Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Prednisolone is an intermediate-acting glucocorticoid used for inflammatory, allergic, autoimmune, and neoplastic conditions; it is the active metabolite of prednisone and is supplied as the free base and as salts/esters (e.g., prednisolone sodium phosphate for oral solution; prednisolone acetate for ophthalmic use).
Brand Names
Orapred, Millipred, PediaPred; numerous generics (formulation-dependent)
Name
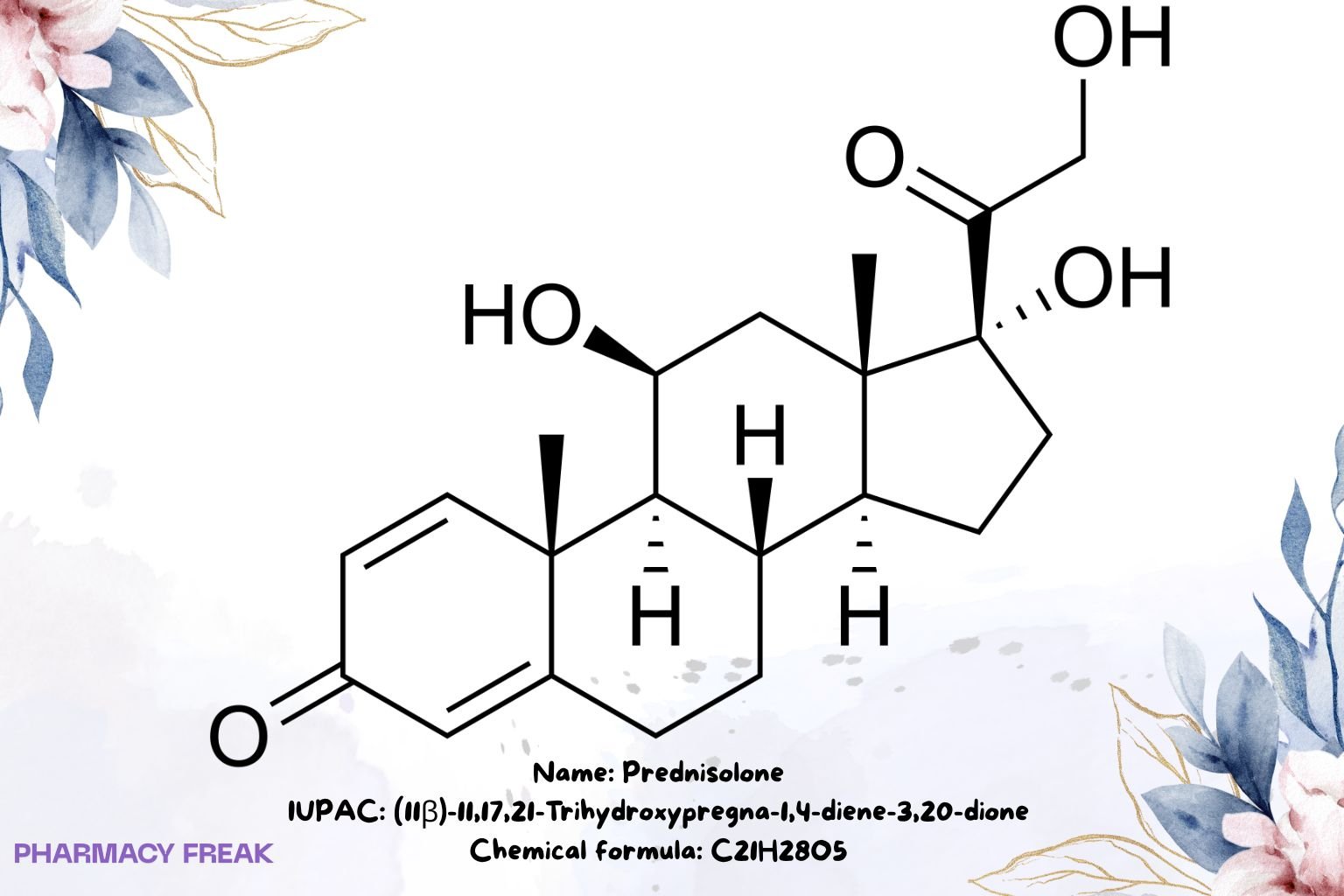
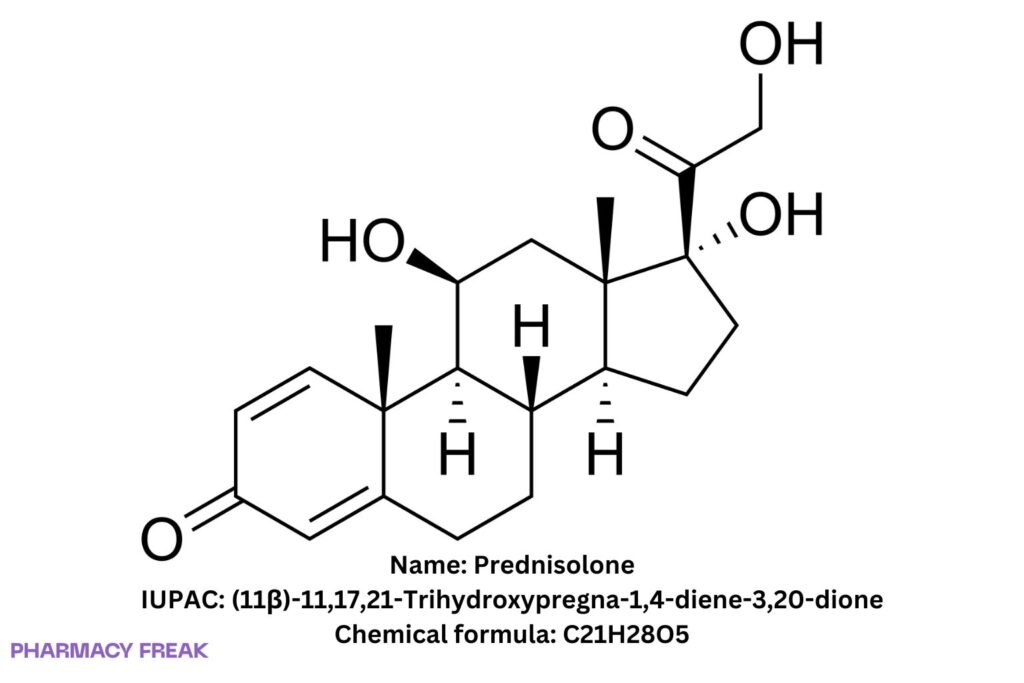
Prednisolone
Background
Synthetic pregnane steroid related to cortisol; predominant glucocorticoid activity with modest mineralocorticoid effect; ophthalmic products commonly use the acetate ester.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
~360.44 g/mol (base)
Chemical Formula
C₂₁H₂₈O₅
Synonyms
(11β)-11,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione; δ¹-hydrocortisone; 1,2-dehydrocortisol
External IDs
CAS: 50-24-8; PubChem CID: 5755; UNII: 9PHQ9Y1OLM; ATC: H02AB06; KEGG: D00472
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Systemic therapy for endocrine (e.g., adrenal insufficiency adjunct), rheumatic, allergic, dermatologic, ophthalmic, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, gastrointestinal, and other steroid-responsive disorders; ophthalmic use primarily as prednisolone acetate.
Associated Conditions
Asthma/COPD exacerbations, autoimmune diseases, uveitis, IBD, nephrotic syndrome, hematologic malignancies (as protocol components), acute allergy.
Associated Therapies
Use with steroid-sparing agents when indicated; tapering protocols to mitigate HPA-axis suppression.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning specific to prednisolone. Contraindicated with serious hypersensitivity and generally contraindicated in systemic fungal infections unless benefits outweigh risks; avoid live vaccines during significant immunosuppression.
Pharmacodynamics
Genomic glucocorticoid-receptor agonism → broad anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects; classified intermediate-acting (biological effect ~18–36 h).
Mechanism of action
Ligand-activated GR modulates transcription (↓ pro-inflammatory cytokines/enzymes; ↑ anti-inflammatory mediators); rapid non-genomic effects may contribute.
Absorption
Well absorbed orally; prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution achieves ~14% higher Cmax and ~20% faster tmax than tablets.
Volume of distribution
Approx. 0.22–0.7 L/kg (formulation- and study-dependent).
Protein binding
~70–90% (albumin and corticosteroid-binding globulin).
Metabolism
Hepatic biotransformation; interconversion with prednisone via 11β-HSD; conjugation pathways (e.g., glucuronidation, sulfation).
Route of elimination
Excreted mainly in urine as glucuronide/sulfate conjugates; minor biliary component.
Half-life
Plasma ~2–4 h (biological duration longer).
Clearance
Predominantly hepatic; exposure influenced by liver function and drug interactions.
Adverse Effects
Dose-/duration-dependent glucocorticoid effects: hyperglycemia, hypertension, fluid retention, mood/sleep changes, infection risk, osteoporosis, cataract/glaucoma (with ophthalmic/systemic exposure), GI irritation/ulcer risk (especially with NSAIDs), skin atrophy/poor wound healing.
Toxicity
Overexposure → Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression; taper after prolonged courses.
Pathways
GR-mediated transcriptional control; conjugative metabolism; renal excretion of conjugates.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No routine PGx; variability in CBG/GR expression and 11β-HSD activity may alter response.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
NSAIDs (↑ GI risk), strong CYP3A inducers/inhibitors (exposure changes), live vaccines (avoid during significant immunosuppression), potassium-depleting agents/diuretics (↑ hypokalemia risk), warfarin (monitor INR—direction variable), antidiabetics (dose adjustments commonly required).
Food Interactions
Administer with food to reduce GI irritation when appropriate; sodium load varies by salt/solution excipients.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
H02AB06 (glucocorticoids, systemic)
Drug Categories
Glucocorticoid; Anti-inflammatory; Immunosuppressant; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Pregnane steroid; Δ¹,⁴-diene; 11β,17α,21-triol; commonly formulated as sodium phosphate (oral/IV) or acetate (ophthalmic)
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
9PHQ9Y1OLM
CAS number
50-24-8
InChI Key
OIGNJSKKLXVSLS-VWUMJDOOSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C21H28O5/c1-19-7-5-13(23)9-12(19)3-4-14-15-6-8-21(26,17(25)11-22)20(15,2)10-16(24)18(14)19/h5,7,9,14-16,18,22,24,26H,3-4,6,8,10-11H2,1-2H3/t14-,15-,16-,18+,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1
IUPAC Name
(11β)-11,17,21-Trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
SMILES
O=C1C=CC2(C(=C1)CCC3C4CCC(O)(C(=O)CO)C4(C)CC(O)C32)C
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary: Prednisolone (CID 5755) — formula C₂₁H₂₈O₅, MW ~360.44; identifiers including SMILES/InChI/InChIKey. pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+2webbook.nist.gov+2
FDA GSRS/UNII — Prednisolone UNII 9PHQ9Y1OLM; molecular data. gsrs.ncats.nih.gov+1
DailyMed/labeling (prednisolone sodium phosphate) — oral solution vs tablets (+14% Cmax, ~20% faster tmax); protein binding 70–90%; t½ ~2–4 h; urinary excretion as glucuronide/sulfate. DailyMed+3DailyMed+3DailyMed+3
FDA label (accessdata) — Vd ~0.22–0.7 L/kg; protein binding and metabolic/elimination statements. FDA Access Data
Peer-reviewed PK sources — adult Vd ~0.64 L/kg; note on larger unbound Vd and intermediate biological half-life. PMC+1
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology — prednisolone ligand entry; formulation notes. guidetopharmacology.org

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com