayleigh and Mie regimes) where particle size, concentration, refractive index, wavelength and measurement angle influence signal. Instrumentation includes a stable light source, sample cell, optics, angle-specific detectors (often 90° for nephelometry), photomultiplier or photodiode, monochromator/filters, and signal processing electronics. Applications in pharmaceutical analysis cover particulate testing of parenterals, suspension quality, protein aggregation, nephelometric immunoassays and stability studies. Understanding calibration (Formazin standards), NTU/FTU units, limitations and interferences is essential for B. Pharm students. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What fundamental phenomenon does nepheloturbidometry primarily measure?
- Absorption of light by dissolved solutes
- Light scattering by suspended particles
- Fluorescence emission from molecules
- Electrical conductivity of suspensions
Correct Answer: Light scattering by suspended particles
Q2. Which detector placement is typical for nephelometric measurements?
- 0° (directly in line with the light source)
- 45° relative to the incident beam
- 90° relative to the incident beam
- 180° (opposite the light source)
Correct Answer: 90° relative to the incident beam
Q3. Which scattering regime applies when particle diameter is much smaller than the wavelength of incident light?
- Mie scattering
- Rayleigh scattering
- Raman scattering
- Brillouin scattering
Correct Answer: Rayleigh scattering
Q4. What is the commonly used primary calibration standard for turbidity/nephelometry?
- Sodium chloride solution
- Potassium permanganate
- Formazin suspension
- Bovine serum albumin standard
Correct Answer: Formazin suspension
Q5. NTU is a unit used to report:
- Absorbance at 260 nm
- Particulate turbidity
- pH of a suspension
- Viscosity of a solution
Correct Answer: Particulate turbidity
Q6. Which factor does NOT directly affect scattered light intensity in nepheloturbidometry?
- Particle concentration
- Particle refractive index
- Ambient humidity around the instrument
- Wavelength of incident light
Correct Answer: Ambient humidity around the instrument
Q7. In pharmaceutical quality control, nepheloturbidometry is MOST commonly used for:
- Determining active pharmaceutical ingredient identity
- Measuring particulate contamination in parenteral solutions
- Assessing tablet dissolution rate
- Measuring lipid solubility
Correct Answer: Measuring particulate contamination in parenteral solutions
Q8. Which instrument component converts scattered photons into an electrical signal?
- Monochromator
- Sample cell
- Detector (e.g., photomultiplier tube)
- Mirror
Correct Answer: Detector (e.g., photomultiplier tube)
Q9. Mie scattering theory is most relevant for particles whose size is:
- Much smaller than the wavelength of light
- Comparable to or larger than the wavelength of light
- Exactly equal to the wavelength of light only
- Only for molecular-scale particles
Correct Answer: Comparable to or larger than the wavelength of light
Q10. Why are shorter wavelengths sometimes chosen for nepheloturbidometric measurements?
- They reduce scattering intensity for small particles
- They increase scattering intensity aiding sensitivity for small particles
- They eliminate the need for calibration
- They prevent detector saturation for high turbidity samples
Correct Answer: They increase scattering intensity aiding sensitivity for small particles
Q11. Which sample property can produce erroneous high turbidity readings if not accounted for?
- High dissolved salt concentration with no particulates
- Strong sample color or intrinsic absorbance
- Low pH only
- Low ionic strength
Correct Answer: Strong sample color or intrinsic absorbance
Q12. Which of the following describes the main difference between turbidimetry and nephelometry?
- Turbidimetry measures fluorescence; nephelometry measures absorbance
- Turbidimetry measures transmitted light loss; nephelometry measures scattered light intensity
- Turbidimetry uses a detector at 90°; nephelometry uses 0°
- They are identical techniques with different names
Correct Answer: Turbidimetry measures transmitted light loss; nephelometry measures scattered light intensity
Q13. Which calibration curve behavior indicates a linear working range for nepheloturbidometry?
- Scattered intensity proportional to concentration
- Scattered intensity inversely proportional to concentration
- Scattered intensity unrelated to concentration
- Scattered intensity exponential with concentration
Correct Answer: Scattered intensity proportional to concentration
Q14. Which particulate property most strongly affects angular distribution of scattered light?
- Particle color only
- Particle shape and size
- Ambient air pressure
- pH of the suspension
Correct Answer: Particle shape and size
Q15. What is a common photodetector used in high-sensitivity nephelometers?
- Thermocouple
- Photomultiplier tube (PMT)
- Glass electrode
- Acoustic sensor
Correct Answer: Photomultiplier tube (PMT)
Q16. Which practice improves reproducibility of turbidity measurements?
- Using dirty cuvettes to increase scattering
- Vigorously bubbling air through the sample before measurement
- Using consistent sample path length and thorough mixing without introducing air bubbles
- Varying measurement wavelength between replicates
Correct Answer: Using consistent sample path length and thorough mixing without introducing air bubbles
Q17. In nephelometric immunoassays, what is measured to infer analyte concentration?
- Change in solution pH
- Light scattering due to immune complex formation
- Electrical conductivity of the mixture
- UV absorbance at 280 nm
Correct Answer: Light scattering due to immune complex formation
Q18. Which interference is most likely when measuring colored pharmaceutical suspensions?
- Viscosity causing detector overload
- Absorbance reducing detected scattered light and biasing results
- Temperature causing colorless phase separation
- pH shifting the detector wavelength
Correct Answer: Absorbance reducing detected scattered light and biasing results
Q19. What does FTU stand for in turbidity measurement?
- Formazin Turbidity Unit
- Fourier Transform Unit
- Fractional Turbidity Unit
- Fluid Turbidity Unit
Correct Answer: Formazin Turbidity Unit
Q20. Which instrument modification increases sensitivity for low turbidity samples?
- Using a broader slit width and ambient light
- Using a photomultiplier and a narrow band monochromatic light source
- Using unfiltered white light and a smartphone camera
- Measuring at 0° transmission only
Correct Answer: Using a photomultiplier and a narrow band monochromatic light source
Q21. Why is Formazin chosen as a turbidity standard?
- It is highly fluorescent and easy to detect
- It produces a stable, reproducible suspension with known scattering properties
- It is colorless and dissolves completely
- It reacts chemically with proteins to form precipitates
Correct Answer: It produces a stable, reproducible suspension with known scattering properties
Q22. How does particle refractive index affect nepheloturbidometric signal?
- Higher refractive index contrast increases scattering intensity
- Refractive index has no impact on scattering
- Lower refractive index contrast always increases scattering
- Refractive index only affects absorption, not scattering
Correct Answer: Higher refractive index contrast increases scattering intensity
Q23. For monitoring suspension stability, which nepheloturbidometric measurement is most informative?
- Single-point absorbance at fixed time only
- Kinetic scattering profile over time to detect aggregation or settling
- Measuring refractive index alone
- Measuring electrical conductivity changes
Correct Answer: Kinetic scattering profile over time to detect aggregation or settling
Q24. Which sample handling step can reduce measurement error from large particulates?
- Not mixing the sample at all
- Filtering with an appropriate pore-size filter when permissible
- Heating the sample to high temperature
- Adding surfactant indiscriminately without validation
Correct Answer: Filtering with an appropriate pore-size filter when permissible
Q25. In which situation would turbidimetry be preferred over nephelometry?
- Measuring very low turbidity near detection limits
- When measuring high turbidity where transmitted light attenuation is informative
- When scattering at 90° is required for specificity
- For detecting fluorescence from aggregates
Correct Answer: When measuring high turbidity where transmitted light attenuation is informative
Q26. Which mathematical approach is often required to model scattering by particles comparable to wavelength?
- Beer-Lambert law without modification
- Mie theory calculations
- Henry’s law
- Simple linear regression without physics
Correct Answer: Mie theory calculations
Q27. Which maintenance step is most important to avoid spurious turbidity readings?
- Ignoring lamp aging since it does not affect results
- Regular cleaning of optical windows and cuvettes and lamp replacement as specified
- Replacing the detector daily regardless of use
- Removing all instrument grounding to improve sensitivity
Correct Answer: Regular cleaning of optical windows and cuvettes and lamp replacement as specified
Q28. How can one correct for background absorbance when measuring scattering in colored samples?
- Use a blank that contains the matrix minus the particles and subtract its signal
- Ignore the background because scattering dominates
- Increase sample concentration to swamp absorbance
- Change detector angle to 0° to avoid absorbance
Correct Answer: Use a blank that contains the matrix minus the particles and subtract its signal
Q29. What is a limitation of nepheloturbidometry compared with particle counting by microscopy or light obscuration?
- Nepheloturbidometry gives direct particle counts and sizes
- It provides less information about particle size distribution and number concentration
- It is always more accurate for regulatory parenteral testing
- It cannot be calibrated
Correct Answer: It provides less information about particle size distribution and number concentration
Q30. Which application describes nepheloturbidometry use in biopharmaceuticals?
- Measuring DNA sequence quality
- Assessing protein aggregation and particulate load in formulated biologics
- Determining excipient melting point
- Measuring tablet hardness
Correct Answer: Assessing protein aggregation and particulate load in formulated biologics

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com