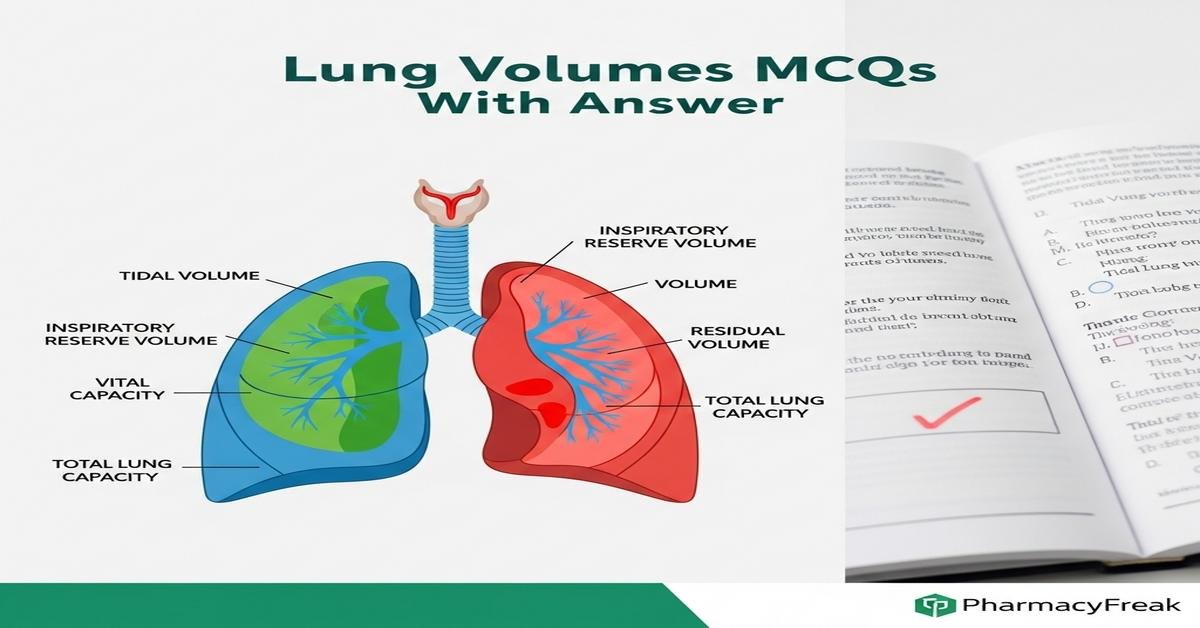
This concise, Student-friendly post on Lung volumes MCQs With Answer is tailored for B. Pharm students studying respiratory physiology and pulmonary function. It covers essential keywords such as lung volumes, spirometry, tidal volume, vital capacity, residual volume, total lung capacity, pulmonary function tests, and clinical interpretation. The content is designed to strengthen understanding of normal values, measurement techniques, factors affecting lung volumes, and differences between obstructive and restrictive patterns. Clear, focused explanations help pharmacy students link physiology to drug effects on respiration and patient assessment. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. What does tidal volume (VT) represent in lung physiology?
- The volume of air moved during a normal, quiet breath
- The maximum volume exhaled after a deep inhalation
- The air remaining in lungs after maximal expiration
- The sum of all lung volumes
Correct Answer: The volume of air moved during a normal, quiet breath
Q2. Which lung volume cannot be measured by simple spirometry?
- Tidal volume (VT)
- Inspiratory capacity (IC)
- Residual volume (RV)
- Vital capacity (VC)
Correct Answer: Residual volume (RV)
Q3. What is the typical approximate value for total lung capacity (TLC) in a healthy adult male?
- ~2.5 liters
- ~4.0 liters
- ~6.0 liters
- ~8.0 liters
Correct Answer: ~6.0 liters
Q4. Which equation correctly relates lung volumes?
- TLC = IC + ERV
- VC = TLC + RV
- TLC = VC + RV
- RV = IC + VT
Correct Answer: TLC = VC + RV
Q5. What does functional residual capacity (FRC) equal?
- RV + ERV
- TLC − RV
- IC + ERV
- VC − VT
Correct Answer: RV + ERV
Q6. Which lung volume is defined as the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal expiration?
- Inspiratory capacity (IC)
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- Tidal volume (VT)
- Residual volume (RV)
Correct Answer: Inspiratory capacity (IC)
Q7. Which clinical pattern typically shows a reduced TLC?
- Obstructive lung disease
- Restrictive lung disease
- Both obstructive and restrictive equally
- Normal aging only
Correct Answer: Restrictive lung disease
Q8. In obstructive diseases like COPD, which lung volume usually increases?
- Vital capacity (VC)
- Residual volume (RV)
- Tidal volume (VT)
- Inspiratory capacity (IC)
Correct Answer: Residual volume (RV)
Q9. Which parameter measured in spirometry best differentiates obstructive from restrictive disease?
- FEV1/FVC ratio
- Tidal volume (VT)
- Inspiratory capacity (IC)
- Residual volume (RV)
Correct Answer: FEV1/FVC ratio
Q10. What does FEV1 represent?
- Forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- Forced expiratory volume in full test
- Functional expiratory volume at rest
- Fractional expiratory ventilation
Correct Answer: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second
Q11. How is vital capacity (VC) defined?
- The volume of air remaining after normal expiration
- The maximum volume that can be inhaled from residual volume
- The total volume exhaled after maximal inhalation
- The air exchanged per minute during quiet breathing
Correct Answer: The total volume exhaled after maximal inhalation
Q12. Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) is best described as:
- Air inhaled during normal breathing
- Additional air inhaled after a normal inspiration
- Air remaining after forced expiration
- Volume used for gas exchange only
Correct Answer: Additional air inhaled after a normal inspiration
Q13. What factor typically decreases lung compliance?
- Emphysema
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Aging-related elastin loss
- Bronchodilator therapy
Correct Answer: Pulmonary fibrosis
Q14. Which measurement requires body plethysmography rather than simple spirometry?
- Forced vital capacity (FVC)
- Residual volume (RV)
- FEV1
- Respiratory rate
Correct Answer: Residual volume (RV)
Q15. Which lung volume increases with age due to loss of elastic recoil?
- Inspiratory capacity (IC)
- Residual volume (RV)
- Vital capacity (VC)
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Correct Answer: Residual volume (RV)
Q16. Which of the following best explains air trapping in obstructive disease?
- Reduced airway resistance
- Increased airway collapse during expiration
- Decreased residual volume
- Increased inspiratory muscle strength
Correct Answer: Increased airway collapse during expiration
Q17. What is the clinical significance of an increased RV/TLC ratio?
- Improved gas exchange
- Indicates air trapping or hyperinflation
- Sign of enhanced lung elasticity
- Normal finding in athletes
Correct Answer: Indicates air trapping or hyperinflation
Q18. Which intervention would most likely decrease FRC?
- Deep inspiration before spirometry
- Administration of bronchodilator
- General anesthesia with muscle relaxation
- Smoking cessation
Correct Answer: General anesthesia with muscle relaxation
Q19. Which gas law underlies measurement of lung volumes with helium dilution?
- Boyle’s law
- Charles’s law
- Dalton’s law
- Henry’s law
Correct Answer: Boyle’s law
Q20. Maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) assesses:
- Static lung volumes only
- Dynamic ventilatory capacity over time
- Only residual volume
- Diffusion capacity across alveoli
Correct Answer: Dynamic ventilatory capacity over time
Q21. Which condition commonly shows increased TLC but reduced FEV1/FVC?
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Obstructive emphysema
- Restrictive chest wall disease
- Neuromuscular weakness
Correct Answer: Obstructive emphysema
Q22. Inspiratory capacity (IC) equals which combination?
- Tidal volume + Expiratory reserve volume
- Tidal volume + Inspiratory reserve volume
- Residual volume + Expiratory reserve volume
- Vital capacity + Residual volume
Correct Answer: Tidal volume + Inspiratory reserve volume
Q23. Which statement about spirometry calibration is true?
- Calibration isn’t necessary for modern devices
- Daily calibration with a 3L syringe is standard practice
- Calibration only required yearly
- Calibration uses oxygen as reference gas
Correct Answer: Daily calibration with a 3L syringe is standard practice
Q24. Which of the following decreases in restrictive lung disease?
- TLC and VC
- RV only
- FEV1/FVC ratio
- Residual volume fraction
Correct Answer: TLC and VC
Q25. Which factor most increases diffusion limitation of oxygen?
- Thicker alveolar-capillary membrane
- Higher alveolar PO2
- Increased cardiac output
- Increased hemoglobin concentration
Correct Answer: Thicker alveolar-capillary membrane
Q26. Which value is most affected by patient effort during spirometry?
- Residual volume (RV)
- Forced vital capacity (FVC)
- TLC measured by plethysmography
- Static functional residual capacity
Correct Answer: Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Q27. Which pattern is suggested by reduced FVC with normal or increased FEV1/FVC?
- Obstructive disease
- Restrictive disease
- Upper airway obstruction
- Neuromuscular disease only
Correct Answer: Restrictive disease
Q28. What is the clinical relevance of measuring diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO)?
- Assesses airway resistance only
- Estimates alveolar-capillary gas transfer
- Measures residual volume directly
- Determines respiratory rate
Correct Answer: Estimates alveolar-capillary gas transfer
Q29. Which drug class can acutely increase airway caliber and affect spirometry results?
- Beta-2 agonists
- ACE inhibitors
- Statins
- Opioids
Correct Answer: Beta-2 agonists
Q30. When comparing supine to upright position, what happens to FRC?
- FRC increases when supine
- FRC decreases when supine
- FRC unchanged by posture
- FRC equals TLC in supine
Correct Answer: FRC decreases when supine
Q31. What is the major physiological determinant of TLC?
- Chest wall tone and respiratory muscle strength
- Airway resistance only
- Diffusion capacity
- Alveolar gas composition
Correct Answer: Chest wall tone and respiratory muscle strength
Q32. Which measurement indicates small airway dysfunction earlier than FEV1?
- Maximal inspiratory pressure
- Mid-expiratory flow rates (FEF25-75%)
- Tidal volume
- Residual volume
Correct Answer: Mid-expiratory flow rates (FEF25-75%)
Q33. What is the effect of obesity on lung volumes?
- Increased TLC and VC
- Reduced FRC and ERV
- Increased RV exclusively
- No effect on lung volumes
Correct Answer: Reduced FRC and ERV
Q34. Which parameter is most useful to monitor bronchodilator response?
- Change in FEV1 post-bronchodilator
- Baseline residual volume
- Tidal volume during sleep
- Total lung capacity by plethysmography
Correct Answer: Change in FEV1 post-bronchodilator
Q35. Which technology is best for measuring thoracic gas volume including trapped gas?
- Helium dilution
- Body plethysmography
- Standard spirometry
- Pulse oximetry
Correct Answer: Body plethysmography
Q36. Which change is characteristic of emphysema?
- Decreased TLC and increased FEV1
- Increased TLC and increased RV
- Reduced RV/TLC ratio
- Improved DLCO
Correct Answer: Increased TLC and increased RV
Q37. Which term describes the largest volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximal inhalation?
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- Vital capacity (VC)
- Functional residual capacity (FRC)
- Residual volume (RV)
Correct Answer: Vital capacity (VC)
Q38. During pregnancy, how are maternal lung volumes typically affected?
- Marked decrease in TLC due to uterine pressure
- Small decrease in FRC, ERV; TLC largely preserved
- Large increase in RV and TLC
- No changes occur
Correct Answer: Small decrease in FRC, ERV; TLC largely preserved
Q39. Which physiologic change increases residual volume (RV)?
- Enhanced elastic recoil of lungs
- Airway obstruction and collapse
- Strenuous inspiratory muscle training
- Bronchodilation before testing
Correct Answer: Airway obstruction and collapse
Q40. Which index is calculated to assess obstructive severity and is age- and sex-dependent?
- TLC measurement
- Predicted FEV1 percentage (FEV1 % predicted)
- Minute ventilation at rest
- Inspiratory reserve volume
Correct Answer: Predicted FEV1 percentage (FEV1 % predicted)
Q41. Which of these reduces airway resistance and may increase flows?
- Cholinergic agonists
- Beta-2 adrenergic agonists
- Mucus hypersecretion
- Bronchoconstrictors
Correct Answer: Beta-2 adrenergic agonists
Q42. Which test would detect restrictive physiology even when spirometry is normal?
- Tidal breathing analysis
- Measurement of TLC by plethysmography
- Pulse oximetry
- Peak expiratory flow only
Correct Answer: Measurement of TLC by plethysmography
Q43. What happens to ERV during exercise?
- ERV increases significantly
- ERV decreases because VT increases into reserve
- ERV converts to RV
- ERV becomes equal to TLC
Correct Answer: ERV decreases because VT increases into reserve
Q44. Which parameter is least likely to change with bronchodilator in fixed airway obstruction?
- Peak expiratory flow
- FEV1
- FEV1/FVC ratio
- Residual volume if severe remodeling present
Correct Answer: Residual volume if severe remodeling present
Q45. What is the significance of an increased closing capacity relative to FRC?
- Improved ventilation at base of lung
- Small airways close during normal tidal breathing, causing V/Q mismatch
- Indicates enhanced elastic recoil
- Normal finding in young adults
Correct Answer: Small airways close during normal tidal breathing, causing V/Q mismatch
Q46. Which pharmacologic agent can reduce respiratory drive and alter measured ventilatory volumes?
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Opioids
- Beta-2 agonists
- Antihistamines only
Correct Answer: Opioids
Q47. How does high altitude affect lung volumes acutely?
- Increases FRC due to hypoxic vasoconstriction
- Little change in static lung volumes but increases ventilation
- Markedly decreases TLC immediately
- Eliminates residual volume
Correct Answer: Little change in static lung volumes but increases ventilation
Q48. Which condition shows low DLCO along with hyperinflation?
- Asthma with good control
- Emphysema
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Pure neuromuscular weakness
Correct Answer: Emphysema
Q49. What practical advice improves reproducibility of spirometry in outpatient testing?
- Allow patient to hold breath for 30 seconds before test
- Provide clear coaching and repeat best of three efforts
- Perform only a single forced expiration to save time
- Give no instructions to prevent bias
Correct Answer: Provide clear coaching and repeat best of three efforts
Q50. For B. Pharm students, why is mastery of lung volumes important?
- Only relevant for physiotherapists
- Essential for understanding drug effects on respiratory mechanics and dosing
- Irrelevant to drug development and clinical pharmacy
- Important solely for cardiology exams
Correct Answer: Essential for understanding drug effects on respiratory mechanics and dosing

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com