Laplace Transforms of elementary functions MCQs With Answer offers B. Pharm students a focused way to master core s-domain techniques used in pharmacokinetic modeling and differential equation solutions. This concise, keyword-rich introduction covers Laplace transforms, inverse Laplace, time and frequency shifting, convolution, derivatives, and common transforms for polynomials, exponentials, sinusoids and step/delta functions. Each concept is tied to practical problem-solving skills useful in drug absorption and compartmental modeling. Clear explanations support exam preparation and conceptual clarity. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
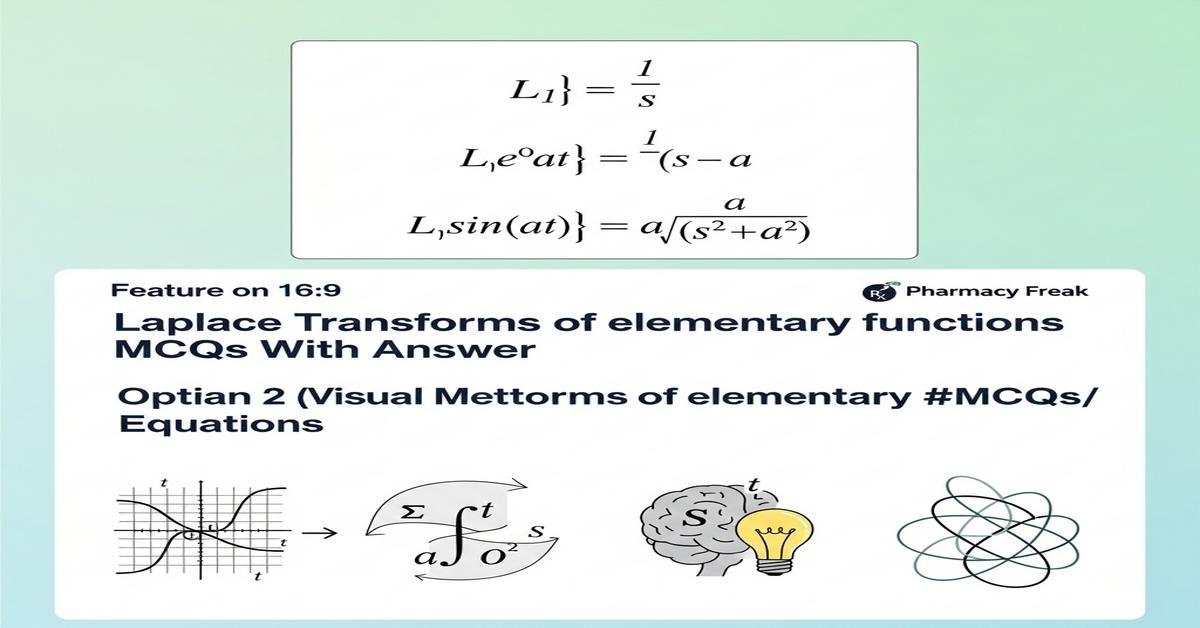
Q1. What is the Laplace transform of 1 for t ≥ 0?
- 1/s
- s
- e^{-s}
- 0
Correct Answer: 1/s
Q2. What is L{t} (the Laplace transform of t)?
- 1/s
- 1/s^2
- 2/s^3
- t/s
Correct Answer: 1/s^2
Q3. For integer n ≥ 0, L{t^n} equals which expression?
- n! / s^{n+1}
- s^{n+1} / n!
- (n+1)! / s^{n}
- Γ(n)/s^n
Correct Answer: n! / s^{n+1}
Q4. What is L{e^{at}} (Laplace transform of exponential e^{at})?
- 1/(s – a)
- 1/(s + a)
- e^{-as}
- s/(s-a)
Correct Answer: 1/(s – a)
Q5. What is the Laplace transform of sin(bt)?
- b/(s^2 + b^2)
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
- b/(s – b)
- 1/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: b/(s^2 + b^2)
Q6. What is L{cos(bt)}?
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
- b/(s^2 + b^2)
- 1/(s^2 + b^2)
- (s^2)/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: s/(s^2 + b^2)
Q7. The Laplace transform of sinh(bt) is which of the following?
- b/(s^2 – b^2)
- s/(s^2 – b^2)
- b/(s^2 + b^2)
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: b/(s^2 – b^2)
Q8. L{cosh(bt)} equals:
- s/(s^2 – b^2)
- b/(s^2 – b^2)
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
- 1/(s^2 – b^2)
Correct Answer: s/(s^2 – b^2)
Q9. Time-shifting property: L{f(t – a)u(t – a)} equals which expression (u is Heaviside)?
- e^{-as}F(s)
- F(s – a)
- e^{as}F(s)
- F(s + a)
Correct Answer: e^{-as}F(s)
Q10. Frequency-shift property: L{e^{at} f(t)} equals which transform?
- F(s – a)
- e^{-as} F(s)
- F(s + a)
- e^{as} F(s)
Correct Answer: F(s – a)
Q11. What is L{f'(t)} in terms of F(s) and initial value f(0)?
- sF(s) – f(0)
- F(s)/s – f(0)
- sF(s) + f(0)
- F(s) – s f(0)
Correct Answer: sF(s) – f(0)
Q12. The Laplace transform of the integral ∫0^t f(τ) dτ is which of the following?
- (1/s) F(s)
- s F(s)
- F(s) – f(0)
- F(s)/t
Correct Answer: (1/s) F(s)
Q13. Final value theorem states lim_{t→∞} f(t) = ? (when conditions hold)
- lim_{s→0} s F(s)
- lim_{s→∞} s F(s)
- lim_{s→0} F(s)
- lim_{s→∞} F(s)
Correct Answer: lim_{s→0} s F(s)
Q14. Initial value theorem gives lim_{t→0+} f(t) equals which limit?
- lim_{s→∞} s F(s)
- lim_{s→0} s F(s)
- lim_{s→∞} F(s)
- lim_{s→0} F(s)
Correct Answer: lim_{s→∞} s F(s)
Q15. Convolution theorem: L{f * g} equals which product?
- F(s) G(s)
- F(s) + G(s)
- F(s)/G(s)
- G(s) – F(s)
Correct Answer: F(s) G(s)
Q16. What is L{δ(t – a)}, where δ is the Dirac delta?
- e^{-as}
- 1
- δ(s – a)
- 1/s
Correct Answer: e^{-as}
Q17. The region of convergence (ROC) for L{e^{at}} is which of the following?
- Re(s) > a
- Re(s) < a
- All s
- Re(s) ≥ 0 only
Correct Answer: Re(s) > a
Q18. What is L{t e^{at}}?
- 1/(s – a)^2
- 1/(s + a)^2
- t/(s – a)
- 2/(s – a)^3
Correct Answer: 1/(s – a)^2
Q19. What is L{t^2}?
- 2/s^3
- 1/s^2
- 6/s^4
- 1/s^3
Correct Answer: 2/s^3
Q20. L{f”(t)} (second derivative) equals which expression?
- s^2 F(s) – s f(0) – f'(0)
- s F(s) – f(0)
- F(s) – f'(0)
- s^2 F(s) + f(0) + f'(0)
Correct Answer: s^2 F(s) – s f(0) – f'(0)
Q21. The inverse Laplace transform of 1/(s – a) is:
- e^{at}
- e^{-at}
- δ(t – a)
- t e^{at}
Correct Answer: e^{at}
Q22. The inverse Laplace of s/(s^2 + b^2) is:
- cos(bt)
- sin(bt)
- e^{bt}
- δ(t – b)
Correct Answer: cos(bt)
Q23. The inverse Laplace of b/(s^2 + b^2) yields:
- sin(bt)
- cos(bt)
- e^{bt}
- t sin(bt)
Correct Answer: sin(bt)
Q24. Multiplication by t in the time domain corresponds to what operation on F(s)?
- -d/ds F(s)
- d/ds F(s)
- s F(s)
- 1/s F(s)
Correct Answer: -d/ds F(s)
Q25. What is L{u(t – a)} (Heaviside step delayed by a)?
- e^{-as}/s
- 1/s
- e^{as}/s
- s e^{-as}
Correct Answer: e^{-as}/s
Q26. Time-scaling property: L{f(at)} equals which of the following (a > 0)?
- (1/a) F(s/a)
- a F(as)
- F(s/a)
- F(as)/a
Correct Answer: (1/a) F(s/a)
Q27. Laplace transform of a rectangular pulse p(t) = u(t) – u(t – T) is:
- (1 – e^{-sT})/s
- e^{-sT}/s
- 1/s^2
- T/s
Correct Answer: (1 – e^{-sT})/s
Q28. The inverse Laplace of 1/(s(s + a)) equals:
- (1/a)(1 – e^{-at})
- e^{-at}/a
- 1/(s + a)
- t e^{-at}
Correct Answer: (1/a)(1 – e^{-at})
Q29. What is L{δ(t)} (Dirac impulse at zero)?
- 1
- 0
- s
- e^{-s}
Correct Answer: 1
Q30. L{e^{-bt} cos(at)} equals which expression?
- (s + b)/((s + b)^2 + a^2)
- (s – b)/((s – b)^2 + a^2)
- (s)/ (s^2 + a^2 + b^2)
- b/((s + b)^2 + a^2)
Correct Answer: (s + b)/((s + b)^2 + a^2)
Q31. L{t^n e^{at}} equals which formula (n integer ≥ 0)?
- n!/(s – a)^{n+1}
- n!/(s + a)^{n+1}
- (s – a)^{n+1}/n!
- n/(s – a)^{n}
Correct Answer: n!/(s – a)^{n+1}
Q32. Using Laplace transforms to solve dx/dt + a x = 0 with x(0)=x0 gives X(s) = ?
- x0/(s + a)
- x0/(s – a)
- 1/(s + a)
- x0 s/(s + a)
Correct Answer: x0/(s + a)
Q33. Multiplication by e^{-as} in the s-domain corresponds to which time-domain operation?
- Delay by a: f(t – a)u(t – a)
- Multiplication by e^{at} in time
- Time-scaling by a
- Conjugation of f(t)
Correct Answer: Delay by a: f(t – a)u(t – a)
Q34. What is L{t sin(bt)}?
- 2 b s/(s^2 + b^2)^2
- b/(s^2 + b^2)
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
- 1/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: 2 b s/(s^2 + b^2)^2
Q35. L{cosh(at)} (repeated concept) equals which of these?
- s/(s^2 – a^2)
- a/(s^2 – a^2)
- s/(s^2 + a^2)
- 1/(s^2 – a^2)
Correct Answer: s/(s^2 – a^2)
Q36. The inverse Laplace of (s + 1)/(s^2 + 2s + 5) is which time function?
- e^{-t} cos(2t)
- e^{t} cos(2t)
- cos(t) e^{-2t}
- sin(2t) e^{-t}
Correct Answer: e^{-t} cos(2t)
Q37. L{(t – a) u(t – a)} equals which of the following?
- e^{-as}/s^2
- e^{-as}/s
- (1/s^2) – e^{-as}
- e^{as}/s^2
Correct Answer: e^{-as}/s^2
Q38. What is L{t^2 e^{at}}?
- 2/(s – a)^3
- 2/(s + a)^3
- 1/(s – a)^2
- n!/(s – a)^{n+1} with n=3
Correct Answer: 2/(s – a)^3
Q39. If F(s) = 1/(s^2 + 4), what is f(0+) using the initial value theorem?
- 0
- 1/2
- 2
- Undefined
Correct Answer: 0
Q40. Convolution example: (1 * t)(t) (convolution of 1 and t) equals which time function?
- t^2/2
- t
- 1/t
- t^2
Correct Answer: t^2/2
Q41. The inverse Laplace of 1/(s + a)^2 is:
- t e^{-a t}
- e^{-a t}
- t^2 e^{-a t}
- e^{a t}
Correct Answer: t e^{-a t}
Q42. Laplace transform of the unit ramp r(t)=t·u(t) is:
- 1/s^2
- 1/s
- 2/s^3
- t/s
Correct Answer: 1/s^2
Q43. L{e^{at} sin(bt)} equals which expression?
- b/((s – a)^2 + b^2)
- s/((s – a)^2 + b^2)
- b/((s + a)^2 + b^2)
- e^{-as} b/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: b/((s – a)^2 + b^2)
Q44. For f(t)=t^2, the ROC of its Laplace transform is which region?
- Re(s) > 0
- Re(s) < 0
- All s
- Re(s) = 0 only
Correct Answer: Re(s) > 0
Q45. Linearity property of Laplace transforms states L{a f + b g} equals:
- a F(s) + b G(s)
- F(s) + G(s)
- ab F(s) G(s)
- F(s)/a + G(s)/b
Correct Answer: a F(s) + b G(s)
Q46. L{sin^2(bt)} can be simplified using identities. Which expression is correct?
- 1/(2s) – s/(2(s^2 + 4 b^2))
- b/(s^2 + b^2)
- s/(s^2 + b^2)
- 1/(s^2 + b^2)
Correct Answer: 1/(2s) – s/(2(s^2 + 4 b^2))
Q47. Which property gives L{t^n f(t)} in terms of derivatives of F(s)?
- (-1)^n d^n/ds^n F(s)
- d^n/ds^n F(s)
- s^n F(s)
- F(s)/s^n
Correct Answer: (-1)^n d^n/ds^n F(s)
Q48. The inverse Laplace of 1/(s(s + a)(s + b)) (distinct a,b>0) is typically found using:
- partial fraction decomposition
- time-scaling
- frequency shifting only
- convolution without decomposition
Correct Answer: partial fraction decomposition
Q49. Using Laplace transforms for a 2nd order ODE, the transform of y”(t) includes which initial terms?
- s^2 Y(s) – s y(0) – y'(0)
- s Y(s) – y(0)
- Y(s) – y'(0)
- s^2 Y(s) + y(0) + y'(0)
Correct Answer: s^2 Y(s) – s y(0) – y'(0)
Q50. Which statement about the Laplace transform is true for causal signals (t ≥ 0)?
- The Laplace transform uniquely maps time-domain causal signals to s-domain functions with an ROC to the right of the rightmost pole.
- The Laplace transform always has ROC to the left of the leftmost pole.
- The Laplace transform is only defined for periodic signals.
- The Laplace transform eliminates initial conditions automatically.
Correct Answer: The Laplace transform uniquely maps time-domain causal signals to s-domain functions with an ROC to the right of the rightmost pole.

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com